Computers & Security, Elsevier, pp. 103-180, 2023. DOI
Abstract
As the number of security and privacy attacks continue to grow around the world, there is an ever increasing need to protect our personal devices. As a matter of fact, more and more manufactures are relying on Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to shield their devices. In particular, ARM TrustZone (TZ) is being widely used in numerous embedded devices, especially smartphones, and this technology is the basis for secure solutions both in industry and academia. However, as shown in this paper, TEE is not bullet-proof and it has been successfully attacked numerous times and in very different ways. To raise awareness among potential stakeholders interested in this technology, this paper provides an extensive analysis and categorization of existing vulnerabilities in TEEs and highlights the design flaws that led to them. The presented vulnerabilities, which are not only extracted from existing literature but also from publicly available exploits and databases, are accompanied by some effective countermeasures to reduce the likelihood of new attacks. The paper ends with some appealing challenges and open issues.

XVII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2022), vol. 265, Ediciones Universidad Cantabria, pp. 192-197, 10/2022.
Abstract
El auge de las plataformas móviles está impulsando el desarrollo de un gran número de aplicaciones, muchas de las cuales salen al mercado sin las convenientes comprobaciones de seguridad. Recientemente, Google está apostando por hacer este problema más visible y concienciar a los usuarios de la necesidad de instalar aplicaciones verificadas por laboratorios independientes. Sin embargo, la certificación de aplicaciones suele ser una tarea ardua y no exenta de errores. Por ello, en este trabajo, presentamos la herramienta AndroCIES, que es capaz de automatizar en gran medida las evaluaciones necesarias para la certificación de aplicaciones móviles, reduciendo en torno a un 20% el tiempo empleado en este proceso.

ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security (TOPS), vol. 25, issue 2, no. 10, Association for Computer Machinery (ACM), pp. 1 - 29, 05/2022. DOI
Abstract
Proximity attacks allow an adversary to uncover the location of a victim by repeatedly issuing queries with fake location data. These attacks have been mostly studied in scenarios where victims remain static and there are no constraints that limit the actions of the attacker. In such a setting, it is not difficult for the attacker to locate a particular victim and quantifying the effort for doing so is straightforward. However, it is far more realistic to consider scenarios where potential victims present a particular mobility pattern. In this paper, we consider abstract (constrained and unconstrained) attacks on services that provide location information on other users in the proximity. We derive strategies for constrained and unconstrained attackers, and show that when unconstrained they can practically achieve success with theoretically optimal effort. We then propose a simple yet effective constraint that may be employed by a proximity service (for example, running in the cloud or using a suitable two-party protocol) as countermeasure to increase the effort for the attacker several orders of magnitude both in simulated and real-world cases.

IEEE Security & Privacy , vol. 20, issue 1, IEEE, pp. 23 - 32, 01/2022. DOI
Abstract
This article introduces a privacy manager for IoT data based on Edge Computing. This poses the advantage that privacy is enforced before data leaves the control of the user, who is provided with a tool to express data sharing preferences based on a novel context-aware privacy language.

VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
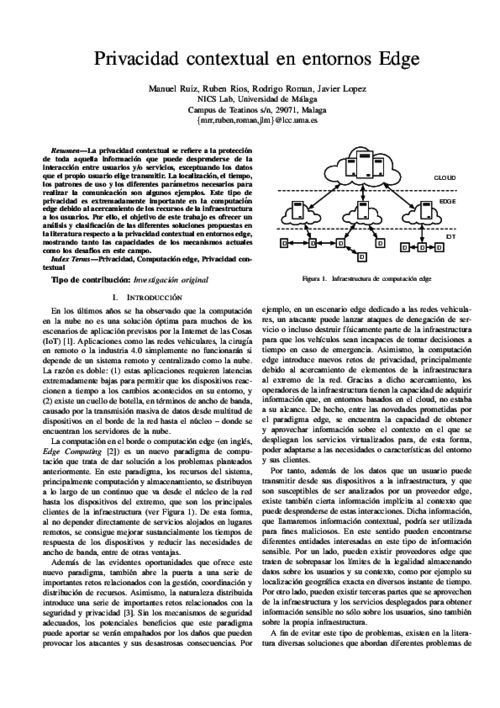
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.
25th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2020), vol. 12308, pp. 174-192, 09/2020. DOI

Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences, vol. 9, no. 1, Springer, pp. 1-23, 2019. DOI
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 3, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 4774-4781, 06/2019. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing are starting to go hand in hand. By providing cloud services close to end-users, edge paradigms enhance the functionality of IoT deployments, and facilitate the creation of novel services such as augmented systems. Furthermore, the very nature of these paradigms also enables the creation of a proactive defense architecture, an immune system, which allows authorized immune cells (e.g., virtual machines) to traverse edge nodes and analyze the security and consistency of the underlying IoT infrastructure. In this article, we analyze the requirements for the development of an immune system for the IoT, and propose a security architecture that satisfies these requirements. We also describe how such a system can be instantiated in Edge Computing infrastructures using existing technologies. Finally, we explore the potential application of immune systems to other scenarios and purposes.

International Conference on Information Systems Education and Research (AIS SIGED 2019), 12/2019.

Security and Privacy for Big Data, Cloud Computing and Applications, Lizhe Wang, Wei Ren, Raymoond Choo and Fatos Xhafa, The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) , 09/2019.

Data Privacy Management, Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
, LNCS, vol. 11025, Springer International Publishing, 2018.
DOI AbstractESORICS 2018 International Workshops, DPM 2018 and CBT 2018, Barcelona, Spain, September 6-7, 2018, Proceedings  |  |
Sensors, vol. 18, issue 2, no. 492, MDPI, 02/2018. DOI
Abstract
IoT-Forensics is a novel paradigm for the acquisition of electronic evidence whose operation is conditioned by the peculiarities of the Internet of Things (IoT) context. As a branch of computer forensics, this discipline respects the most basic forensic principles of preservation, traceability, documentation, and authorization. The digital witness approach also promotes such principles in the context of the IoT while allowing personal devices to cooperate in digital investigations by voluntarily providing electronic evidence to the authorities. However, this solution is highly dependent on the willingness of citizens to collaborate and they may be reluctant to do so if the sensitive information within their personal devices is not sufficiently protected when shared with the investigators. In this paper, we provide the digital witness approach with a methodology that enables citizens to share their data with some privacy guarantees. We apply the PRoFIT methodology, originally defined for IoT-Forensics environments, to the digital witness approach in order to unleash its full potential. Finally, we show the feasibility of a PRoFIT-compliant digital witness with two use cases.

23rd European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2018), LNCS 11099, Springer, pp. 373-392, 2018. DOI
Abstract
Location privacy has mostly focused on scenarios where users remain static. However, investigating scenarios where the victims present a particular mobility pattern is more realistic. In this paper, we consider abstract attacks on services that provide location information on other users in the proximity. In that setting, we quantify the required effort of the attacker to localize a particular mobile victim. We prove upper and lower bounds for the effort of an optimal attacker. We experimentally show that a Linear Jump Strategy (LJS) practically achieves the upper bounds for almost uniform initial distributions of victims. To improve performance for less uniform distributions known to the attacker, we propose a Greedy Updating Attack Strategy (GUAS). Finally, we derive a realistic mobility model from a real-world dataset and discuss the performance of our strategies in that setting.

Computers & Security, vol. 77 , issue August 2018, Elsevier, pp. 773-789, 2018. DOI
Abstract
Trust negotiations are mechanisms that enable interaction between previously unknown users. After exchanging various pieces of potentially sensitive information, the participants of a negotiation can decide whether or not to trust one another. Therefore, trust negotiations bring about threats to personal privacy if not carefully considered. This paper presents a framework for representing trust negotiations in the early phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The framework can help software engineers to determine the most suitable policies for the system by detecting conflicts between privacy and trust requirements. More precisely, we extend the SI* modelling language and provide a set of predicates for defining trust and privacy policies and a set of rules for describing the dynamics of the system based on the established policies. The formal representation of the model facilitates its automatic verification. The framework has been validated in a distributed social network scenario for connecting drivers with potential passengers willing to share a journey.

16th IEEE International Conference On Trust, Security And Privacy In Computing And Communications (TrustCom 2017), IEEE, pp. 642-649, 08/2017. DOI
Abstract
The digital witness approach defines the collaboration between IoT devices - from wearables to vehicles - to provide digital evidence through a Digital Chain of Custody to an authorised entity. As one of the cores of the digital witness, binding credentials unequivocally identify the user behind the digital witness. The objective of this article is to perform a critical analysis of the digital witness approach from the perspective of privacy, and to propose solutions that help include some notions of privacy in the scheme (for those cases where it is possible). In addition, digital anonymous witnessing as a tradeoff mechanism between the original approach and privacy requirements is proposed. This is a clear challenge in this context given the restriction that the identities of the links in the digital chain of custody should be known.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 75, Elsevier, pp. 46–57, 10/2017. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) envisions a world covered with billions of smart, interacting things capable of offering all sorts of services to near and remote entities. The benefits and comfort that the IoT will bring about are undeniable, however, these may come at the cost of an unprecedented loss of privacy. In this paper we look at the privacy problems of one of the key enablers of the IoT, namely wireless sensor networks, and analyse how these problems may evolve with the development of this complex paradigm. We also identify further challenges which are not directly associated with already existing privacy risks but will certainly have a major impact in our lives if not taken into serious consideration.

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

16th IEEE International Conference On Trust, Security And Privacy In Computing And Communications (TrustCom 2017), IEEE, pp. 626-633, 08/2017. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) brings new challenges to digital forensics. Given the number and heterogeneity of devices in such scenarios, it bring extremely difficult to carry out investigations without the cooperation of individuals. Even if they are not directly involved in the offense, their devices can yield digital evidence that might provide useful clarification in an investigation. However, when providing such evidence they may leak sensitive personal information. This paper proposes PRoFIT; a new model for IoT-forensics that takes privacy into consideration by incorporating the requirements of ISO/IEC 29100:2011 throughout the investigation life cycle. PRoFIT is intended to lay the groundwork for the voluntary cooperation of individuals in cyber crime investigations.

XIII Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL 2017), vol. Libro de actas, Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València, pp. 302-309, 01/2018, 2017. DOI

32nd International Conference on ICT Systems Security and Privacy Protection (IFIP SEC 2017), S. De Capitan di Vimercati, and F. Martinelli Eds., IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology (AICT) 502, Springer, pp. 141–154, 05/2017. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) promises to revolutionize the way we interact with the physical world. Even though this paradigm is still far from being completely realized, there already exist Sensing-as-a-Service (S2aaS) platforms that allow users to query for IoT data. While this model offers tremendous benefits, it also entails increasingly challenging privacy issues. In this paper, we concentrate on the protection of user privacy when querying sensing devices through a semi-trusted S2aaS platform. In particular, we build on techniques inspired by proxy re-encryption and k-anonymity to tackle two intertwined problems, namely query privacy and query confidentiality. The feasibility of our solution is validated both analytically and empirically.

III Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2017), vol. Actas del JNIC 2017, Servicio de Publicaciones de la URJC, pp. 51-58, 2017.

XIV Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información, pp. 209-213, 10/2016.
Abstract
La Internet de las Cosas (en inglés, Internet of Things (IoT)) es una evolución de la Internet tal y como lo conocemos. Esta nueva versión de Internet incorpora objetos de la vida cotidiana, rompiendo así barrera de los digital y extendiéndose al mundo físico. Estos objetos interactuarán entre sí y con otras entidades tanto de manera local como remota, y estarán dotados de cierta capacidad computacional y sensores para que sean conscientes de lo que ocurre en su entorno. Esto traerá consigo un sinfín de posibilidades y nuevos servicios, pero también dará lugar a nuevos y mayores riesgos de privacidad para los ciudadanos. En este artículo, estudiamos los problemas de privacidad actuales de una de las tecnologías claves para el desarrollo de este prometedor paradigma, las redes de sensores, y analizamos como pueden evolucionar y surgir nuevos riesgos de privacidad al ser completamente integradas en la Internet.

|
"Location Privacy in Wireless Sensor Networks", CRC Series in Security, Privacy and Trust, Taylor & Francis, 2016.  |  |
12th International Workshop on Security and Trust Management (STM), vol. LNCS 9871, Springer, pp. 98-105, 09/2016. DOI
Abstract
Software engineering and information security have traditionally followed divergent paths but lately some efforts have been made to consider security from the early phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). This paper follows this line and concentrates on the incorporation of trust negotiations during the requirements engineering phase. More precisely, we provide an extension to the SI* modelling language, which is further formalised using answer set programming specifications to support the automatic verification of the model and the detection of privacy conflicts caused by trust negotiations.

Information Sciences, vol. 321, Elsevier, pp. 205 - 223, 07/2015. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are continually exposed to many types of attacks. Among these, the attacks targeted at the base station are the most devastating ones since this essential device processes and analyses all traffic generated in the network. Moreover, this feature can be exploited by a passive adversary to determine its location based on traffic analysis. This receiver-location privacy problem can be reduced by altering the traffic pattern of the network but the adversary may still be able to reach the base station if he gains access to the routing tables of a number of sensor nodes. In this paper we present HISP-NC (Homogenous Injection for Sink Privacy with Node Compromise protection), a receiver-location privacy solution that consists of two complementary schemes which protect the location of the base station in the presence of traffic analysis and node compromise attacks. The HISP-NC data transmission protocol prevents traffic analysis by probabilistically hiding the flow of real traffic with moderate amounts of fake traffic. Moreover, HISP-NC includes a perturbation mechanism that modifies the routing tables of the nodes to introduce some level of uncertainty in attackers capable of retrieving the routing information from the nodes. Our scheme is validated both analytically and experimentally through extensive simulations.

XIII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2014), Universidad de Alicante, pp. 333-338, 09/2014.
Abstract
Continuamente aparecen nuevos estudios así como nuevos desarrollos de canales encubiertos. Como veremos, existen más de cien diseños distintos para redes de ordenadores, pero no hemos encontrado en la literatura ningún análisis, diseño e implementación de canales encubiertos sobre redes de sensores. En este artículo presentamos los resultados del diseño e implementación de un canal multitasa basado en los tiempos de monitorización sobre una red de sensores. En este proceso se han establecido las principales propiedades necesarias y, en base a ellas, se desarrolla e implementa el canal encubierto. Se describe el proceso de desarrollo y se analiza su detectabilidad.

Foundations of Security Analysis and Design VII, vol. 8604, no. LNCS, Springer, pp. 244-282, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Privacy preservation is gaining popularity in Wireless Sensor Network (WSNs) due to its adoption in everyday scenarios. There are a number of research papers in this area many of which concentrate on the location privacy problem. In this paper we review and categorise these solutions based on the information available to the adversary and his capabilities. But first we analyse whether traditional anonymous communication systems conform to the original requirements of location privacy in sensor networks. Finally, we present and discuss a number of challenges and future trends that demand further attention from the research community.

Information Security Practice and Experience (ISPEC 2014), vol. 8434, Springer, pp. 15-27, 05/2014. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are exposed to many different types of attacks. Among these, the most devastating attack is to compromise or destroy the base station since all communications are addressed exclusively to it. Moreover, this feature can be exploited by a passive adversary to determine the location of this critical device. This receiver-location privacy problem can be reduced by hindering traffic analysis but the adversary may still obtain location information by capturing a subset of sensor nodes in the field. This paper addresses, for the first time, these two problems together in a single solution

Computers & Security, vol. 39, Part A, Elsevier, pp. 34 - 46, Nov 2013. DOI
Abstract
Covert channels are a form of hidden communication that may violate the integrity of systems. Since their birth in Multi-Level Security systems in the early 70’s they have evolved considerably, such that new solutions have appeared for computer networks mainly due to vague protocols specifications. In this paper we concentrate on short-range covert channels and analyze the opportunities of concealing data in various extensively used protocols today. From this analysis we observe several features that can be effectively exploited for subliminal data transmission in the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). The result is a proof-of-concept implementation, HIDE\_DHCP, which integrates three different covert channels each of which accommodate to different stealthiness and capacity requirements. Finally, we provide a theoretical and experimental analysis of this tool in terms of its reliability, capacity, and detectability.

XI Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL 2013), J. E. Díaz Verdejo, J. Navarro Ortiz, and J. J. Ramos Muñoz Eds., Asociación de Telemática, pp. 481-486, Oct 2013.
Abstract
La estación base es el elemento más importante en un red de sensores y, por tanto, es necesario evitar que un atacante pueda hacerse con el control de este valioso dispositivo. Para ello, el atacante puede valerse tanto de técnicas de análisis de tráfico como de la captura de nodos. En este trabajo presentamos un esquema que consta de dos fases, la primera está dedicada a homogeneizar los patrones de tráfico y la segunda encargada de perturbar las tablas de rutas de los nodos. Ambas fases permiten mantener a la estación base fuera del alcance del atacante con un coste computacional insignificante y un consumo energético moderado. La validez de nuestro esquema ha sido validada analíticamente y a través de numerosas simulaciones.

Computers & Security, vol. 39 (B), Elsevier, pp. 117-126, 11/2013. DOI
Abstract
Continuous authentication is mainly associated with the use of biometrics to guarantee that a resource is being accessed by the same user throughout the usage period. Wireless devices can also serve as a supporting technology for continuous authentication or even as a complete alternative to biometrics when accessing proximity-based services. In this paper we present the implementation of a secure, non-invasive continuous authentication scheme supported by the use of Wearable Wireless Devices (WWD), which allow users to gain access to proximity-based services while preserving their privacy. Additionally we devise an improved scheme that circumvents some of the limitations of our implementation.

IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 7, no. 2, IEEE Systems Council, pp. 298 - 310, Jun 2013. DOI
Abstract
Anonymous communication systems have been extensively studied by the research community to prevent the disclosure of sensitive information from the analysis of individuals’ traffic patterns. Many remarkable solutions have been developed in this area, most of which have proven to be effective in the protection of user privacy against different types of attacks. Recently, the privacy preservation problem has also been considered in the realm of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) due to their imminent adoption in real-world scenarios. A special challenge that arises from the analysis of the flow of sensor nodes’ communications is the location privacy problem. In this work we concentrate on analyzing the suitability of traditional anonymous communication systems originally designed for the Internet to the original scenario of sensor networks. The results show that, in most cases, traditional solutions do not provide the adequate protection means for the particular problem of location privacy, while other solutions are too resource-consuming for the restricted capabilities of sensor nodes.

XII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2012), U.. Zurutuza, R.. Uribeetxeberria, and I.. Arenaza-Nuño Eds., pp. 309-314, Sep 2012.
Abstract
Los patrones de tráfico característicos de las redes inalámbricas de sensores (WSNs) dan lugar al problema de la privacidad de localización. De manera similar, el tráfico de los usuarios en Internet revela información sensible que puede ser protegida mediante sistemas de comunicación anónima (ACS). Por ello, este trabajo analiza la posibilidad de adaptar las soluciones de anonimato tradicionales al problema particular de las redes de sensores. Hasta el momento estas soluciones habían sido rechazadas sin un análisis riguroso, argumentando simplemente que eran demasiado exigentes computacionalmente para los nodos sensores. Nuestros resultados demuestran que, en general, algunos ACS no cumplen los requisitos de privacidad necesarios en WSNs mientras que otros, que si los cumplen, se valen de una cantidad de recursos que superan la capacidad de los sensores.

Proceedings of the 27th IFIP TC 11 International Information Security and Privacy Conference (SEC 2012), D. Gritzalis, S. Furnell, and M. Theoharidou Eds., IFIP AICT 376, Springer Boston, pp. 162-173, June 2012. DOI
Abstract
Covert channels are a form of hidden communication that may violate the integrity of systems. Since their birth in multilevel security systems in the early 70’s they have evolved considerably, such that new solutions have appeared for computer networks mainly due to vague protocols specifications. We analyze a protocol extensively used today, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), in search of new forms of covert communication. From this analysis we observe several features that can be effectively exploited for subliminal data transmission. This results in the implementation of HIDE_DHCP, which integrates three covert channels that accommodate to different stealthiness and bandwidth requirements

Proceedings of the 27th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC 2012), S. Ossowski, and P. Lecca Eds., ACM, pp. 1463-1469, 26-30 March 2012. DOI
Abstract
The ubiquity of positioning devices poses a natural security challenge: users want to take advantage of location-related services as well as social sharing of their position but at the same time have security concerns about how much information should be shared about their exact position. This paper discusses different location-privacy problems, their formalization and the novel notion of indistinguishability regions that allows one to proof that a given obfuscation function provides a good trade-off between location sharing and privacy.

17th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2012), S. Foresti, M. Yung, and F. Martinelli Eds., LNCS 7459, Springer, pp. 163-180, Sep 2012. DOI
Abstract
The singular communication model in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) originate pronounced traffic patterns that allow a local observer to deduce the location of the base station, which must be kept secret for both strategical and security reasons. In this work we present a new receiver-location privacy solution called HISP (Homogenous Injection for Sink Privacy). Our scheme is based on the idea of hiding the flow of real traffic by carefully injecting fake traffic to homogenize the transmissions from a node to its neighbors. This process is guided by a lightweight probabilistic approach ensuring that the adversary cannot decide with sufficient precision in which direction to move while maintaining a moderate amount of fake traffic. Our system is both validated analytically and experimentally through simulations.

IET Communications, vol. 5, Institution of Engineering and Technology, pp. 2518 - 2532, Nov 2011. DOI
Abstract
Extensive work has been done on the protection of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) from the hardware to the application layer. However, only recently, the privacy preservation problem has drawn the attention of the research community because of its challenging nature. This problem is exacerbated in the domain of WSNs due to the extreme resource limitation of sensor nodes. In this paper we focus on the location privacy problem in WSNs, which allows an adversary to determine the location of nodes of interest to him. We provide a taxonomy of solutions based on the power of the adversary and the main techniques proposed by the various solutions. In addition, we describe and analyse the advantages and disadvantages of different approaches. Finally, we discuss some open challenges and future directions of research.

The Computer Journal, vol. 54, Oxford University Press, pp. 1603-1615, Sept 2011. DOI
Abstract
The source-location privacy problem in Wireless Sensor Networks has been traditionally tackled by the creation of random routes for every packet transmitted from the source nodes to the base station. These schemes provide a considerable protection level at a high cost in terms of message delivery time and energy consumption. This overhead is due to the fact that the data routing process is done in a blind way, without knowledge about the location of the attacker. In this work we propose the Context-Aware Location Privacy (CALP) approach, which takes advantage of the ability of sensor nodes to perceive the presence of a mobile adversary in their vicinity in order to transmit data packets in a more energy-efficient and privacy-preserving manner. In particular, we apply the concepts of CALP to the development of a shortest-path CALP routing algorithm. A permissive and a strict version of the protocol are studied for different adversarial models and the proposed schemes are evaluated through simulation experiments in terms of privacy protection and energy consumption. Finally, we present the conclusions of the paper as well as possible extensions of this work.

IX Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’10), Y. Dimitriadis, and M. Jesús Ver Pérez Eds., pp. 237 - 244, Sept., 2010.
Abstract
Las aplicaciones basadas en localización proporcionan a los usuarios servicios personalizados dependiendo de su ubicación. Las estimaciones prevén que estos servicios se extenderán enormemente en los próximos años reportando grandes beneficios tanto a la industria como a los usuarios finales. Sin embargo, para que estos avances sean posibles se hace necesario analizar en profundidad las distintas implicaciones de seguridad y privacidad que la utilización de tales servicios pueden traer consigo a los usuarios. En este trabajo proponemos un sistema de localización que da soporte a la provisión de servicios basados en localización para entornos indoor y que se fundamenta en la tecnología de redes de sensores inalámbricos. En este esquema hemos tenido en cuenta diversos aspectos de seguridad y privacidad, prestando especial atención a la limitación extrema de recursos característica de las redes de sensores. Finalmente hemos desarrollado una prueba de concepto para comprobar la viabilidad de nuestro esquema dentro del ámbito del proyecto OSAmI.

4th International Symposium of Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence (UCAmI’10), L. Fuentes, N. Gámez, and J. Bravo Eds., IBERGARCETA PUBLICACIONES, S.L., pp. 29 - 38, Sept., 2010.
Abstract
Wireless Sensor Networks are considered to be one of the cornerstones of Ambient Intelligence since they can be used in countless applications, where sensors are unobtrusively embedded into the environment to perform operations like monitoring, tracking and reporting. In such scenarios, privacy issues must be carefully considered since the mere observation of the network operation might reveal great amounts of private information to unauthorised parties. One of the problems that is gaining more attention in the realm of privacy, is the location privacy problem, which aims to prevent an attacker from obtaining the location of specific nodes of interest to him. In this paper we provide a general overview of the proposed solutions to counter this threat. Finally, we will also discuss some open challenges and future directions of research for a convenient management of privacy issues in smart environments.

X Reunión Española de Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI’08), L. Hernández Encinas, and A. Martin del Rey Eds., pp. 325-336, Sept., 2008.
Abstract
Los canales encubiertos son una forma de comunicación oculta que puede vulnerar la integridad de los sistemas. Desde sus inicios en sistemas de seguridad multinivel a principios de los años 70 han evolucionado considerablemente, apareciendo soluciones para redes de computadores debido a la especificación de algunos protocolos. Por este motivo, se hace un estudio sobre las técnicas que se han utilizado para crear los canales, así como sobre las distintos obstáculos que han tratado de mermar su actividad. Asimismo, se presenta una nueva clasificación que trata de albergar la mayor cantidad de canales encubiertos existentes en la actualidad. Por último, se analiza un protocolo ampliamente extendido en la actualidad, DHCP, en busca de posibilidades de albergar información encubierta. A partir de este análisis se implementan distintas versiones de un canal encubierto haciendo uso de este protocolo.

 ]
] 