 ]
] VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
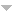
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.
VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.

VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.

18th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS’20), vol. 12147, Springer, pp. 297-320, 10/2020. DOI

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 78, issue 1, Elsevier, pp. 680-698, 01/2018. DOI
Abstract
For various reasons, the cloud computing paradigm is unable to meet certain requirements (e.g. low latency and jitter, context awareness, mobility support) that are crucial for several applications (e.g. vehicular networks, augmented reality). To fulfil these requirements, various paradigms, such as fog computing, mobile edge computing, and mobile cloud computing, have emerged in recent years. While these edge paradigms share several features, most of the existing research is compartmentalised; no synergies have been explored. This is especially true in the field of security, where most analyses focus only on one edge paradigm, while ignoring the others. The main goal of this study is to holistically analyse the security threats, challenges, and mechanisms inherent in all edge paradigms, while highlighting potential synergies and venues of collaboration. In our results, we will show that all edge paradigms should consider the advances in other paradigms.

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

Information Security Solutions Europe 2012, N. Pohlmann, H. Reimer, and W. Schneider Eds., Springer Vieweg, pp. 195-206, 2012. DOI
Abstract
The paper describes the experience with integration of automatic cyber identity technology with policy controlled virtualisation environment. One identity technology has been used to enable strong authentication of users (human beings) as well as machines (host systems) to the virtualization management system. The real experimental evaluation has been done in PASSIVE project (Policy-Assessed system-level Security of Sensitive Information processing in Virtualised Environments - SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME ICT-2009.1.4 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES - Small or medium-scale focused research project - Grant agreement no.: 257644).
1st International Workshop on Security and Trust for Applications in Virtualised Environments (STAVE 2011), C. Lee, J-M. Seigneur, J. J. Park, and R. R. Wagner Eds., Communications in Computer and Information Science 187, Springer, pp. 190-197, June, 2011. DOI
Abstract
In this paper we identify some areas where cryptography can help a rapid adoption of cloud computing. Although secure storage has already captured the attention of many cloud providers, offering a higher level of protection for their customer’s data, we think that more advanced techniques such as searchable encryption and secure outsourced computation will become popular in the near future, opening the doors of the Cloud to customers with higher security requirements.
