III Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’01), pp. 397-404, Septiembre, 2001.
Abstract
Virtual Private Network (VPN) solutions mainly focus on security aspects. However, when security is considered the unique problem, some collateral ones arise. VPN users suffer from restrictions in their access to the network. They are not free to use traditional Internet services such as electronic mail exchange and audio/video conference with non-VPN users, and to access Web and Ftp servers external to the organization. In this paper we present a new solution, located at the TCP/IP transport layer and oriented to UDP applications that, while maintaining strong security features, allows the open use of traditional network services. The solution does not require the addition of new hardware because it is an exclusively software solution. As a consequence, the application is totally portable.

International Conference on Infrastructure Security (InfraSec’02), LNCS 2437, Springer-Verlag, pp. 325-337, October, 2002.
Abstract
The main aims of Virtual Private Network (VPN) are to isolate a distributed network from outsiders, as well as to protect the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information traversing a non-trusted network such as the Internet. However, some problems arise when security is considered as the unique problem because VPN users suffer from restrictions in their access to the network. They are not free to use traditional Internet services such as electronic mail exchange with non-VPN users, and to access Web and FTP servers external to the organization. This paper presents a new solution that allows the open use of traditional network services running over TCP and UDP layers, while maintaining strong security features. The new scheme works at the TCP/IP transport layer and does not require the addition of new hardware because it is a totally software solution. As a consequence, the application is totally portable. Moreover, and because of its implementation at the transport layer, there is no need to modify any traditional communication applications previously installed in the network system.

V Jornadas de Ingenería Telemática (JITEL’05), pp. 335-343, Septiembre, 2005.
Abstract
The design and development of security infrastructures and protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks is a difficult task, due to several factors like the constraints of the sensor nodes and the public nature of the communication channels. The intrinsic features of these networks create numerous security problems. In this paper, we analyze and put into perspective those problems.

Simposio sobre Computación Ubicua e Inteligencia Ambiental (UCAmI’05), pp. 113-120, September, 2005.
Abstract
Los sistemas de detección de intrusiones (IDS) son una herramienta imprescindible de seguridad a la hora de proteger una red. Recientemente se han investigado y desarrollado arquitecturas de IDS para redes inalámbricas, en concreto para redes "Ad Hoc". No obstante, no existe un trabajo previo que desarrolle una arquitectura de IDS para una red de sensores. En este artículo, analizamos porque los sistemas IDS de redes "Ad Hoc" no pueden aplicarse a redes de sensores, e introducimos una arquitectura de IDS para redes de sensores que incorpora una nueva técnica para vigilar las comunicaciones de la red en ciertos escenarios.

International Journal of Computer Systems Science & Engineering, vol. 3, CRL Publishing, pp. 185-192, 2005.
Abstract
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a cost-effective way for securing communications using public and insecure networks like the Internet. The main purpose of a VPN is to securely and transparently connect two or more remote networks to form virtually a single network, using centralized security policies for better management and protection. However, in certain scenarios, users may not require such a transparent access to the resources within their networks, but only want temporary secure access to internal services based on their own demands. We call the network architecture with such a feature as Casual VPN. In this paper, we present the notion of Casual VPN, and explain why traditional VPN architectures and protocols are unable to offer Casual VPN services. We also propose and define the operation of a particular Casual VPN architecture, C-VPN, which additionally allows the management of TCP and UDP-based protocols.

III Simposio Español de Comercio Electrónico, pp. 95-104, June, 2005.
Abstract
Los sistemas electrónicos de pago permiten que un comprador adquiera a un vendedor una serie de productos y servicios de forma virtual. Sin embargo, estos sistemas no tienen en cuenta el escenario en el que un comprador se convierte en donante, accediendo al servicio de forma gratuita. En este artículo se presenta el concepto y características de las microdonaciones, o la donación de cantidades tan pequeñas como un céntimo de euro en el contexto del comercio electrónico. También se muestra como la microdonación es algo necesario en el contexto actual de Internet, y como es posible su implementación basándose en sistemas de micropago.

5th Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT’05), IEEE, pp. 472-477, 2005.
Abstract
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is an umbrella term for any of several arrangements which allows a vendor of content in electronic form to control the material and restrict its usage in various ways that can be specified by the vendor. These arrangements are provided through security techniques, mainly encryption, and the distribution, in a detached manner, of content and rights. This allows free access to the content by the consumers, but only those carrying the proper Right Object (RO) will be able to process such content. As a security service considered in different layers of the security framework defined by ITU X.805, almost all applications need to consider non-repudiation in the very beginning of their design. Unfortunately this has not been done so far in DRM specifications due to practical issues and the type of content distributed. We analyze this service for the a DRM framework and provide a solution which allows the right objects acquisition to be undeniable.

V Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’05), pp. 375-382, September, 2005.
Abstract
Spam is considered to be one of the biggest problems in messaging systems. In the area of email Spam, A high number of anti-spam schemes have been proposed and deployed, but the problem has yet been well addressed. In this paper, we introduce a new scheme, called pre-challenge scheme, which avoids problems that exists in other schemes such as delay of service and denial of service. Some new mechanisms are employed to reach a good balance between security against Spam and convenience to email users. In addition, our scheme can be used for protecting other types of messaging systems, such as Instant Messaging (IM) and Blogs, against Spam.

20th IFIP International Information Security Conference (IFIP-SEC’05), R. Sasaki, S. Qing, E. Okamoto, and H. Yoshiura Eds., Springer, pp. 281-294, May, 2005.
Abstract
Spam turns out to be an increasingly serious problem to email users. A number of anti-spam schemes have been proposed and deployed, but the problem has yet been well addressed. One of those schemes is challenge-response, in which a challenge is imposed on an email sender. However, such a scheme introduces new problems for the users, e.g., delay of service and denial of service attacks. In this paper, we introduce a pre-challenge scheme that avoids those problems. It assumes each user has a challenge that is defined by the user himself/herself and associated with his/her email address, in such a way that an email sender can simultaneously retrieve a new receiver’s email address and challenge before sending an email in the first contact. Some new mechanisms are employed to reach a good balance between security against spam and convenience to email users.

Computational Science and Its Applications (ICCSA’05), LNCS 3482, Springer, pp. 681-690, May, 2005. DOI
Abstract
Wireless Sensor Networks are extremely vulnerable against any kind of internal or external attacks, due to several factors such as resource-constrained nodes and lack of tamper-resistant packages. As a result, security must be an important factor to have in mind when designing the infrastructure and protocols of sensor networks. In this paper we survey the state-of-the-art security issues in sensor networks and highlight the open areas of research.security issues in sensor networks and highlight the open areas of research.

Computer Communications, vol. 29, no. 15, Elsevier, pp. 2739-2749, 2006. DOI
Abstract
Unsolicited Commercial Email, or Spam, is nowadays an increasingly serious problem to email users. A number of anti-spam schemes have been proposed in the literature and some of them have been deployed in email systems, but the problem has yet been well addressed. One of those schemes is challenge-response, in which a challenge, ranging from a simple mathematical problem to a hard-AI problem, is imposed on an email sender in order to forbid machine-based spam reaching receivers’ mailboxes. However, such a scheme introduces new problems for the users, e.g., delay of service and denial of service. In this paper, we introduce the pre-challenge scheme, which is based on the challenge-response mechanism and takes advantage of some features of email systems. It assumes each user has a challenge that is defined by the user himself/herself and associated with his/her email address, in such a way that an email sender can simultaneously retrieve a new receiver’s email address and challenge before sending an email in the first contact. Some new mechanisms are employed in our scheme to reach a good balance between security against spam and convenience to normal email users. Our scheme can be also used for protecting other messaging systems, like Instant Messaging and Blog comments.

IEEE Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC 2006), IEEE, pp. 640-644, January, 2006. DOI
Abstract
The research of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is a mature area in wired networks, and has also attracted many attentions in wireless ad hoc networks recently. Nevertheless, there is no previous work reported in the literature about IDS architectures in wireless sensor networks. In this paper, we discuss the general guidelines for applying IDS to static sensor networks, and introduce a novel technique to optimally watch over the communications of the sensors’ neighborhood on certain scenarios.

1st International Workshop on Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS’06), LNCS 4347, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, pp. 166-178, 2006. DOI
Abstract
It is commonly agreed that Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is one of the technologies that better fulfills features like the ones required by Critical (Information) Infrastructures. However, a sensor network is highly vulnerable against any external or internal attacks, thus network designers must know which are the tools that they can use in order to avoid such problems. In this paper we describe in detail a procedure (the KMS Guidelines), developed under our CRISIS project, that allows network designers to choose a certain Key Management System, or at least to know which protocol need to improve in order to satisfy the network requirements.

IX Reunion Española sobre Criptologia y Seguridad de la Informacion (RECSI’06), UOC S.L., pp. 129-141, 2006.
Abstract
Digital Rights Management (DRM) es un término general para cualesquiera de las soluciones que permite a un vendedor de contenido en forma electrónica controlar el material y restringir su uso de distintas maneras. Estas soluciones son posibles, por un lado gracias a técnicas de la Seguridad de la Información, principalmente cifrado de datos, y por otro a la distribución, de manera independiente, de contenido y derechos digitales. Esto permite que los consumidores puedan acceder libremente al contenido, pero sólo aquellos que adquieran el derecho digital apropiado (RO) podrán procesarlo. Como servicio de seguridad considerado en diversas capas del marco de seguridad definido por la recomendación ITU X.805, casi todas las aplicaciones necesitan considerar la propiedad de no repudio en las etapas iniciales de su diseño. Desafortunadamente, esto no ha sido así en general, y más concretamente en especificaciones DRM; debido a consideraciones en la práctica y al tipo de contenido a distribuir. Analizamos este servicio para un marco de DRM y proporcionamos una solución que permita que la adquisición de derechos digitales sea un operación que no pueda repudiarse.

2nd International Workshop on Security Privacy and Trust in Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (SecPerU’06), IEEE Press, pp. 1-6, June, 2006.
Abstract
The extraordinary growth of the Information Society is originating a high dependency on ICT. This provokes that those strongly interrelated technological infrastructures, as well as the information systems that underpin them, become highly critical, since their disruption would lead to high economical, material and, sometimes, human loss. As a consequence, the protection of these Critical Information Infrastructures is becoming a major objective for governments and companies. In this paper, we give an overview of the main challenges and open research issues on Critical Information Infrastructure security, and introduce an on-going research project that, using wireless sensor networks as an underlying technology, is dealing with those problems. Our research project focuses on the development of protection, control, evaluation, maintenance and verification mechanisms, integrated into a secure service-oriented architecture.

VI Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’07), pp. 401-408, September, 2007.
Abstract
Security in wireless sensor networks is very limited due to highly-constrained hardware of sensor nodes. To protect services is necessary to use secure foundations, known as security primitives, like part of a protocol. Theses primitives must assure at least confidentiality in the communication channel, authentication of the peers involved in an information exchange, and integrity of the messages. There are many primitives such as symmetric encryption, hash functions and public key cryptography, but not all of them can be supported by sensor nodes since require high resource levels, for example memory. This paper contains a deep analysis of available and suitable security primitives for sensor nodes, as well as an analysis of hardware and software implementations. Besides, it has been developed an experiment with two implementations, and it has been created a new and improved version using the optimizations of each.

European PKI Workshop: Theory and Practice (EuroPKI’07), LNCS 4582, Springer, pp. 313-320, June, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are becoming a key technology in the support of pervasive and ubiquitous services. The previous notion of PKC is too expensive for WSN has changed partially due to the existence of new hardware and software prototypes based on Elliptic Curve Cryptography and other PKC primitives. Then, it is necessary to analyze whether it is both feasible and convenient to have a Public Key Infrastructure for sensor networks that would allow the creation of PKC-based services like Digital Signatures.

Information Security Technical Report, vol. 12, no. 3, Elsevier, pp. 179-185, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Spam is a big problem for email users. The battle between spamming and anti-spamming technologies has been going on for many years. Though many advanced anti-spamming technologies are progressing significantly, spam is still able to bombard many email users. The problem worsens when some anti-spamming methods unintentionally filtered legitimate emails instead! In this paper, we first review existing anti-spam technologies, then propose a layered defense framework using a combination of anti-spamming methods. Under this framework, the server-level defense is targeted for common spam while the client-level defense further filters specific spam for individual users. This layered structure improves on filtering accuracy and yet reduces the number of false positives. A sub-system using our pre-challenge method is implemented as an add-on in Microsoft Outlook 2002. In addition, we extend our client-based pre-challenge method to a domain-based solution thus further reducing the individual email users’ overheads.

1st International Conference on Autonomic Computing and Communication Systems (Autonomics’07), ICST, October, 2007.
Abstract
Research on trust management systems for wireless sensor networks is still at a very early stage and few works have done so far. It seems that for those works which deal with the topic general features of how these systems should be are not clearly identified. In this paper we try to identify the main features that a trust management system should have and justify their importance for future developments.

Telecommunications Systems, vol. 35, pp. 161-176, September, 2007.
Abstract
In any kind of electronic transaction, it is extremely important to assure that any of the parties involved can not deny their participation in the information exchange. This security property, which is called non-repudiation, becomes more important in Digital Rights Management (DRM) scenarios, where a consumer can freely access to certain contents but needs to obtain the proper Right Object (RO) from a vendor in order to process it. Any breach in this process could result on financial loss for any peer, thus it is necessary to provide a service that allows the creation of trusted evidence. Unfortunately, non-repudiation services has not been included so far in DRM specifications due to practical issues and the type of content distributed. In this paper we analyze how to allow the integration of non-repudiation services to a DRM framework, providing a set of protocols that allows the right objects acquisition to be undeniable, alongside with a proof-of-concept implementation and a validation process.

On Foundations of Security Analysis and Design IV, FOSAD 2006/2007, Springer, LNCS 4677, pp. 160-182, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructures are complex and highly interconnected systems that are crucial for the well-being of the society. Any type of failure can cause significant damage, affecting one or more sectors due to their inherent interdependency. Not only the infrastructures are critical, but also the information infrastructures that manage, control and supervise them. Due to the seriousness of the consequences, the protection of these critical (information) infrastructures must have the highest priority. It is the purpose of this book chapter to review and discuss about these infrastructures, to explain their elements, and to highlight their research and development issues. This chapter will also discuss the role of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) technology in the protection of these infrastructures.

Information Security Technical Report, vol. 12, no. 1, Elsevier, pp. 24-31, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructures, such as energy, banking, and transport, are an essential pillar to the well-being of the national and international economy, security and quality of life. These infrastructures are dependent on a spectrum of highly interconnected information infrastructures for their smooth, reliable and continuous operation. The field of protecting such Critical Information Infrastructures, or CIIP, faces numerous challenges, such as managing the secure interaction between peers, assuring the resilience and robustness of the overall system, and deploying warning and alert systems, amongst others. In this tapestry of CIIP, Wireless Sensor Networks can be used as an invaluable tool due to their intelligent distributed control capabilities, alongside with their capability to work under severe conditions. In this paper, we justify why Wireless Sensor Networks technology is suitable for providing security for these scenarios, describing both their advantages and research issues and their role in the overall scheme of protecting the Critical Information Infrastructures.

Mobile Networks and Applications, vol. 12, no. 4, Springer, pp. 231-244, August, 2007. DOI
Abstract
In a wireless sensor network environment, a sensor node is extremely constrained in terms of hardware due to factors such as maximizing lifetime and minimizing physical size and overall cost. Nevertheless, these nodes must be able to run cryptographic operations based on primitives such as hash functions, symmetric encryption and public key cryptography in order to allow the creation of secure services. Our objective in this paper is to survey how the existing research-based and commercial-based sensor nodes are suitable for this purpose, analyzing how the hardware can influence the provision of the primitives and how software implementations tackles the task of implementing instances of those primitives. As a result, it will be possible to evaluate the influence of provision of security in the protocols and applications/scenarios where sensors can be used.

3rd International Workshop on Security, Privacy and Trust in Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (SecPerU’07), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 25-30, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Trust plays an important role in human life environments and virtual organizations. In the context of a network, trust may help its elements to decide whether another member of the same network is being uncooperative or malicious. Trust becomes quite important in self-configurable and autonomous systems, such as wireless sensor networks (WSN). However, very little effort has been done in the field of trust management in WSN. On the other hand, some efforts have been made in quite related fields such as Ad-hoc and P2P networks. In this paper we give an overview of existing trust management solutions, mainly those developed for Ad-Hoc and P2P networks and, more importantly, investigate their suitability to WSN. We also provide some guidelines to aid the development of trust management systems for WSN according to the nature of these networks.

VI Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’08), pp. 437, September, 2008.
Abstract
Las infraestructuras críticas, como el sector energético, la banca, el transporte, y muchas otras, son un pilar esencial para en bienestar de la sociedad y la economía de un país. Estas infraestructuras dependen a su vez de ciertas infraestructuras de información, las cuales permiten su correcto funcionamiento. La tarea de proteger esas infraestructuras (de información) críticas es compleja y multidimensional, con una gran cantidad de desafíos por resolver. Precisamente, las redes de sensores pueden ser de gran ayuda para esta tarea, debido a suscapacidades de control distribuidas y a su habilidad de funcionar en situaciones extremas. Este artículo analiza la utilidad de las redes de sensores en este contexto, describiendo tanto sus capacidades como sus posibles roles y mecanismos de integración para la protección de infraestructuras (de información) críticas.

X Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI’08), pp. 231-236, September, 2008.
Abstract
Wireless sensors are battery-powered devices which are highly constrained in terms of computational capabilities, memory, and communication bandwidth. While battery life is their main limitation, they require considerable energy to communicate data. Due to this, the energy saving of computationally inexpensive security primitives (like those using symmetric key cryptography) can be nullified by the bigger amount of data they require to be sent. In this work we study the energy cost of key agreement protocols between peers in a network using public key cryptography techniques. Our concern is to reduce the amount of data to be exchanged. Our main news is that a computationally very demanding security primitive, such as identity-based authenticated key exchange, can present energy-wise a better performance than traditional public key based key exchange in realistic scenarios such as Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Such a result is not to be expected in wired networks.

Nuevas tendencias en gestión de redes, Novática, no. 196, CEPIS, pp. 20-25, December, 2008.
Abstract
En el momento que se introduce en el mercado nuevas tecnologías basadas en entornos distribuidos comienzan a surgir en paralelo nuevos problemas de seguridad en los sistemas SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), los cuales monitorizan y gestionan otras infraestructuras de gran complejidad y escala. Un fallo o una interrupción en uno de sus componentes podría suponer un impacto negativo sobre la funcionalidad de otras infraestructuras, por lo que se hace necesario realizar frecuentes análisis de seguridad para así mantener actualizado el conocimiento y proveer recomendaciones y/o soluciones para mitigar o evitar futuras ocurrencias, garantizando una gestión de red fiable y siempre disponible.

Wireless Sensor Network Security, J. Lopez, and J. Zhou Eds., IOS Press, 2008.
Abstract
Security has been proven a crucial factor in the provision of data services and especially in the computer-related environments. While wired and wireless networks come to all sectors of everyday life, security tries to satisfy the growing needs for confidentiality, integrity and non-repudiation. There are many instances of security primitives and each one of them has different requirements in terms of processing power, word size, etc. Therefore, it is important to review the functionality of the less resource-demanding encryption algorithms in order to analyze their theoretical suitability to the existent sensor node hardware. Still, the constraints inherent to the sensor nodes advise against the total dependence on software-based implementations, even more in the case of expensive primitives.

5th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS’08), IEEE, pp. 796-801, September, 2008. DOI
Abstract
An out-of-band (OoB) channel can be defined as an extra channel, different from the main wireless channel, that has additional security properties. They are specially suitable for protecting spontaneous interactions and exchanging sensitive data between previously unknown devices. Due to the vulnerable nature of wireless sensor networks (WSN), these kind of channels might be useful for protecting certain sensor network operations. In this paper we analyze the applicability of out-of-band channels to wireless sensor networks, and specify why an optical channel should be a good candidate for implementing an extra channel in sensor nodes. Also, we analyze how the existing security threats may affect this type of channel. Finally, the suitability and usability of optical channels for sensor networks is demonstrated by means of a prototype.

Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Cryptology and Network Security (CANS’08), LNCS 5339, Springer, pp. 120-132, December, 2008. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensors are low power devices which are highly constrained in terms of computational capabilities, memory, and communication bandwidth. While battery life is their main limitation, they require considerable energy to communicate data. The latter is specially dramatic in underwater wireless sensor networks (UWSN), where the acoustic transmission mechanisms are less reliable and more energy-demanding. Saving in communication is thus the primary concern in underwater wireless sensors. With this constraint in mind, we argue that non-interactive identity-based key agreement built on pairings provides the best solution for key distribution in large UWSN when compared to the state of the art. At first glance this claim is surprising, since pairing computation is very demanding. Still, pairing-based non-interactive key establishment requires minimal communication and at the same time enjoys excellent properties when used for key distribution.

XVIII Jornadas Telecom I+D, October, 2008.
Abstract
Los sistemas distribuidos en dispositivos embebidos representan un nuevo reto en el desarrollo de software. Estos sistemas han supuesto una importante revolución en el paradigma de la computación distribuida donde se intenta fragmentar un problema grande en múltiples problemas más pequeños. El nuevo escenario tiende entonces hacia sistemas en los cuales todos los elementos de la red se consideran iguales y los mecanismos de comunicación estãn basados en redes ad-hoc que se forman dinámicamente. De esta forma cualquier usuario de la red (en realidad cualquier elemento, hasta el más simple dispositivo) adquiere valor, a mayor colaboración, mayor éxito del sistema. Sin embargo, desde el punto de vista de la seguridad, estos sistemas son extremadamente vulnerables. En este artículo se presenta SMEPP, un middleware diseñado especialmente para sistemas P2P incluyendo aspectos de seguridad. SMEPP está diseñado para poder ser ejecutado en un amplio rango de dispositivos (desde redes de sensores hasta PC), y trata de facilitar el desarrollo de aplicaciones ocultando los detalles de la plataforma y otros aspectos tales como escalabilidad, adaptabilidad e interoperabilidad. Además el artículo presenta dos aplicaciones de alto nivel que utilizando este middleware pasan a ser más personales, más sociales y más baratas, haciendo que todos los usuarios de la red cobren mayor importancia.

Novatica, New Trends in Network Management, vol. 9, no. 6, Cepis UPGRADE, pp. 22-28, December, 2008.
Abstract
When a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system monitors and manages other complex infrastructures through the use of distributed technologies, it becomes a critical infrastructure by itself: A failure or disruption in any of its components could implicate a serious impact on the performance of the other infrastructures. The connection with other systems makes a SCADA system more vulnerable against attacks, generating new security problems. As a result, it is essential to perform diverse security analysis frequently in order to keep an updated knowledge and to provide recommendations and/or solutions to mitigate or avoid anomalous events. This will facilitate the existence of a suitable, reliable, and available control network.

IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 46, no. 4, IEEE, pp. 102-107, April, 2008. DOI
Abstract
A wireless sensor network should be able to operate for long periods of time with little or no external management. There is a requirement for this autonomy: the sensor nodes must be able to configure themselves in the presence of adverse situations. Therefore, the nodes should make use of situation awareness mechanisms to determine the existence of abnormal events in their surroundings. This work approaches the problem by considering the possible abnormal events as diseases, thus making it possible to diagnose them through their symptoms, namely, their side effects. Considering these awareness mechanisms as a foundation for high-level monitoring services, this article also shows how these mechanisms are included in the blueprint of an intrusion detection system.

6th International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business (TrustBus’09), Springer-Verlag, pp. 86-94, September, 2009. DOI
Abstract
SCADA systems represent a challenging scenario where the management of critical alarms is crucial. Their response to these alarms should be efficient and fast in order to mitigate or contain undesired effects. This work presents a mechanism, the Adaptive Assignment Manager (AAM) that will aid to react to incidences in a more efficient way by dynamically assigning alarms to the most suitable human operator. The mechanism uses various inputs for identifying the operators such as their availability, workload and reputation. In fact, we also define a reputation component that stores the reputation of the human operators and uses feedback from past experiences.

Foundations of Security Analysis and Design 2009, LNCS 5705, Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, pp. 289-338, August, 2009. DOI
Abstract
As sensor networks are more and more being implemented in real world settings, it is necessary to analyze how the different requirements of these real-world applications can influence the security mechanisms. This paper offers both an overview and an analysis of the relationship between the different security threats, requirements, applications, and security technologies. Besides, it also overviews some of the existing sensor network standards, analyzing their security mechanisms.

3rd CompanionAble Workshop - Future Internet of People, Things and Services (IoPTS) eco-Systems, xxxx, pp. xxxx, December, 2009.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks are considered as an integral part of the Internet of Things paradigm. Not only they provide a virtual presence to elements of the real world, but also allow any computationalsystem to know about the physical state of those elements thanks to the use of embedded sensors. In order to belong to the Internet of Things, the elements of a sensor network can implement Internet protocols and services such as the TCP/IP stack and web services. Still, a question that must be raised at this point of time is whether all sensor network applications should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. The purpose of this paper is to analyze this question, reviewing the challenges and security requirements of Internet-enabled sensor networks.

Internet Research, vol. 19, no. 2, Emerald, pp. 246-259, Mar 2009. DOI
Abstract
Purpose: This paper aims to analyze the security issues that arise when integrating wireless sensor networks (WSN) and the internet. Also, it seeks to review whether existing technology mechanisms are suitable and can be applied in this context.
Design/methodology/approach: The paper considers the possible approaches that can be used to connect a WSN with the internet, and analyzes the security of their interactions.
Findings: By providing the services of the network through a front-end proxy, a sensor network and the internet can interact securely. There are other challenges to be solved if the sensor nodes are integrated into the internet infrastructure, although there exists interesting advances on his matter.
Research limitations and implications: The complete integration of sensor networks and the internet still remains as an open issue.
Practical implications: With the current state of the art, it is possible to develop a secure sensor network that can provide its services to internet hosts with certain security properties.
Originality/value: The paper studies the interactions between sensor networks and the internet from the point of view of security. It identifies both solutions and research challenges.

ICT Mobile and Wireless Communications Summit (ICT-MobileSummit’09), June, 2009.
Abstract
The increasing presence of embedded devices with internet access capabilities constitutes a new challenge in software development. These devices are now cooperating in a distributed manner towards what has been called as "Internet of Things". In this new scenario the client-server model is sometimes not adequate and dynamic ad-hoc networks are more common than before. However, security poses as a hard issue as these systems are extremely vulnerable. In this paper, we introduce SMEPP project, which aims at developing a middleware designed for P2P systems with a special focus on embedded devices and security. SMEPP is designed to be deployed in a wide range of devices. It tries to ease the development of applications hiding platforms details and other aspects such as scalability, adaptability and interoperability. A full implementation of this middleware is already available that incorporates security features specially designed for low-resource devices. Moreover, we describe two business applications being developed using this middleware in the context of "Digital Home" and "Environmental Monitoring in Industrial Environments".

Security and Privacy in Mobile and Wireless Networking, S. Gritzalis, T. Karygiannis, and C. Skianis Eds., Troubador Publishing Ltd, pp. 105-128, 2009.
Abstract
The concept of trust has become very relevant in the late years as a consequence of the growth of fields such as internet transactions or electronic commerce. In general, trust has become of paramount importance for any kind of distributed networks, such as wireless sensor networks (WSN in the following). In this chapter of the book, we try to give a general overview of the state of the art on trust management systems for WSN and also try to identify the main features of the architectures of these trust management systems.

XI Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2010), pp. 337-342, September, 2010.
Abstract
Las Infraestructuras Críticas (ICs) son monitorizadas por sistemas altamente complejos, conocidos como sistemas SCADA (Sistemas de Control y Adquisición de Datos), cuyo principal soporte se encuentra en las subestaciones, las cuales miden de primera instancia el estado real de tales ICs. Para mejorar este control, la industria está actualmente demandando la integración en el modelo tradicional de dos avances tecnológicos: Internet y las redes de sensores inalámbricas. Sin embargo, su incorporación requiere analizar los requisitos de seguridad que surgen en dicho contexto, así como diversos aspectos correlacionados (ej. mantenimiento, rendimiento, seguridad y optimización) y, en base a estos, la estrategia de integración más adecuada para satisfacer dichos requisitos. Este artículo proporciona dicho análisis en profundidad con el fin de ofrecer un modelo de integración seguro adecuado para entornos críticos.

Revista SIC, vol. 88, Ediciones CODA, pp. 66-73, Feb 2010.
Abstract
El paradigma de la Internet de los Objetos, donde todos aquellos objetos físicos que nos rodean tendrán la capacidad de generar y consumir información en el ámbito de un mundo virtual, se encuentra cada vez más cerca. Es ahora un buen momento para llamar la atención sobre sus principales desafíos de seguridad, tanto desde un punto de vista global como asociados a sus elementos más importantes (la tecnología RFID y las redes de sensores). Así, este paradigma puede ser plenamente comprendido y protegido, evolucionando hacia uno de los nuevos pilares del futuro.

Computer Communications, vol. 33, no. 9, Elsevier, pp. 0140-3664, 2010. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have been proven a useful technology for perceiving information about the physical world and as a consequence has been used in many applications such as measurement of temperature, radiation, flow of liquids, etc. The nature of this kind of technology, and also their vulnerabilities to attacks make the security tools required for them to be considered in a special way. The decision making in a WSN is essential for carrying out certain tasks as it aids sensors establish collaborations. In order to assist this process, trust management systems could play a relevant role. In this paper, we list the best practices that we consider are essential for developing a good trust management system for WSN and make an analysis of the state of the art related to these practices.

1st International Workshop on the Security of the Internet of Things (SecIoT’10), IEEE, pp. xxxx, December, 2010.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) behave as a digital skin, providing a virtual layer where the information about the physical world can be accessed by any computational system. As a result, they are an invaluable resource for realizing the vision of the Internet of Things (IoT). However, it is necessary to consider whether the devices of a WSN should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. In this paper, we tackle this question from the perspective of security. While we will mention the different security challenges that may arise in such integration process, we will focus on the issues that take place at the network level.

X Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL 2011), K. Hackbarth, R. Agüero, and R. Sanz Eds., Universidad de Cantabria, pp. 104 - 111, 09/2011.
Abstract
El paradigma de red personal (PN) permitirá la interacción y colaboración del creciente abanico de dispositivos personales. Con tal fin la PN ha de integrar en su seno múltiples tecnologías heterogéneas con diversas capacidades computacionales y de comunicación de forma segura. En particular, la incorporación de la tecnología RFID en objetos personales conlleva múltiples riesgos de seguridad y privacidad que han suscitado un elevado interés de la comunidad investigadora en los últimos años. Más allá de su seguridad de forma aislada, su integración en la PN y la interacción de ésta con redes de área extensa como Internet of Things requieren una arquitectura de red personal adecuada para tal contexto. Este artículo proporciona los fundamentos de tal arquitectura segura incluyendo el análisis de aspectos como la incorporación e inicialización de las restringidas etiquetas RFID en la red personal, la autenticación tanto de miembros de la PN como de usuarios y servicios remotos en su acceso a las tecnologías de contexto, el control de las políticas de privacidad y el establecimiento de canales seguros de comunicación supervisados.
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, vol. 11, Wiley, pp. 267-276, 2011. DOI
Abstract
The wireless sensor networks (WSN) paradigm is especially vulnerable against external and internal attacks. Therefore, it is necessary to develop security mechanisms and protocols to protect them. These mechanisms must become an integral part of the software architecture and network stack of a sensor node. A question that remains is how to achieve this integration. In this paper we check how both academic and industrial solutions tackle this issue, and we present the concept of a transversal layer, where all the different security mechanisms could be contained. This way, all the elements of the architecture can interact with the security mechanisms, and the security mechanisms can have a holistic point of view of the whole architecture. We discuss the advantages of this approach, and also present how the transversal layer concept was applied to a real middleware architecture.

Digital Home Networking
, Wiley-ISTE, 2011.
 |  |
Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, E. Exposito, R. Roman, and M. Diaz Eds., no. 7130, John Wiley & Sons Inc., pp. 60-96, 2011.
Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, E. Exposito, R. Roman, and M. Diaz Eds., no. 7130, John Wiley & Sons Inc., pp. 60-96, 2011.
Computers & Electrical Engineering, vol. 37, Elsevier, pp. 147-159, Mar 2011. DOI
Abstract
If a wireless sensor network (WSN) is to be completely integrated into the Internet as part of the Internet of Things (IoT), it is necessary to consider various security challenges, such as the creation of a secure channel between an Internet host and a sensor node. In order to create such a channel, it is necessary to provide key management mechanisms that allow two remote devices to negotiate certain security credentials (e.g. secret keys) that will be used to protect the information flow. In this paper we will analyse not only the applicability of existing mechanisms such as public key cryptography and pre-shared keys for sensor nodes in the IoT context, but also the applicability of those link-layer oriented key management systems (KMS) whose original purpose is to provide shared keys for sensor nodes belonging to the same WSN.

Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, E. Exposito, and R. Roman Eds., Wiley-ISTE, pp. 17 - 58, 2011.
Concurrency and Computation Practice & Experience, vol. 23, no. 12, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 1414-1430, Aug 2011. DOI
Abstract
Energy distribution systems are becoming increasingly widespread in today’s society. One of the elements that is used to monitor and control these systems are the SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. In particular, these control systems and their complexities, together with the emerging use of the Internet and wireless technologies, bring new challenges that must be carefully considered. Examples of such challenges are the particular bene¯ts of the integration of those new technologies, and also the e®ects they may have on the overall SCADA security. The main task of this paper is to provide a framework that shows how the integration of di®erent state-of-the-art technologies in an energy control system, such as Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETs), and the Internet, can bring some interesting benefits such as status management and anomaly prevention, while maintaining the security of the whole system.

IEEE Computer, vol. 44, no. 9, IEEE, pp. 51 -58, Sept 2011. DOI
Abstract
This paper presents security of Internet of things. In the Internet of Things vision, every physical object has a virtual component that can produce and consume services Such extreme interconnection will bring unprecedented convenience and economy, but it will also require novel approaches to ensure its safe and ethical use. The Internet and its users are already under continual attack, and a growing economy-replete with business models that undermine the Internet’s ethical use-is fully focused on exploiting the current version’s foundational weaknesses.

Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, M. Diaz, E. Exposito, and R. Roman Eds., pp. 139-202, 2011.
Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, M. Diaz, E. Exposito, and R. Roman Eds., pp. 139-202, 2011.
5th International Symposium on Security and Multimodality in Pervasive Environments (SMPE’11), IEEE, March, 2011. DOI
Abstract
Key Management Schemes (KMS) are a very important security mechanism for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), as they are used to manage the credentials (i.e. secret keys) that are needed by the security primitives. There is a large number of available KMS protocols in the literature, but it is not clear what should network designers do to choose the most suitable protocol for the needs of their applications. In this paper, we consider that given a certain set of application requirements, the network designer can check which properties comply with those requirements and select the KMS protocols that contains those particular properties. Therefore, we study the relationship between requirements and properties, and we provide a web tool, the SenseKey tool, that can be used to automatically obtain an optimal set of KMS protocols.

Workshop on Wireless Cooperative Network Security (WCNS’11), Springer, May, 2011. DOI
Abstract
Cognitive Radio Networks (CRNs) arise as a promising solution to the scarcity of spectrum. By means of cooperation and smart decisions influenced by previous knowledge, CRNs are able to detect and profit from the best spectrum opportunities without interfering primary licensed users. However, besides the well-known attacks to wireless networks, new attacks threat this type of networks. In this paper we analyze these threats and propose a set of intrusion detection modules targeted to detect them. Provided method will allow a CRN to identify attack sources and types of attacks, and to properly react against them.

Information Systems Frontiers, vol. 14, Springer, pp. 527-540, July 2012. DOI
Abstract
Our society is becoming increasingly more IT-oriented, and the images and sounds that reflect our daily life are being stored mainly in a digital form. This digital personal life can be part of the home multimedia contents, and users demand access and possibly share these contents (such as photographs, videos, and music) in an ubiquitous way: from any location and with any device. The purpose of this article is twofold. First, we introduce the Feel@Home system, whose main objective is to enable the previously mentioned vision of an ubiquitous digital personal life. Second, we describe the security architecture of Feel@Home, analyzing the security and privacy requirements that identify which threats and vulnerabilities must be considered, and deriving the security building blocks that can be used to protect both IMS-based and VPN-based solutions.

Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, vol. 12, Wiley, pp. 133-143, Jan 2012. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensors are battery-powered devices which are highly constrained in terms of computational capabilities, memory and communication bandwidth. While battery life is their main limitation, they require considerable energy to communicate data. Due to this, it turns out that the energy saving of computationally inexpensive primitives (like symmetric key cryptography (SKC)) can be nullified by the bigger amount of data they require to be sent. In this work, we study the energy cost of key agreement protocols between peers in a network using asymmetric key cryptography. Our main concern is to reduce the amount of data to be exchanged, which can be done by using special cryptographic paradigms like identity-based and self-certified cryptography. The main news is that an intensive computational primitive for resource-constrained devices, such as non-interactive identity-based authenticated key exchange, performs comparably or even better than traditional authenticated key exchange (AKE) in a variety of scenarios. Moreover, protocols based in this primitive can provide better security properties in real deployments than other simple protocols based on symmetric cryptography. Our findings illustrate to what extent the latest implementation advancements push the efficiency boundaries of public key cryptography (PKC) in wireless sensor networks (WSNs).

7th International Workshop on Security and Trust Management (STM’11), LNCS 7170, Springer, pp. 207-222, 2012. DOI
Abstract
The secure integration of RFID technology into the personal network paradigm, as a context-aware technology which complements body sensor networks, would provide notable benefits to applications and potential services of the PN. RFID security as an independent technology is reaching an adequate maturity level thanks to research in recent years; however, its integration into the PN model, interaction with other network resources, remote users and service providers requires a specific security analysis and a PN architecture prepared to support these resource-constrained pervasive technologies. This paper provides such PN architecture and analysis. Aspects such as the management of personal tags as members of the PN, the authentication and secure communication of PN nodes and remote users with the context-aware technologies, and the enforcement of security and privacy policies are discussed in the architecture.

Computers & Security, vol. 31, no. 38, Elsevier, pp. 956–966, Nov 2012. DOI
Abstract
Key management in wireless sensor networks (WSN) is an active research topic. Due to the fact that a large number of key management schemes (KMS) have been proposed in the literature, it is not easy for a sensor network designer to know exactly which KMS best fits in a particular WSN application. In this article, we offer a comprehensive review on how the application requirements and the properties of various key management schemes influence each other. Based on this review, we show that the KMS plays a critical role in determining the security performance of a WSN network with given application requirements. We also develop a method that allows the network designers to select the most suitable KMS for a specific WSN network setting. In addition, the article also addresses the issues on the current state-of-the-art research on the KMS for homogeneous (i.e. non-hierarchical) networks to provide solutions for establishing link-layer keys in various WSN applications and scenarios.

Computer Networks, vol. 57, Elsevier, pp. 2266–2279, July 2013. DOI
Abstract
In the Internet of Things, services can be provisioned using centralized architectures, where central entities acquire, process, and provide information. Alternatively, distributed architectures, where entities at the edge of the network exchange information and collaborate with each other in a dynamic way, can also be used. In order to understand the applicability and viability of this distributed approach, it is necessary to know its advantages and disadvantages – not only in terms of features but also in terms of security and privacy challenges. The purpose of this paper is to show that the distributed approach has various challenges that need to be solved, but also various interesting properties and strengths.

Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 11, Elsevier, pp. 1091–1104, 2013. DOI
Abstract
The main objective of remote substations is to provide the central system with sensitive information from critical infrastructures, such as generation, distribution or transmission power systems. Wireless sensor networks have been recently applied in this particular context due to their attractive services and inherent benefits, such as simplicity, reliability and cost savings. However, as the number of control and data acquisition systems that use the Internet infrastructure to connect to substations increases, it is necessary to consider what connectivity model the sensor infrastructure should follow: either completely isolated from the Internet or integrated with it as part of the Internet of Things paradigm. This paper therefore addresses this question by providing a thorough analysis of both security requirements and infrastructural requirements corresponding to all those TCP/IP integration strategies that can be applicable to networks with constrained computational resources.

Computers & Security, vol. 38, Elsevier, pp. 14-27, OCT 2013. DOI
Abstract
Any deliberate or unsuitable operational action in control tasks of critical infrastructures, such as energy generation, transmission and distribution systems that comprise sub-domains of a Smart Grid, could have a significant impact on the digital economy: without energy, the digital economy cannot live. In addition, the vast majority of these types of critical systems are configured in isolated locations where their control depends on the ability of a few, supposedly trustworthy, human operators. However, this assumption of reliabilty is not always true. Malicious human operators (criminal insiders) might take advantage of these situations to intentionally manipulate the critical nature of the underlying infrastructure. These criminal actions could be not attending to emergency events, inadequately responding to incidents or trying to alter the normal behaviour of the system with malicious actions. For this reason, in this paper we propose a smart response mechanism that controls human operators’ operational threats at all times. Moreover, the design of this mechanism allows the system to be able to not only evaluate by itself, the situation of a particular scenario but also to take control when areas are totally unprotected and/or isolated. The response mechanism, which is based on Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (IWSNs) for the constant monitoring of observed critical infrastructures, on reputation for controlling human operators’ actions, and on the ISA100.11a standard for alarm management, has been implemented and simulated to evaluate its feasibility for critical contexts.

Security and Communication Networks, vol. 6, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 1177–1197, Oct 2013. DOI
Abstract
A personal network (PN) should enable the collaboration of user’s devices and services in a flexible, self-organizing and friendly manner. For such purpose, the PN must securely accommodate heterogeneous technologies with uneven computational and communication resources. In particular, personal RFID tags can enable seamless recognition of user’s context, provide user authentication and enable novel services enhancing the quality and quantity of data handled by the PN. However, the highly constrained features of common RFID tags and their passive role in the network highlights the need of an adequate secure communication model with personal tags which enables their participation as a member of the PN. In this paper, we present our concept of PN, with special emphasis on the role of RFID and sensor networks, and define a secure architecture for PNs including methods for the secure access to context-aware technologies from both local PN members and the Internet of Things. The PN architecture is designed to support differentiated security mechanisms to maximize the level of security for each type of personal device. Furthermore, we analyze which security solutions available in the literature can be adapted for our architecture, as well as the challenges and security mechanisms still necessary in the secure integration of personal tags.
España, C. Autón./Reg. de explotación: Andalucía, Invention Patent, vol. P201500764, G06F 21/00, 10/2015.
XIV Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información, pp. 168-173, 10/2016.
Abstract
En la Internet de los Objetos (IoT, por sus siglas en inglés), los ataques pueden ser perpetrados desde dispositivos que enmascaran su rastro ayudándose de la densidad de objetos y usuarios. Actualmente la idea de que los dispositivos de usuario almacenan evidencias que pueden ser muy valiosas para frenar ataques es bien conocida. Sin embargo, la colaboración de éstos para denunciar posibles abusos telemáticos aún está por definir. Los testigos digitales son dispositivos concebidos para definir la participación de dispositivos de usuario en una cadena de custodia digital. La idea es que las evidencias se generan, almacenan y transfieren siguiendo los requisitos marcados por las normas actuales (p.ej. UNE 71505), pero respetando las restricciones en recursos de los dispositivos. En este artículo proponemos una arquitectura funcional para la implementación del concepto de testigo digital en dispositivos heterogéneos de la IoT.

ERCIM News, no. 106, ERCIM EEIG, pp. 9-9, 07/2016.
IEEE Network, IEEE Communications Society, pp. 12-19, 2016. DOI
Abstract
Personal devices contain electronic evidence associated with the behaviour of their owners and other devices in their environment, which can help clarify the facts of a cyber-crime scene. These devices are usually analysed as containers of proof. However, it is possible to harness the boom of personal devices to define the concept of digital witnesses, where personal devices are able to actively acquire, store, and transmit digital evidence to an authorised entity, reliably and securely. This article introduces this novel concept, providing a preliminary analysis on the management of digital evidence and the technologies that can be used to implement it with security guarantees in IoT environments. Moreover, the basic building blocks of a digital witness are defined.

Revista SIC, vol. 122, Ediciones CODA, pp. 94-98, Nov 2016.
Abstract
El creciente número de dispositivos interconectados trae consigo problemas de seguridad bien conocidos; por ejemplo, aquellos debidos a las vulnerabilidades en protocolos muy diversos –muchos de ellos propietarios– y al factor de error humano introducido por los usuarios. Sin embargo, cabe preguntarse cómo podemos usar el despliegue de tales dispositivos en beneficio de la ciberseguridad. En el proyecto IoTest se está desarrollando una solución, el Testigo Digital, que permitirá a los dispositivos personales con arquitectura de seguridad embebida reaccionar ante ataques virtuales, protegiéndonos de los ciberataques emergentes.

II Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2016), pp. 109-116, 06/2016.
Abstract
En un mundo en el que los usuarios dependen cada vez más de sus dispositivos, éstos almacenan gran cantidad de datos y son una fuente muy valiosa de información sobre su entorno. Sin embargo, la heterogeneidad y la densidad de los objetos conectados, características propias de la Internet de las Cosas (IoT), sirven de velo para ocultar conductas maliciosas que afectan a estos dispositivos, sin que quede rastro de tales acciones. En este artículo definimos el concepto de testigo digital: funcionalidad que permitirá a los dispositivos personales y otros objetos colaborar para implementar una cadena de custodia digital en la IoT. El fin perseguido es ofrecer soluciones que mitiguen los efectos de la ciberdelincuencia, amparándose en la colaboración de los dispositivos con arquitecturas de seguridad embebidas para alertar de conductas maliciosas, y dejar constancia de éstas.

14th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2017), vol. 6, SciTePress, pp. 116-128, 2017. DOI

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

European CIIP Newsletter, vol. 11, issue 26, no. 1, European CIIP Newsletter, pp. 27-29, 03/2017.

The 12th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security, vol. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 10707, Springer, pp. 119-130, 08/2018.

IEEE Computer, vol. 51, issue 7, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 16-25, 07/2018. DOI
KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, vol. 12, no. 8, KSII, pp. 3567-3588, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
In the Internet of Things (IoT) concept, devices communicate autonomously with applications in the Internet. A significant aspect of IoT that makes it stand apart from present-day networked devices and applications is a) the very large number of devices, produced by diverse makers and used by an even more diverse group of users; b) the applications residing and functioning in what were very private sanctums of life e.g. the car, home, and the people themselves. Since these diverse devices require high-level security, an operational model for an IoT system is required, which has built-in security. We have proposed the societal model as a simple operational model. The basic concept of the model is borrowed from human society – there will be infants, the weak and the handicapped who need to be protected by guardians. This natural security mechanism works very well for IoT networks which seem to have inherently weak security mechanisms. In this paper, we discuss the requirements of the societal model and examine its feasibility by doing a proof-of-concept implementation.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 78, issue 1, Elsevier, pp. 680-698, 01/2018. DOI
Abstract
For various reasons, the cloud computing paradigm is unable to meet certain requirements (e.g. low latency and jitter, context awareness, mobility support) that are crucial for several applications (e.g. vehicular networks, augmented reality). To fulfil these requirements, various paradigms, such as fog computing, mobile edge computing, and mobile cloud computing, have emerged in recent years. While these edge paradigms share several features, most of the existing research is compartmentalised; no synergies have been explored. This is especially true in the field of security, where most analyses focus only on one edge paradigm, while ignoring the others. The main goal of this study is to holistically analyse the security threats, challenges, and mechanisms inherent in all edge paradigms, while highlighting potential synergies and venues of collaboration. In our results, we will show that all edge paradigms should consider the advances in other paradigms.

European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2018), vol. 11098, Springer, pp. 555-574, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
Advanced persistent threats pose a serious issue for modern industrial environments, due to their targeted and complex attack vectors that are difficult to detect. This is especially severe in critical infrastructures that are accelerating the integration of IT technologies. It is then essential to further develop effective monitoring and response systems that ensure the continuity of business to face the arising set of cyber-security threats. In this paper, we study the practical applicability of a novel technique based on opinion dynamics, that permits to trace the attack throughout all its stages along the network by correlating different anomalies measured over time, thereby taking the persistence of threats and the criticality of resources into consideration. The resulting information is of essential importance to monitor the overall health of the control system and correspondingly deploy accurate response procedures.

Computers & Security Journal, vol. 87, Elsevier, 11/2019. DOI
Abstract
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) have become a serious hazard for any critical infrastructure, as a single solution to protect all industrial assets from these complex attacks does not exist. It is then essential to understand what are the defense mechanisms that can be used as a first line of defense. For this purpose, this article will firstly study the spectrum of attack vectors that APTs can use against existing and novel elements of an industrial ecosystem. Afterwards, this article will provide an analysis of the evolution and applicability of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that have been proposed in both the industry and academia.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 3, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 4774-4781, 06/2019. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing are starting to go hand in hand. By providing cloud services close to end-users, edge paradigms enhance the functionality of IoT deployments, and facilitate the creation of novel services such as augmented systems. Furthermore, the very nature of these paradigms also enables the creation of a proactive defense architecture, an immune system, which allows authorized immune cells (e.g., virtual machines) to traverse edge nodes and analyze the security and consistency of the underlying IoT infrastructure. In this article, we analyze the requirements for the development of an immune system for the IoT, and propose a security architecture that satisfies these requirements. We also describe how such a system can be instantiated in Edge Computing infrastructures using existing technologies. Finally, we explore the potential application of immune systems to other scenarios and purposes.

Journal of Computer Security, vol. 27, issue 5, Elsevier, pp. 521-546, 09/2019.
25th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2020), vol. 12308, pp. 174-192, 09/2020. DOI

IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16, issue 10, no. 6575-6583, IEEE, 10/2020. DOI
Abstract
In Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) scenarios, where a plethora of IoT technologies coexist with consolidated industrial infrastructures, the integration of security mechanisms that provide protection against cyber-security attacks becomes a critical challenge. Due to the stealthy and persistent nature of some of these attacks, such as Advanced Persistent Threats, it is crucial to go beyond traditional Intrusion Detection Systems for the traceability of these attacks. In this sense, Opinion Dynamics poses a novel approach for the correlation of anomalies, which has been successfully applied to other network security domains. In this paper, we aim to analyze its applicability in the IIoT from a technical point of view, by studying its deployment over different IIoT architectures and defining a common framework for the acquisition of data considering the computational constraints involved. The result is a beneficial insight that demonstrates the feasibility of this approach when applied to upcoming IIoT infrastructures.

XVII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2022), vol. 265, Ediciones Universidad Cantabria, pp. 192-197, 10/2022.
Abstract
El auge de las plataformas móviles está impulsando el desarrollo de un gran número de aplicaciones, muchas de las cuales salen al mercado sin las convenientes comprobaciones de seguridad. Recientemente, Google está apostando por hacer este problema más visible y concienciar a los usuarios de la necesidad de instalar aplicaciones verificadas por laboratorios independientes. Sin embargo, la certificación de aplicaciones suele ser una tarea ardua y no exenta de errores. Por ello, en este trabajo, presentamos la herramienta AndroCIES, que es capaz de automatizar en gran medida las evaluaciones necesarias para la certificación de aplicaciones móviles, reduciendo en torno a un 20% el tiempo empleado en este proceso.

IEEE Security & Privacy , vol. 20, issue 1, IEEE, pp. 23 - 32, 01/2022. DOI
Abstract
This article introduces a privacy manager for IoT data based on Edge Computing. This poses the advantage that privacy is enforced before data leaves the control of the user, who is provided with a tool to express data sharing preferences based on a novel context-aware privacy language.

VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
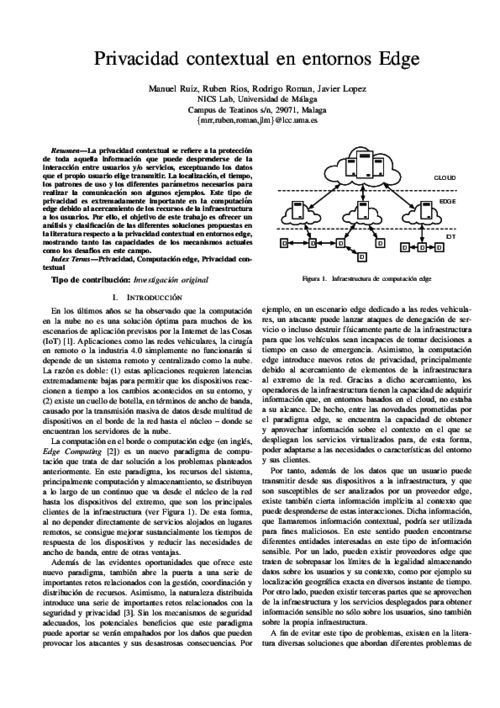
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.
Computers & Security, Elsevier, pp. 103-180, 2023. DOI
Abstract
As the number of security and privacy attacks continue to grow around the world, there is an ever increasing need to protect our personal devices. As a matter of fact, more and more manufactures are relying on Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to shield their devices. In particular, ARM TrustZone (TZ) is being widely used in numerous embedded devices, especially smartphones, and this technology is the basis for secure solutions both in industry and academia. However, as shown in this paper, TEE is not bullet-proof and it has been successfully attacked numerous times and in very different ways. To raise awareness among potential stakeholders interested in this technology, this paper provides an extensive analysis and categorization of existing vulnerabilities in TEEs and highlights the design flaws that led to them. The presented vulnerabilities, which are not only extracted from existing literature but also from publicly available exploits and databases, are accompanied by some effective countermeasures to reduce the likelihood of new attacks. The paper ends with some appealing challenges and open issues.

IEEE Security & Privacy, IEEE, In Press.
 ]
] 
