 ] Year
] Year |
"Security and Privacy Trends in the Industrial Internet of Things", Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications, Springer, 2019.  |  |
Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and Applications, no. Intelligent Data-Centric Systems, Academic Press, pp. 305 - 317, 2017. DOI
Abstract
Abstract Cyber-physical systems (CPSs), integrated in critical infrastructures, could provide the minimal services that traditional situational awareness (SA) systems demand. However, their application in SA solutions for the protection of large control distributions against unforeseen faults may be insufficient. Dynamic protection measures have to be provided not only to locally detect unplanned deviations but also to prevent, respond, and restore from these deviations. The provision of these services as an integral part of the SA brings about a new research field known as wide-area situational awareness (WASA), highly dependent on CPSs for control from anywhere across multiple interconnections, and at any time. Thus, we review the state-of-the art of this new paradigm, exploring the different preventive and corrective measures considering the heterogeneity of CPSs, resulting in a guideline for the construction of automated WASA systems.

Digital Home Networking, R. Carbou, E. Exposito, R. Roman, and M. Diaz Eds., no. 7130, John Wiley & Sons Inc., pp. 60-96, 2011.
Wireless Sensor Network Security, J. Lopez, and J. Zhou Eds., IOS Press, 2008.
Abstract
Security has been proven a crucial factor in the provision of data services and especially in the computer-related environments. While wired and wireless networks come to all sectors of everyday life, security tries to satisfy the growing needs for confidentiality, integrity and non-repudiation. There are many instances of security primitives and each one of them has different requirements in terms of processing power, word size, etc. Therefore, it is important to review the functionality of the less resource-demanding encryption algorithms in order to analyze their theoretical suitability to the existent sensor node hardware. Still, the constraints inherent to the sensor nodes advise against the total dependence on software-based implementations, even more in the case of expensive primitives.

Accountability and Security in the Cloud, M. Felici, and C. Fernandez-Gago Eds., Lecture Notes in Computer Science 8937, Springer International Publishing, pp. 114-125, 2015. DOI
Abstract
In this paper we tackle the problem of privacy and confidentiality in Identity Management as a Service (IDaaS). The adoption of cloud computing technologies by organizations has fostered the externalization of the identity management processes, shaping the concept of Identity Management as a Service. However, as it has happened to other cloud-based services, the cloud poses serious risks to the users, since they lose the control over their data. As part of this work, we analyze these concerns and present a model for privacy-preserving IDaaS, called BlindIdM, which is designed to provide data privacy protection through the use of cryptographic safeguards.
On Foundations of Security Analysis and Design IV, FOSAD 2006/2007, Springer, LNCS 4677, pp. 160-182, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructures are complex and highly interconnected systems that are crucial for the well-being of the society. Any type of failure can cause significant damage, affecting one or more sectors due to their inherent interdependency. Not only the infrastructures are critical, but also the information infrastructures that manage, control and supervise them. Due to the seriousness of the consequences, the protection of these critical (information) infrastructures must have the highest priority. It is the purpose of this book chapter to review and discuss about these infrastructures, to explain their elements, and to highlight their research and development issues. This chapter will also discuss the role of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) technology in the protection of these infrastructures.

Digital Privacy: Theory, Technologies, and Practices, A.. Acquisti, S. Gritzalis, C.. Lambrinoudakis, and S. De Capitan di Vimercati Eds., Auerbach Publications, pp. 285-306, December, 2007.
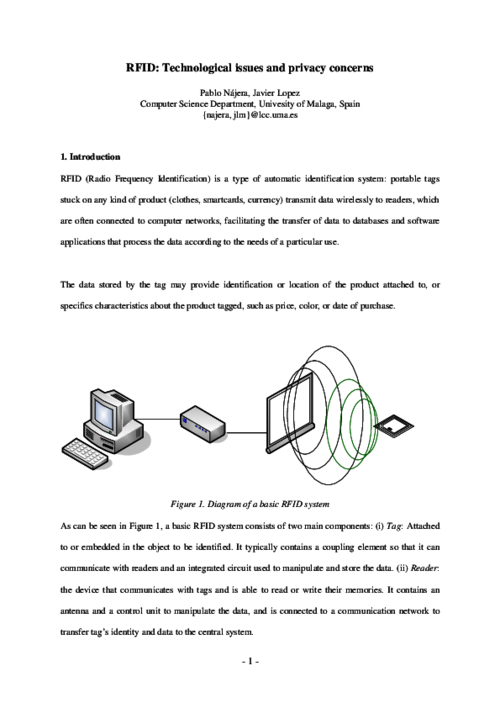
Advances in Core Computer Science-Based Technologies, Springer International Publishing, pp. 157-173, 2021. DOI
Abstract
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have enabled Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to become fully interconnected. This connectivity however has radically changed their threat landscape. Existing risk assessment methodologies often fail to identify various attack paths that stem from the new connectivity/functionality features of IoT-enabled CPS. Even worse, due to their inherent characteristics, IoT systems are usually the weakest link in the security chain and thus many attacks utilize IoT technologies as their key enabler. In this paper we review risk assessment methodologies for IoT-enabled CPS. In addition, based on our previous work (Stellios et al. in IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 20:3453–3495, 2018, [47]) on modeling IoT-enabled cyberattacks, we present a high-level risk assessment approach, specifically suited for IoT-enabled CPS. The mail goal is to enable an assessor to identify and assess non-obvious(indirect or subliminal) attack paths introduced by IoT technologies, that usually target mission critical components of an CPS.
Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience: Theories, Methods, Tools and Technologies, no. Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications book series (ASTSA), Springer International Publishing, pp. 201-217, 01/2019. DOI
Abstract
Increasingly, the society is witnessing how today’s industry is adapting the new technologies and communication protocols to offer more optimal and reliable services to end-users, with support for inter-domain communication belonging to diverse critical infrastructures. As a consequence of this technological revolution, interconnection mechanisms are required to offer transparency in the connections and protection in the different application domains, without this implying a significant degradation of the control requirements. Therefore, this book chapter presents a reference architecture for the new Industry 4.0 where the interconnection core is mainly concentrated in the Policy Decision Points (PDP), which can be deployed in high volume data processing and storage technologies such as cloud and fog servers. Each PDP authorizes actions in the field/plant according to a set of factors (entities, context and risks) computed through the existing access control measures, such as RBAC+ABAC+Risk-BAC (Role/Attribute/Risk-Based Access Control, respectively), to establish coordinated and constrained accesses in extreme situations. Part of these actions also includes proactive risk assessment measures to respond to anomalies or intrusive threats in time.

Security Solutions and Applied Cryptography in Smart Grid Communications, IGI Global, USA, IGI Global, pp. 137-158, 2017. DOI
Abstract
Transparency in control transactions under a secure network architecture is a key topic that must be discussed when aspects related to interconnection between heterogeneous cyber-physical systems (CPSs) arise. The interconnection of these systems can be addressed through an enforcement policy system responsible for managing access control according to the contextual conditions. However, this architecture is not always adequate to ensure a rapid interoperability in extreme crisis situations, and can require an interconnection strategy that permits the timely authorized access from anywhere at any time. To do this, a set of interconnection strategies through the Internet must be studied to explore the ability of control entities to connect to the remote CPSs and expedite their operations, taking into account the context conditions. This research constitutes the contribution of this chapter, where a set of control requirements and interoperability properties are identified to discern the most suitable interconnection strategies.

Critical Infrastructure Protection: Information Infrastructure Models, Analysis, and Defense, J. Lopez, S.. Wolthunsen, and R. Setola Eds., Advances in Critical Infrastructure Protection: Information Infrastructure Models, Analysis, and Defense. LNCS 7130. 7130, Springer-Verlag, pp. 120-149, September 2012.
Abstract
SCADA Systems can be seen as a fundamental component in Critical Infrastructures, having an impact in the overall performance of other Critical Infrastructures interconnected. Currently, these systems include in their network designs different types of Information and Communication Technology systems (such as the Internet and wireless technologies), not only to modernize operational processes but also to ensure automation and real-time control. Nonetheless, the use of these new technologies will bring new security challenges, which will have a significant impact on both the business process and home users. Therefore, the main purpose of this Chapter is to address these issues and to analyze the interdependencies of Process Control Systems with ICT systems, to discuss some security aspects and to offer some possible solutions and recommendations.

Encyclopedia of Cryptography, Security and Privacy, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 1--3, 08/2021. DOI
IFIP Sumer School 2015 on Privacy and Identity Management. Time for a Revolution?, vol. 476, AICT Series, Springer, pp. 61-78, 07/2016.
X Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL 2011), K. Hackbarth, R. Agüero, and R. Sanz Eds., Universidad de Cantabria, pp. 104 - 111, 09/2011.
Abstract
El paradigma de red personal (PN) permitirá la interacción y colaboración del creciente abanico de dispositivos personales. Con tal fin la PN ha de integrar en su seno múltiples tecnologías heterogéneas con diversas capacidades computacionales y de comunicación de forma segura. En particular, la incorporación de la tecnología RFID en objetos personales conlleva múltiples riesgos de seguridad y privacidad que han suscitado un elevado interés de la comunidad investigadora en los últimos años. Más allá de su seguridad de forma aislada, su integración en la PN y la interacción de ésta con redes de área extensa como Internet of Things requieren una arquitectura de red personal adecuada para tal contexto. Este artículo proporciona los fundamentos de tal arquitectura segura incluyendo el análisis de aspectos como la incorporación e inicialización de las restringidas etiquetas RFID en la red personal, la autenticación tanto de miembros de la PN como de usuarios y servicios remotos en su acceso a las tecnologías de contexto, el control de las políticas de privacidad y el establecimiento de canales seguros de comunicación supervisados.
XI Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2010), pp. 337-342, September, 2010.
Abstract
Las Infraestructuras Críticas (ICs) son monitorizadas por sistemas altamente complejos, conocidos como sistemas SCADA (Sistemas de Control y Adquisición de Datos), cuyo principal soporte se encuentra en las subestaciones, las cuales miden de primera instancia el estado real de tales ICs. Para mejorar este control, la industria está actualmente demandando la integración en el modelo tradicional de dos avances tecnológicos: Internet y las redes de sensores inalámbricas. Sin embargo, su incorporación requiere analizar los requisitos de seguridad que surgen en dicho contexto, así como diversos aspectos correlacionados (ej. mantenimiento, rendimiento, seguridad y optimización) y, en base a estos, la estrategia de integración más adecuada para satisfacer dichos requisitos. Este artículo proporciona dicho análisis en profundidad con el fin de ofrecer un modelo de integración seguro adecuado para entornos críticos.

6th International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business (TrustBus’09), Springer-Verlag, pp. 86-94, September, 2009. DOI
Abstract
SCADA systems represent a challenging scenario where the management of critical alarms is crucial. Their response to these alarms should be efficient and fast in order to mitigate or contain undesired effects. This work presents a mechanism, the Adaptive Assignment Manager (AAM) that will aid to react to incidences in a more efficient way by dynamically assigning alarms to the most suitable human operator. The mechanism uses various inputs for identifying the operators such as their availability, workload and reputation. In fact, we also define a reputation component that stores the reputation of the human operators and uses feedback from past experiences.

6th International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business (TrustBus’09), Springer-Verlag, pp. 86-94, September, 2009. DOI
Abstract
SCADA systems represent a challenging scenario where the management of critical alarms is crucial. Their response to these alarms should be efficient and fast in order to mitigate or contain undesired effects. This work presents a mechanism, the Adaptive Assignment Manager (AAM) that will aid to react to incidences in a more efficient way by dynamically assigning alarms to the most suitable human operator. The mechanism uses various inputs for identifying the operators such as their availability, workload and reputation. In fact, we also define a reputation component that stores the reputation of the human operators and uses feedback from past experiences.

9th IFIP International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility & Security, 2018.

6th International Conference on Network and System Security (NSS 2012), LNCS 7645 7645, Springer-Verlag, pp. 58-71, November 2012. DOI
Abstract
Control and situational awareness are two very important aspects within critical control systems, since potential faults or anomalous behaviors could lead to serious consequences by hiding the real status of supervised critical infrastructures. Examples of these infrastructures are energy generation, transmission or distribution systems that belong to Smart Grid systems. Given the importance of these systems for social welfare and its economy, a situational awareness-based model, composed of a set of current technologies, is proposed in this paper. The model focuses on addressing and offering a set of minimum services for protection, such as prevention, detection, response, self-evaluation and maintenance, thereby providing a desirable protection in unplanned situations.

XII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2012), U.. Zurutuza, R.. Uribeetxeberria, and I.. Arenaza-Nuño Eds., pp. 309-314, Sep 2012.
Abstract
Los patrones de tráfico característicos de las redes inalámbricas de sensores (WSNs) dan lugar al problema de la privacidad de localización. De manera similar, el tráfico de los usuarios en Internet revela información sensible que puede ser protegida mediante sistemas de comunicación anónima (ACS). Por ello, este trabajo analiza la posibilidad de adaptar las soluciones de anonimato tradicionales al problema particular de las redes de sensores. Hasta el momento estas soluciones habían sido rechazadas sin un análisis riguroso, argumentando simplemente que eran demasiado exigentes computacionalmente para los nodos sensores. Nuestros resultados demuestran que, en general, algunos ACS no cumplen los requisitos de privacidad necesarios en WSNs mientras que otros, que si los cumplen, se valen de una cantidad de recursos que superan la capacidad de los sensores.

VI Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’08), pp. 437, September, 2008.
Abstract
Las infraestructuras críticas, como el sector energético, la banca, el transporte, y muchas otras, son un pilar esencial para en bienestar de la sociedad y la economía de un país. Estas infraestructuras dependen a su vez de ciertas infraestructuras de información, las cuales permiten su correcto funcionamiento. La tarea de proteger esas infraestructuras (de información) críticas es compleja y multidimensional, con una gran cantidad de desafíos por resolver. Precisamente, las redes de sensores pueden ser de gran ayuda para esta tarea, debido a suscapacidades de control distribuidas y a su habilidad de funcionar en situaciones extremas. Este artículo analiza la utilidad de las redes de sensores en este contexto, describiendo tanto sus capacidades como sus posibles roles y mecanismos de integración para la protección de infraestructuras (de información) críticas.

VI Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’07), pp. 401-408, September, 2007.
Abstract
Security in wireless sensor networks is very limited due to highly-constrained hardware of sensor nodes. To protect services is necessary to use secure foundations, known as security primitives, like part of a protocol. Theses primitives must assure at least confidentiality in the communication channel, authentication of the peers involved in an information exchange, and integrity of the messages. There are many primitives such as symmetric encryption, hash functions and public key cryptography, but not all of them can be supported by sensor nodes since require high resource levels, for example memory. This paper contains a deep analysis of available and suitable security primitives for sensor nodes, as well as an analysis of hardware and software implementations. Besides, it has been developed an experiment with two implementations, and it has been created a new and improved version using the optimizations of each.

I Simposio Español de Comercio Electrónico (SEC’01), pp. 145-160, Octubre, 2001.
Abstract
La presente ponencia aborda el desarrollo de un entorno seguro escalable para el Comercio Electrónico. Se ha tratado la cuestión en dos fases: primero, idear un prototipo generalizado distribuido seguro formado por diferentes entidades genéricas con el objetivo de permitir que los clientes realicen sus compras y transacciones bancarias con un nivel de seguridad escalable; y en segundo lugar, implantar en la práctica un prototipo de grado de escalabilidad reducido como modelo empírico.
14th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2017), vol. 6, SciTePress, pp. 116-128, 2017. DOI

Foundations of Security Analysis and Design 2009, LNCS 5705, Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, pp. 289-338, August, 2009. DOI
Abstract
As sensor networks are more and more being implemented in real world settings, it is necessary to analyze how the different requirements of these real-world applications can influence the security mechanisms. This paper offers both an overview and an analysis of the relationship between the different security threats, requirements, applications, and security technologies. Besides, it also overviews some of the existing sensor network standards, analyzing their security mechanisms.

The 16th IEEE International Conference on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing (DASC 2018), pp. 536-543, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
In the current telecommunications landscape, different devices, systems and platforms are constantly communicating with each other. This heterogeneous environment creates the perfect situation for attacks to pass from one platform to another. This is a particularly worrying scenario, because of the new technologies being used (such as network slicing in 5G), the increasing importance of connected devices in our lives (IoT), and the unpredictable consequences that an attack of this type could have. The current approaches in attack analysis do not take into account these sitations, and the attacker/victim paradigm usually followed may fall short when dealing with these attacks. Thus, in this paper, an architecture for the analysis of cross-platform attacks will be presented, aiming to help understand better this kind of threats and offering solutions to mitigate and track them.

European PKI Workshop: Theory and Practice (EuroPKI’07), LNCS 4582, Springer, pp. 313-320, June, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are becoming a key technology in the support of pervasive and ubiquitous services. The previous notion of PKC is too expensive for WSN has changed partially due to the existence of new hardware and software prototypes based on Elliptic Curve Cryptography and other PKC primitives. Then, it is necessary to analyze whether it is both feasible and convenient to have a Public Key Infrastructure for sensor networks that would allow the creation of PKC-based services like Digital Signatures.

1st International Workshop on Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS’06), LNCS 4347, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, pp. 166-178, 2006. DOI
Abstract
It is commonly agreed that Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is one of the technologies that better fulfills features like the ones required by Critical (Information) Infrastructures. However, a sensor network is highly vulnerable against any external or internal attacks, thus network designers must know which are the tools that they can use in order to avoid such problems. In this paper we describe in detail a procedure (the KMS Guidelines), developed under our CRISIS project, that allows network designers to choose a certain Key Management System, or at least to know which protocol need to improve in order to satisfy the network requirements.

3rd international conference on Mobile multimedia communications (MobiMedia ’07), ICST, pp. 43:1–43:6, 2007.
Abstract
When delegation is implemented using the attribute certificates in a Privilege Management Infrastructure (PMI), this one reaches a considerable level of distributed functionality. However, the approach is not flexible enough for the requirements of ubiquitous environments. Additionally, the PMI can become a too complex solution for devices such as smartphones and PDAs, where resources are limited. In this work, we solve the previous limitations by defining a second class of attributes, called domain attributes, which are managed directly by users and are not right under the scope of the PMI, thus providing a light solution for constrained devices. The two classes of attributes are related by defining a simple ontology. We also introduce in the paper the concept of Attribute Federation which is responsible for supporting domain attributes and the corresponding ontology.

10th IFIP TC-6 TC-11 International Conference on Communications and Multimedia on Security (CMS’06), LNCS 4237, Springer, pp. 54-66, October, 2006. DOI
Abstract
This paper presents a model for delegation based on partial orders, proposing the subclass relation in OWL as a way to represent the partial orders. Delegation and authorization decisions are made based on the context. In order to interact with the context, we define the Type of a credential as a way to introduce extra information regarding context constraints. When reasoning about delegation and authorization relationships, our model benefits from partial orders, defining them over entities, attributes and the credential type. Using these partial orders, the number of credentials required is reduced. It also classifies the possible criteria for making authorization decisions based on the context, in relation to the necessary information.

The 16th IEEE International Conference on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing (DASC 2018), IEEE, pp. 520-527, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
The fifth generation of cellular networks (5G) will enable different use cases where security will be more critical than ever before (e.g. autonomous vehicles and critical IoT devices). Unfortunately, the new networks are being built on the certainty that security problems can not be solved in the short term. Far from reinventing the wheel, one of our goals is to allow security software developers to implement and test their reactive solutions for the capillary network of 5G devices. Therefore, in this paper a solution for analysing proximity-based attacks in 5G environments is modelled and tested using OMNET++. The solution, named CRAT, is able to decouple the security analysis from the hardware of the device with the aim to extend the analysis of proximity-based attacks to different use-cases in 5G. We follow a high-level approach, in which the devices can take the role of victim, offender and guardian following the principles of the routine activity theory.
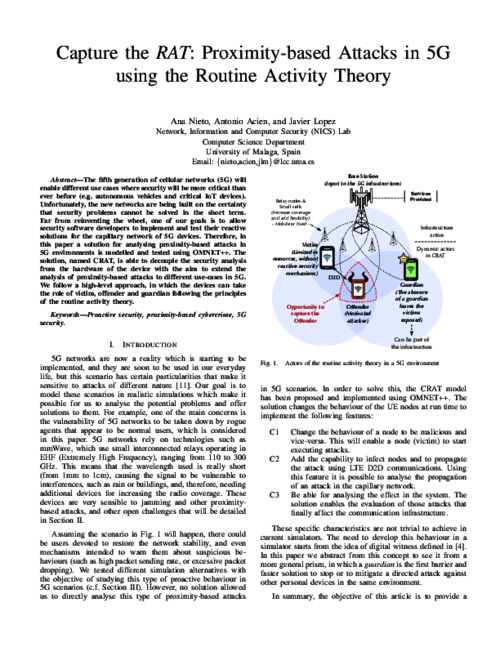
The 27th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2022), vol. 13555, Springer, Cham, pp. 716–736, 09/2022. DOI
Abstract
In recent years, the deployment of charging infrastructures has been increasing exponentially due to the high energy demand of electric vehicles, forming complex charging networks. These networks pave the way for the emergence of new unknown threats in both the energy and transportation sectors. Economic damages and energy theft are the most frequent risks in these environments. Thus, this paper aims to present a solution capable of accurately detecting unforeseen events and possible fraud threats that arise during charging sessions at charging stations through the current capabilities of the Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. However, these algorithms have the drawback of not fitting well in large networks and generating a high number of false positives and negatives, mainly due to the mismatch with the distribution of data over time. For that reason, a Collaborative Anomaly Detection System for Charging Stations (here referred to as CADS4CS) is proposed as an optimization measure. CADS4CS has a central analysis unit that coordinates a group of independent anomaly detection systems to provide greater accuracy using a voting algorithm. In addition, CADS4CS has the feature of continuously retraining ML models in a collaborative manner to ensure that they are adjusted to the distribution of the data. To validate the approach, different use cases and practical studies are addressed to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the solution.

XII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información - RECSI 2012, Mondragon, pp. 297-302, Sep 2012.

15th International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business (TrustBus 2018), vol. LNCS 11033, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, pp. 229–243, 09/2018. DOI
Abstract
Recent news have raised concern regarding the security on the IoT field. Vulnerabilities in devices are arising and honeypots are an excellent way to cope with this problem. In this work, current solutions for honeypots in the IoT context, and other solutions adaptable to it are analyzed in order to set the basis for a methodology that allows deployment of IoT honeypot.

V Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC), 06/2019.
Abstract
Cada día es más frecuente encontrar servicios en internet gestionados desde plataformas online y con la expansión de la tecnología IoT, los smartphones, las smartTV y otros tantos dispositivos: la autenticación, la distribución y al fin y al cabo, la comunicación entre extremos puede verse seriamente comprometida si dicha plataforma es atacada. La inclusión de nuevas medidas de seguridad en este tipo de ecosistemas requiere de un cambios sustancial de la arquitectura subyacente en muchos casos, por lo que su avance es lento.
En este trabajo se trata de forma concreta el desarrollo de una alternativa OpenSource a uno de estos servicios, la telefonía IP (VoIP), que esta expandiéndose cada día más, empezando por redes locales y privadas y llegando a grandes centralitas de conmutación de tele operadoras, consiguiendo así una transmisión de voz segura extremo a extremo transparente para los servidores VoIP, que no requiera modificar la infraestructura subyacente.

2022 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (IEEE CSR), IEEE, pp. 82-89, 08/2022. DOI
Abstract
Cyber-attacks against Industrial Control Systems (ICS) can lead to catastrophic events which can be prevented by the use of security measures such as the Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). In this work we experimentally demonstrate how to exploit the configuration vulnerabilities of SNORT one of the most adopted IPSs to significantly degrade the effectiveness of the IPS and consequently allowing successful cyber-attacks. We illustrate how to design a batch script able to retrieve and modify the configuration files of SNORT in order to disable its ability to detect and block Denial of Service (DoS) and ARP poisoning-based Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks against a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) in an ICS network. Experimental tests performed on a water distribution testbed show that, despite the presence of IPS, the DoS and ARP spoofed packets reach the destination causing respectively the disconnection of the PLC from the ICS network and the modification of packets payload.
9th International Conference on Risks and Security of Internet and Systems , vol. 8924, Springer International Publishing, pp. 17-34, 04/2015. DOI
Abstract
Anomaly-based detection applied in strongly interdependent systems, like Smart Grids, has become one of the most challenging research areas in recent years. Early detection of anomalies so as to detect and prevent unexpected faults or stealthy threats is attracting a great deal of attention from the scientific community because it offers potential solutions for context-awareness. These solutions can also help explain the conditions leading up to a given situation and help determine the degree of its severity. However, not all the existing approaches within the literature are equally effective in covering the needs of a particular scenario. It is necessary to explore the control requirements of the domains that comprise a Smart Grid, identify, and even select, those approaches according to these requirements and the intrinsic conditions related to the application context, such as technological heterogeneity and complexity. Therefore, this paper analyses the functional features of existing anomaly-based approaches so as to adapt them, according to the aforementioned conditions. The result of this investigation is a guideline for the construction of preventive solutions that will help improve the context-awareness in the control of Smart Grid domains in the near future.

1st International Workshop on Security and Trust for Applications in Virtualised Environments (STAVE 2011), C. Lee, J-M. Seigneur, J. J. Park, and R. R. Wagner Eds., Communications in Computer and Information Science 187, Springer, pp. 190-197, June, 2011. DOI
Abstract
In this paper we identify some areas where cryptography can help a rapid adoption of cloud computing. Although secure storage has already captured the attention of many cloud providers, offering a higher level of protection for their customer’s data, we think that more advanced techniques such as searchable encryption and secure outsourced computation will become popular in the near future, opening the doors of the Cloud to customers with higher security requirements.

XV Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información, 10/2018.
Abstract
Con la revolución tecnológica que ha supuesto la Internet de las Cosas (Internet of Things, IoT) se han presentado escenarios donde la preocupación por la seguridad en dicho entorno es cada vez más relevante. Están comenzando a surgir vulnerabilidades en varios dispositivos, y los sistemas trampa son una excelente manera de lidiar con este problema. En este trabajo se analizan soluciones para honeypots en el entorno IoT (y en otros que se puedan adaptar) para sentar las bases de una metodología que permita el despliegue de honeypots IoT.

IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom 2014), IEEE, pp. 374-379, 12/2014. DOI
Abstract
Among Big Data technologies, Hadoop stands out for its capacity to store and process large-scale datasets. However, although Hadoop was not designed with security in mind, it is widely used by plenty of organizations, some of which have strong data protection requirements. Traditional access control solutions are not enough, and cryptographic solutions must be put in place to protect sensitive information. In this paper, we describe a cryptographically-enforced access control system for Hadoop, based on proxy re-encryption. Our proposed solution fits in well with the outsourcing of Big Data processing to the cloud, since information can be stored in encrypted form in external servers in the cloud and processed only if access has been delegated. Experimental results show that the overhead produced by our solution is manageable, which makes it suitable for some applications.

5th International Workshop on Formal Aspects in Security and Trust (FAST’08), LNCS 5491, Springer, pp. 302-315, 2008. DOI
Abstract
When delegation in real world scenarios is considered, the delegator (the entity that posses the privileges) usually passes the privileges on to the delegatee (the entity that receives the privileges) in such a way that the former looses these privileges while the delegation is effective. If we think of a physical key that opens a door, the privilege being delegated by the owner of the key is opening the door. Once the owner of the key delegates this privilege to another entity, by handing over the key, he is not able to open the door any longer. This is due to the fact that the key is not copied and handed over but handed over to the delegatee. When delegation takes place in the electronic world, the delegator usually retains also the privileges. Thus, both users have them simultaneously. This situation, which in most cases is not a problem, may be undesirable when dealing with certain kind of resources. In particular, if we think of finite resources, those in which the number of users accessing simultaneously is finite, we can not allow that a user delegating his access privilege is also granted access when the delegation if effective. In this paper we propose an approach where each user is delegated an access quota for a resource. If further delegating of the delegated quota occurs, this is subtracted from his quota. That is, when delegating, part of the quota remains with the delegator and another part goes to the delegatee. This allows a more fairly access to the resource. Moreover, we show that this approach can also be applied to any kind of resources by defining appropriate authorization policies.

Fifth International Network Conference (INC’05), pp. 157-164, 2005.

XIV Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL 2019), 10/2019.
Abstract
En los nuevos paradigmas de movilidad surgidos durante los últimos años y en aquellos aún por llegar ha quedado patente la necesidad de modernizar la infraestructura viaria y los elementos de señalización y gestión del tráfico. En el presente trabajo se presenta una propuesta para esta nueva generación de dispositivos de gestión del tráfico: un prototipo de semáforo inteligente conectado que implementa diversas medidas de seguridad. Además de las tradicionales señales luminosas, los usuarios de la vía pueden conocer a través de sus dispositivos el estado del semáforo, además de otra información complementaria a través de la difusión de mensajes BLE firmados con criptografía de curva elíptica. A su vez, el semáforo puede ser gestionado remotamente a través de la tecnología LTE Cat M1 protegida por TLS. Esto abre la puerta, entre otros, a facilitar el tránsito de los vehículos de emergencia cuando estos se acercan a un cruce o modificar el tiempo de los estados del ciclo en función de las necesidades del tráfico.

XI Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (RECSI 2010), September, 2010.
Abstract
En la actualidad, cada vez son más frecuentes los ataques software mediante la utilización de malware o sustitución de programas (o componentes) en los repositorios a los cuales los usuarios finales (o máquinas) acceden. Esta situación se ve de alguna manera acentuada con el dinamismo existente en la programación y ejecución de estos componentes, en la que distintos desarrolladores pueden participar para desplegar un determinado servicio o parte de él. Por ello, en este artículo se presenta una solución para la distribución de código de forma segura usando OpenID y firmas con certificados de clave pública de corta duración. De esta forma, se consigue un compromiso de seguridad que permite distribuir código firmado sin la necesidad de que los desarrolladores dispongan a priori de un certificado específico. Presentamos además algunos detalles acerca de la implementación realizada para hacer realidad este diseño.

25th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2020), vol. 12308, pp. 174-192, 09/2020. DOI

3rd CompanionAble Workshop - Future Internet of People, Things and Services (IoPTS) eco-Systems, xxxx, pp. xxxx, December, 2009.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks are considered as an integral part of the Internet of Things paradigm. Not only they provide a virtual presence to elements of the real world, but also allow any computationalsystem to know about the physical state of those elements thanks to the use of embedded sensors. In order to belong to the Internet of Things, the elements of a sensor network can implement Internet protocols and services such as the TCP/IP stack and web services. Still, a question that must be raised at this point of time is whether all sensor network applications should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. The purpose of this paper is to analyze this question, reviewing the challenges and security requirements of Internet-enabled sensor networks.

Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (SECRYPT 2016), pp. 19-27, 2016. DOI
Abstract
Increasingly, automatic restoration is an indispensable security measure in control systems (e.g. those used in critical infrastructure sectors) due to the importance of ensuring the functionality of monitoring infrastructures. Modernizing the interconnection of control systems to provide interoperability between different networks, at a low cost, is also a critical requirement in control systems. However, automated recovery mechanisms are currently costly, and ensuring interoperability particularly at a low cost remains a topic of scientific challenge. This is the gap we seek to address in this paper. More specifically, we propose a restoration model for interconnected contexts, taking into account the theory of supernode and structural controllability, as well as the recommendations given by the IEC-62351-8 standard (which are mainly based on the implementation of a role-based access control system).

5th International conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS’10), LNCS 6712, Springer, pp. 55-67, September, 2010.
Abstract
A way of controlling a cascading effect caused by a failure or a threat in a critical system is using intelligent mechanisms capable of predicting anomalous behaviours and also capable of reacting against them in advance. These mechanisms are known as Early Warning Systems (EWS) and this will be precisely the main topic of this paper. Specially, we present an EWS design based on a Wireless Sensor Network (using the ISA100.11a standard) that constantly supervise the application context. This EWS is also based on forensic techniques to provide dynamic learning capacities. As a result, this new approach will aid to provide a reliable control of incidences by offering a dynamic alarm management, identification of the most suitable field operator to attend an alarm, reporting of causes and responsible operators, and learning from new anomalous situations.

European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS2019), vol. 11736, pp. 263-280, 09/2019. DOI

VIII Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (VIII RECSI), pp. 225-235, Sep 2004.
III Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2017), 2017.
Abstract
Debido a la necesidad de proteger los sistemas industriales ante amenazas, se hace necesario comprender cual es el verdadero alcance de los mecanismos capaces de detectar potenciales anomalías e intrusiones. Es por tanto el objetivo de este artículo analizar el estado y la evolución, tanto académica como industrial, de los mecanismos de detección de intrusiones en este campo, así como estudiar su aplicabilidad actual y futura.

4th Workshop on Security and Trust Management (STM’08), ENTCS 224, Elsevier, pp. 3-12, 2008. DOI
Abstract
In this paper we propose a trust model, where besides considering trust and distrust, we also consider another parameter that measures the reliability on the stability of trust or distrust. The inclusion of this new parameter will allow us to use trust in a more accurate way. We consider trust is not static but dynamic and trust values can change along time. Thus, we will also take time into account, using it as a parameter of our model. There is very little work done about the inclusion of time as an influence on trust. We will show the applicability of our model in the scenario of the process of reviewing papers for a conference. Sometimes for these kind of processes the Chair of the conference should first find the suitable reviewers. He can make this selection by using our model. Once the reviewers are selected they send out their reviews to the Chair who can also use our model in order to make the final decision about acceptance of papers.

31st Annual IFIP WG 11.3 Conference on Data and Applications Security and Privacy (DBSec'17), vol. LNCS 10359, Springer, pp. 453-472, 07/2017. DOI
Abstract
In this paper, we analyze how key compromise affects the protocol by Nguyen et al. presented at ESORICS 2016, an authenticated key agreement protocol mediated by a proxy entity, restricted to only symmetric encryption primitives and intended for IoT environments. This protocol uses long-term encryption tokens as intermediate values during encryption and decryption procedures, which implies that these can be used to encrypt and decrypt messages without knowing the cor- responding secret keys. In our work, we show how key compromise (or even compromise of encryption tokens) allows to break forward secu- rity and leads to key compromise impersonation attacks. Moreover, we demonstrate that these problems cannot be solved even if the affected user revokes his compromised secret key and updates it to a new one. The conclusion is that this protocol cannot be used in IoT environments, where key compromise is a realistic risk.

18th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS’20), vol. 12147, Springer, pp. 297-320, 10/2020. DOI

11th Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy (ACISP’06), LNCS 4058, Springer, pp. 383-394, 2006. DOI
Abstract
This paper elaborates on a solution to represent authorization and delegation in a graphical way, allowing users to better interpret delegation relationships. We make use of Weighted Trust Graph (WTG) as an instrument to represent delegation and authorization, extending it to cope with more complicated concepts, and providing a graphical representation of the level of confidence that exists between two entities regarding a resource or attribute. We represent the level of confidence for each pair of entities as a point in an axis diagram, as a set of points, or as a set of triangular regions depending on the accuracy we need. Then, we use the same diagram to represent the set of acceptable confidence level, that we call authorization policy set. In this way, a single diagram can be used to decide about authorization, thus providing a powerful tool for systems in which interaction of users is needed.

1st International Workshop on Security and Trust for Applications in Virtualised Environments (STAVE 2011), vol. 187, pp. 198-204, June, 2011. DOI
Abstract
Intercloud notion is gaining a lot of attention lately from both enterprise and academia, not only because of its benefits and expected results but also due to the challenges that it introduces regarding interoperability and standardisation. Identity management services are one of the main candidates to be outsourced into the Intercloud, since they are one of the most common services needed by companies and organisations. This paper addresses emerging identity management challenges that arise in intercloud formations, such as naming, identification, interoperability, identity life cycle management and single sign-on.

IX Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática (JITEL’10), Y. Dimitriadis, and M. Jesús Ver Pérez Eds., pp. 237 - 244, Sept., 2010.
Abstract
Las aplicaciones basadas en localización proporcionan a los usuarios servicios personalizados dependiendo de su ubicación. Las estimaciones prevén que estos servicios se extenderán enormemente en los próximos años reportando grandes beneficios tanto a la industria como a los usuarios finales. Sin embargo, para que estos avances sean posibles se hace necesario analizar en profundidad las distintas implicaciones de seguridad y privacidad que la utilización de tales servicios pueden traer consigo a los usuarios. En este trabajo proponemos un sistema de localización que da soporte a la provisión de servicios basados en localización para entornos indoor y que se fundamenta en la tecnología de redes de sensores inalámbricos. En este esquema hemos tenido en cuenta diversos aspectos de seguridad y privacidad, prestando especial atención a la limitación extrema de recursos característica de las redes de sensores. Finalmente hemos desarrollado una prueba de concepto para comprobar la viabilidad de nuestro esquema dentro del ámbito del proyecto OSAmI.

3rd international conference on Mobile multimedia communications (MobiMedia ’07), ICST, pp. 50:1–50:6, 2007.
Abstract
In this paper we simulate an authorization and delegation system using knowledge based technology. This proposal is part of a visual tool that is intended to be an implementation of the theoretical model weighted trust graph (WTG). A brief description of WTG Model and its associated tool is included in the text. In essence, the model is based on the inclusion of real numbers between zero and one in certificates to represent the trust level between the entities involved in them. This trust level is used to control delegation. Moreover, attributes from di_erent domains may be interrelated, so attribute delegation is also taken into account. The proposed Simulation Engine supports one directional and bidirectional search algorithms.

VII Jornadas Nacionales en Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 172-179, 06/2022.
Abstract
El interés actual por desplegar infraestructuras de carga de vehículos eléctricos para el ahorro energético y la sostenibilidad es cada vez más palpable, lo que llama la atención a muchas comunidades, especialmente a la científica, para explorar, entre otras cosas, la influencia de las nuevas tecnologías de información en los procesos operacionales. Teniendo en cuenta este escenario, este artículo, por tanto, analiza cómo el uso de los sistemas de multi-agente pueden beneficiar las tareas de monitorización, mantenimiento y de seguridad, y propone una arquitectura específica en base a los actores especificados en el protocolo OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol). Esta arquitectura constituye la base para analizar los diversos tipos de amenazas que agentes software pueden sufrir, clasificándolas de acuerdo a las características funcionales e interacciones con los diversos elementos de la infraestructura. Esta agrupación y el conjunto de ataques abordados están basados en el SP-800-19 definido por el National Institute of Standards and Technology, y formalizados siguiendo la metodología de árboles de ataque. El estudio revela la importancia que tiene analizar los riesgos que esta tecnología puede traer a este escenario, proporcionando, además, un conjunto de recomendaciones que sirvan de guía para aplicaciones futuras.

IEEE CloudCom 2012, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 241 - 248, Dec 2012. DOI
Abstract
The inclusion of identity management in the cloud computing landscape represents a new business opportunity for providing what has been called Identity Management as a Service (IDaaS). Nevertheless, IDaaS introduces the same kind of problems regarding privacy and data confidentiality as other cloud services; on top of that, the nature of the outsourced information (users’ identity) is critical. Traditionally, cloud services (including IDaaS) rely only on SLAs and security policies to protect the data, but these measures have proven insufficient in some cases; recent research has employed advanced cryptographic mechanisms as an additional safeguard. Apart from this, there are several identity management schemes that could be used for realizing IDaaS systems in the cloud; among them, OpenID has gained crescent popularity because of its open and decentralized nature, which makes it a prime candidate for this task. In this paper we demonstrate how a privacy-preserving IDaaS system can be implemented using OpenID Attribute Exchange and a proxy re-encryption scheme. Our prototype enables an identity provider to serve attributes to other parties without being able to read their values. This proposal constitutes a novel contribution to both privacy and identity management fields. Finally, we discuss the performance and economical viability of our proposal.

IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications, 06/2023.
Abstract
In the last few years we have seen many different approaches to incorporate privacy features to blockchains. In the area of cryptocurrencies that would normally mean protecting the identity of the owner of some funds, but there are other applications where privacy is even more important, especially in permissioned blockchains.
Permissioned blockchain platforms, such as Hyperledger Besu or Hyperledger Fabric, already include the concept of private transactions, which essentially defines a sub-group of the blockchain where their participants share some private data.
We want to go one step ahead and propose an extended model for private transactions where the different participants can have a separated view of the same transaction, allowing the integration of Multi-party Computation protocols in the blockchain.
Our work extends Hyperledger Besu's design for private transactions, offering better security properties and a finer grain customization. We cover two specific MPC examples, Private Set Intersection and Byzantine Fault-Tolerant Random Number Generation, and propose a mechanism to run them using smart contract interfaces.

Ph.D Symposium of the European Conference on Service-Oriented and Cloud Computing (ESOCC) 2013, September 2013.
Abstract
The advent of cloud computing has provided the opportunity to externalize the identity management processes, shaping what has been called Identity Management as a Service (IDaaS). However, as in the case of other cloud-based services, IDaaS brings with it great concerns regarding security and privacy, such as the loss of control over the outsourced data. As part of this PhD thesis, we analyze these concerns and propose BlindIdM, a model for privacy-preserving IDaaS with a focus on data privacy protection through the use of proxy re-encryption.

IEEE CloudCom 2011, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 527-531, Nov-Dec 2011. DOI
Abstract
During the last decade, the Cloud Computing paradigm has emerged as a panacea for many problems in traditional IT infrastructures. Much has been said about the potential of Cloud Computing in the Smart Grid context, but unfortunately it is still relegated to a second layer when it comes to critical systems. Although the advantages of outsourcing those kind of applications to the cloud is clear, data confidentiality and operational privacy stand as mayor drawbacks. In this paper, we try to give some hints on which security mechanisms and more specific, which cryptographic schemes, will help a better integration of Smart Grids and Clouds. We propose the use of Virtual SCADA in the Cloud (VS-Cloud) as a mean to improve reliability and efficiency whilst maintaining the same protection level as in traditional SCADA architectures.

IEEE CloudCom 2011, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 527-531, Nov-Dec 2011. DOI
Abstract
During the last decade, the Cloud Computing paradigm has emerged as a panacea for many problems in traditional IT infrastructures. Much has been said about the potential of Cloud Computing in the Smart Grid context, but unfortunately it is still relegated to a second layer when it comes to critical systems. Although the advantages of outsourcing those kind of applications to the cloud is clear, data confidentiality and operational privacy stand as mayor drawbacks. In this paper, we try to give some hints on which security mechanisms and more specific, which cryptographic schemes, will help a better integration of Smart Grids and Clouds. We propose the use of Virtual SCADA in the Cloud (VS-Cloud) as a mean to improve reliability and efficiency whilst maintaining the same protection level as in traditional SCADA architectures.

VIII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC), 06/2023, In Press.
VI Reunion Española de Criptología y Seguridad de la Información (VI RECSI), pp. 193-200, Septiembre, 2000.
Abstract
La presente comunicación presenta un mecanismo de micropagos flexible, de bajo costo que puede utilizarse para realizar pagos en línea entre el cliente y el vendedor y fuera de línea con el agente de negocios. Este mecanismo evita grandes almacenamientos de datos y cálculos largos. Se puede implantar en software para el cliente y en hardware/software para el vendedor.

5th International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business (TrustBus’08), LNCS 5185, Springer, pp. 28-37, 2008. DOI
Abstract
Trust is an important factor in any kind of network essential, for example, in the decision-making process. As important as the definition of trust is the way to compute it. In this paper we propose a model for defining trust based on graph theory and show examples of some simple operators and functions that will allow us to compute trust.

IV Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2018), Servicio Editorial de Mondragon Unibertsitatea, 06/2018.
Abstract
Los ataques cross-platform suponen un serio desafío para los mecanismos de seguridad cuando los portadores de un ataque dirigido no son conscientes de su participacion en el mismo. Es por ello que, con dispositivos y tecnologías cada vez mas entrelazadas, en constante comunicación, numerosos ataques pasan desapercibidos hasta que alcanzan su objetivo final. Estos nuevos escenarios hacen posible una vía de transmision a tener en cuenta, y que se debe abordar cuanto antes, ya que sus consecuencias, especialmente en el panorama de telecomunicaciones actual, podrían ser desoladoras. La rapida transmisión de estos ataques, y la dificultad que supone su prevencion, detección y mitigación antes de que se hagan efectivos, hacen que el problema sea particularmente preocupante. En este artículo se presentará una arquitectura para el analisis de los ataques cross-platform silenciosos, cuyo objetivo es ayudar a comprender mejor este tipo de amenazas y ofrecer soluciones que permitan mitigarlas y rastrearlas.

Sixth European Workshop on Public Key Services, Applications and Infrastructures (EuroPKI’09), LNCS 6391, Springer, pp. 225-238, 2009. DOI
Abstract
Deciding who to trust in the internet of services paradigm is an important and open question. How to do it in an optimal way is not always easy to determine. Trust is usually referred to a particular context whereas a single user may interact in more than one given context. We are interested in investigating how a Federated Reputation System can help exporting trust perceptions from one context to another. We propose a model for deriving trust in online services. In this context, trust is defined as the level of confidence that the service provider holds on the subject interacting with it to behave in a proper way while using the service. Thus, we derive trust by using the reputation values that those users have gained for interacting with these services.

The 16th Information Security Conference (ISC), vol. 7807, Springer, pp. 140–151, 09/2015. DOI
Abstract
The notion of controllability, informally the ability to force a system into a desired state in a finite time or number of steps, is most closely associated with control systems such as those used to maintain power networks and other critical infrastructures, but has wider relevance in distributed systems. It is clearly highly desirable to understand under which conditions attackers may be able to disrupt legitimate control, or to force overriding controllability themselves. Following recent results by Liu et al., there has been considerable interest also in graph-theoretical interpretation of Kalman controllability originally introduced by Lin, structural controllability. This permits the identification of sets of driver nodes with the desired state-forcing property, but determining such nodes is aW[2]-hard problem. To extract these nodes and represent the control relation, here we apply the POWER DOMINATING SET problem and investigate the effects of targeted iterative multiple-vertex removal. We report the impact that different attack strategies with multiple edge and vertex removal will have, based on underlying non-complete graphs, with an emphasis on power-law random graphs with different degree sequences.

10th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security (AsiaCCS), pp. 179-189, 04/2015. DOI
Abstract
The use of alternative foundations for constructing more secure and efficient cryptographic schemes is a topic worth exploring. In the case of proxy re-encryption, the vast majority of schemes are based on number theoretic problems such as the discrete logarithm. In this paper we present NTRUReEncrypt, a new bidirectional and multihop proxy re-encryption scheme based on NTRU, a widely known lattice-based cryptosystem. We provide two versions of our scheme: the first one is based on the conventional NTRU encryption scheme and, although it lacks a security proof, remains as efficient as its predecessor; the second one is based on a variant of NTRU proposed by Stehlé and Steinfeld, which is proven CPA-secure under the hardness of the Ring-LWE problem. To the best of our knowledge, our proposals are the first proxy re-encryption schemes to be based on the NTRU primitive. In addition, we provide experimental results to show the efficiency of our proposal, as well as a comparison with previous proxy re-encryption schemes, which confirms that our first scheme outperforms the rest by an order of magnitude.

XIV Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información, pp. 174-179, 10/2016.
Abstract
El recifrado delegado (proxy re-encryption) es un tipo de cifrado de clave pública que permite delegar la capacidad de transformar textos cifrados de una clave pública a otra, sin que se pueda obtener ninguna información sobre el mensaje subyacente. Por este motivo, representa un candidato natural para construir mecanismos criptográficos de control de acceso. En este artículo estudiamos algunos de los problemas de seguridad de este tipo de criptosistemas. En primer lugar, examinamos las nociones de seguridad e identificamos una nueva familia paramétrica de modelos de ataque, que considera la disponibilidad tanto del oráculo de descifrado como de recifrado. En segundo lugar, estudiamos la aplicabilidad de transformaciones genéricas para mejorar la seguridad, centrándonos en la transformación Fujisaki-Okamoto, y formulamos las condiciones que nos permiten aplicarla.

IEEE 16th Conference on Emerging Technologies Factory Automation (ETFA 2011), IEEE, pp. 1-10, Sep 2011. DOI
Abstract
Today we live in an environment surrounded with networked converging devices. Human computer interactions are becoming personalized and a new concept of a global and cross-domain platform is emerging to exploit the full potential of the network in all business areas. In this convergence process, the software platform should be able to personalize itself dynamically in devices according to the context. OSAmI-Commons, an ITEA2 project for developing an open-source common approach to such a dynamic service-based platform, allows any type of device to connect and exchange information and services. OSAMI consortium is contributing to defining the foundations of a cross-platform open-services ecosystem. The sustainability of this platform is an objective beyond the project duration.
28th IEEE Computer Security Foundations Symposium, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 290-301, 07/2015. DOI
Abstract
Proxy Re-Encryption (PRE) is a type of Public-Key Encryption (PKE) which provides an additional re-encryption functionality. Although PRE is inherently more complex than PKE, attack models for PRE have not been developed further than those inherited from PKE. In this paper we address this gap and define a parametric family of attack models for PRE, based on the availability of both the decryption and re-encryption oracles during the security game. This family enables the definition of a set of intermediate security notions for PRE that ranges from ``plain'' IND-CPA to ``full'' IND-CCA. We analyze some relations among these notions of security, and in particular, the separations that arise when the re-encryption oracle leaks re-encryption keys. In addition, we discuss which of these security notions represent meaningful adversarial models for PRE. Finally, we provide an example of a recent ``CCA1- secure'' scheme from PKC 2014 whose security model does not capture chosen-ciphertext attacks through re-encryption and for which we describe an attack under a more realistic security notion. This attack emphasizes the fact that PRE schemes that leak re-encryption keys cannot achieve strong security notions.

7th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS 2012), vol. 7722, pp. 22–33, 2013.
Abstract
Prevention, detection and response are nowadays considered to be three priority topics for protecting critical infrastructures, such as energy control systems. Despite attempts to address these current issues, there is still a particular lack of investigation in these areas, and in particular in dynamic and automatic proactive solutions. In this paper we propose a mechanism, which is called PDR, with the capability of anticipating anomalies, detecting anomalous behaviours and responding to them in a timely manner. PDR is based on a conglomeration of technologies and on a set of essential components with the purpose of offering situational awareness irrespective of where the system is located. In addition, the mechanism can also compute its functional capacities by evaluating its efficacy and precision in the prediction and detection of disturbances. With this, the entire system is able to know the real reliability of its services and its activity in remote substations at all times.

International Conference on Information Systems Education and Research (AIS SIGED 2019), 12/2019.

IX Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la información (RECSI’06), pp. 311-322, Septiembre, 2006.

European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, vol. 10493, 22nd European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2017), pp. 402-418, 09/2017.

I Congreso Nacional Turismo y Tecnología de la Información y las Comunicaciones (TURITEC’99), pp. 99-110, Septiembre, 1999.
Abstract
Uno de los servicios que cada día cobra más importancia y que promete un cambio radical para las empresas es el comercio electrónico en Internet, pero tradicionalmente las empresas relacionadas con el turismo sólo han empleado la red para darse a conocer y ofertar sus productos. La razón esencial es la desconfianza que existe sobre la seguridad de las transacciones llevadas a cabo en la red. La criptografía de clave pública proporciona servicios adecuados para garantizar la seguridad de esas transacciones. Pero en la actualidad, algunos de esos servicios están menos desarrollados que otros; un ejemplo de ellos es el servicio de No-Repudio. En este artículo se estudian distintas formas de ofrecer servicios de no-repudio y se analizan sus ventajas y desventajas en función de las necesidades del entorno en que se utilicen.
XIV Jornadas de Ingeniería Telemática, pp. 50-53, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Este trabajo pretende analizar el paradigma de la Computación Segura Multiparte y sus posibles aplicaciones en el campo de la criptografía. Se plantea como modelo alternativo, mas escalable y seguro al uso de módulos hardware de seguridad para aplicaciones que requieran de Terceras Partes Confiables. Concretamente, se ha integrado un protocolo de criptografía RSA multiparte con la librería certbuilder, para la creación de certificados X.509. De esta forma se asegura que la creación de los certificados raíz de la Infraestructura de Clave Publica se realiza de forma que la generación de claves y firma de este se ejecute íntegramente sobre el sistema multiparte, con un modelo de tres partes que trabaja con circuitos aritméticos, sin que ninguna de ellas, de forma aislada, tenga posibilidad de comprometer la clave privada correspondiente. Para comprobar la viabilidad del sistema se han realizado pruebas de generación de certificados con diferentes longitudes de clave, siendo el proceso determinante la creación de las claves. Los elevados tiempos hacen que una aplicación como esta no sea asumible en otros escenarios, pero creemos que para el caso de la creación de los certificados raíz de una infraestructura de clave pública las garantías avanzadas de seguridad compensan el tiempo extra.

19th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2022), Scitepress, pp. 249-260, 07/2022. DOI
Abstract
Crowd Counting is a very interesting problem aiming at counting people typically based on density averages and/or aerial images. This is very useful to prevent crowd crushes, especially on urban environments with high crowd density, or to count people in public demonstrations. In addition, in the last years, it has become of paramount importance for pandemic management. For those reasons, giving users automatic mechanisms to anticipate high risk situations is essential. In this work, we analyze ID-based Crowd Counting, and propose a real-time Crowd Counting system based on the Ephemeral ID broadcast by contact tracing applications on wearable devices. We also performed some simulations that show the accuracy of our system in different situations.

Eighth IFIP WG 11.10 International Conference on Critical Infrastructure Protection, SRI International, Arlington, Virginia, USA , vol. 441, Springer, pp. 47-63, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Fundamental problems in control systems theory are controllability and observability, and designing control systems so that these properties are satisfied or approximated sufficiently. However, it is prudent to as- sume that an attacker will not only be able to subvert measurements but also control the system. Moreover, an advanced adversary with an understanding of the control system may seek to take over control of the entire system or parts thereof, or deny the legitimate operator this capability. The effectiveness of such attacks has been demonstrated in previous work. Indeed, these attacks cannot be ruled out given the likely existence of unknown vulnerabilities, increasing connectivity of nominally air-gapped systems and supply chain issues. The ability to rapidly recover control after an attack has been initiated and to detect an adversary’s presence is, therefore, critical. This paper focuses on the problem of structural controllability, which has recently attracted substantial attention through the equivalent problem of the power dom- inating set introduced in the context of electrical power network control. However, these problems are known to be NP-hard with poor approx- imability. Given their relevance to many networks, especially power networks, this paper studies strategies for the efficient restoration of controllability following attacks and attacker-defender interactions in power-law networks.

3th International Conference on Trust Management (iTRUST’05), LNCS 3477, Springer, pp. 9-22, May, 2005. DOI
Abstract
Logic languages establish a formal framework to solve authorization and delegation conflicts. However, we consider that a visual representation is necessary since graphs are more expressive and understandable than logic languages. In this paper, and after overviewing previous works using logic languages, we present a proposal for graph representation of authorization and delegation statements. Our proposal is based on Varadharajan et al. solution, though improve several elements of that work. We also discuss about the possible implementation of our proposal using attribute certificates.

The 21st European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2016), vol. 9879, Springer, pp. 471-489, 2016.
Abstract
Automatic restoration of control wireless networks based on dynamic cyber-physical systems has become a hot topic in recent years, since most of their elements tend to have serious vulnerabilities that may be exploited by attackers. In fact, any exploitation may rapidly extend to the entire control network due to its problem of non-locality, where control properties of a system and its structural controllability can disintegrate over time. Unfortunately, automated self-healing processes may become costly procedures in which the reliability of the strategies and the time-critical of any recovery of the control can become key factors to re-establish the control properties in due time. This operational need is precisely the aim of this paper, in which four reachability-based recovery strategies from a thereotical point of view are proposed so as to find the best option/s in terms of optimization, robustness and complexity. To do this, new definitions related to structural controllability in relation to the type of distribution of the network and its control load capacity are given in this paper, resulting in an interesting practical study.

14th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS 2019), vol. 11777, Springer, Cham, pp. 169-175, 12/2019. DOI
Abstract
In recent years, the Smart Grid has increasingly integrated cutting-edge technologies that generate several benefits for all the stakeholders involved, such as a more accurate billing system and enhanced Demand Response procedures. However, this modernization also brings with it diverse cyber security and privacy issues, which sets the necessity for developing a security platform specifically tailored to this scenario. In this paper, we present SealedGRID, which proposes a flexible architecture that provides security services at all levels by implementing Trusted Execution Environments on their devices, together with advanced authentication and authorization mechanisms, as well as privacy preserving techniques. These technologies are presented in depth and a final security analysis is conducted, which highlights the contributions of this project.

Fourth International Conference on Networked Computing and Advanced Information Management (NCM’08), vol. 1, IEEE, pp. 631-635, September, 2008. DOI
Abstract
This paper presents a service oriented architecture for real-time integration of services, how to distribute them in a local domain and how to define a secure way of accessing resources using users’ and services’ authorization and authentication. This work take advantage of previous European R amp;D projects focused on del.ivering applications and utilities in embedded real-time environments and the convergence of different worlds like Internet and digital TV.
International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies (CompSysTech09), ACM, pp. 11.7.1-11.7.6, 2009. DOI
Abstract
Assurance has been a major topic for critical systems. Assurance is usually associated with safety conditions but has also an important role for checking security requirements. Security is best assured if it is addressed holistically, systematically, and from the very beginning in the software’s development process. We propose to integrate assurance and system development by letting the different stages of the system development life-cycle be mapped to the structure of the assurance case.

The 11th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security, vol. 10242, pp. 176-188, 2017.
Abstract
The introduction of the Smart Grid brings with it several benefits to society, because its bi-directional communication allows both users and utilities to have better control over energy usage. However, it also has some privacy issues with respect to the privacy of the customers when analysing their consumption data. In this paper we review the main privacy-preserving techniques that have been proposed and compare their efficiency, to accurately select the most appropriate ones for undertaking control operations. Both privacy and performance are essential for the rapid adoption of Smart Grid technologies.

5th International Symposium on Security and Multimodality in Pervasive Environments (SMPE’11), IEEE, March, 2011. DOI
Abstract
Key Management Schemes (KMS) are a very important security mechanism for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), as they are used to manage the credentials (i.e. secret keys) that are needed by the security primitives. There is a large number of available KMS protocols in the literature, but it is not clear what should network designers do to choose the most suitable protocol for the needs of their applications. In this paper, we consider that given a certain set of application requirements, the network designer can check which properties comply with those requirements and select the KMS protocols that contains those particular properties. Therefore, we study the relationship between requirements and properties, and we provide a web tool, the SenseKey tool, that can be used to automatically obtain an optimal set of KMS protocols.

III Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad, URJC, pp. 174-175, 06/2017.
Abstract
En este artículo presentamos un sistema que permite delegación de acceso a información cifrada para Apache Hadoop, de forma segura y transparente al usuario. Para ello usamos técnicas criptográficas avanzadas basadas en el recifrado delegado. Con este sistema, es posible almacenar en Hadoop los datos de forma cifrada y delegar de forma segura el acceso a los nodos de computación. El funcionamiento es transparente ya que se integra con la capa del sistema de ficheros nativa HDFS. Además, el recifrado delegado permite hacer rotación de claves de cifrado de forma segura y rápida.
21st International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 1-5, Jul 2012. DOI
Abstract
Migration to an electronically controlled electrical grid to transmit, distribute, and deliver power to consumers has helped enhance the reliability and efficiency of conventional electricity systems. At the same time, this digitally enabled technology called the Smart Grid has brought new challenges to businesses and consumers alike. A key component of such a grid is the smart-metering technology, which is used to collect energy consumption data from homes and transmitting it back to power distributors. A crucial concern is the privacy related to the collection and use of energy consumption data. We present an analysis of Smart Grid privacy issues and discuss recently proposed solutions that can protect the privacy of Smart Grid users.
5th international conference on Computer systems and technologies (CompSysTech ’04), ACM, pp. 1-6, 2004. DOI
Abstract
With the grown of internet and distributed applications, security requirements are going inherent to the software development process. Each time one communicates with some other one there are relevant security risk that must be taken in account. This is what is happening in the new soft-ware applications using client/server architecture. We propose including security requirements at the top level of development process, together with functional requirements because they are much related. With this information we are able to extract all communication protocols that are involved in our application and their associated security goals. This is the input to a verification phase in which we look for security flaws. The last step, and the more useful (and the not yet finished) is to use this information to modify our initial specification at the top level of the development process
Information Security Solutions Europe 2012, N. Pohlmann, H. Reimer, and W. Schneider Eds., Springer Vieweg, pp. 195-206, 2012. DOI
Abstract
The paper describes the experience with integration of automatic cyber identity technology with policy controlled virtualisation environment. One identity technology has been used to enable strong authentication of users (human beings) as well as machines (host systems) to the virtualization management system. The real experimental evaluation has been done in PASSIVE project (Policy-Assessed system-level Security of Sensitive Information processing in Virtualised Environments - SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME ICT-2009.1.4 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES - Small or medium-scale focused research project - Grant agreement no.: 257644).
8th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security, vol. 8328, Springer, pp. 120-132, 2013. DOI
Abstract
The problem of controllability of networks arises in a number of different domains, including in critical infrastructure systems where control must be maintained continuously. Recent work by Liu et al. has renewed interest in the seminal work by Lin on structural controllability, providing a graph-theoretical interpretation. This allows the identification of driver nodes capable of forcing the system into a desired state, which implies an obvious target for attackers wishing to disrupt the network control. Several methods for identifying driver nodes exist, but require undesirable computational complexity. In this paper, we therefore investigate the ability to regain or maintain controllability in the presence of adversaries able to remove vertices and implicit edges of the controllability graph. For this we rely on the POWER DOMINATING SET (PDS) formulation for identifying the control structure and study different attack strategies for multiple network models. As the construction of a PDS for a given graph is not unique, we further investigate different strategies for PDS construction, and provide a simulative evaluation.

Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Engineering Secure Software and Systems (ESSoS 2012), G. Barthe, B. Livshits, and R. Scandariato Eds., LNCS 7159, Springer, pp. 76–89, Feb 2012. DOI
Abstract
Trust has become essential in computer science as a way of assisting the process of decision-making, such as access control. In any system, several tasks may be performed, and each of these tasks might pose different associated trust values between the entities of the system. For instance, in a file system, reading and overwriting a file are two tasks that pose different trust values between the users who can carry out these tasks. In this paper, we propose a simple model for automatically establishing trust relationships between entities considering an established order among tasks.

10th International IFIP Summer School on Privacy and Identity Management, pp. 187-204, 2016. DOI
Abstract
Transparency and verifiability are necessary aspects of accountability, but care needs to be taken that auditing is done in a privacy friendly way. There are situations where it would be useful for certain actors to be able to make restricted views within service provision chains on accountability evidence, including logs, available to other actors with specific governance roles. For example, a data subject or a Data Protection Authority (DPA) might want to authorize an accountability agent to act on their behalf, and be given access to certain logs in a way that does not compromise the privacy of other actors or the security of involved data processors. In this paper two cryptographic-based techniques that may address this issue are proposed and assessed.

9th IFIP Summer School on Privacy and Identity Management for the Future Internet in the Age of Globalisation, vol. 457, Springer IFIP AICT, pp. 219-236, 2015. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing is becoming a key IT infrastructure technology being adopted progressively by companies and users. Still, there are issues and uncertainties surrounding its adoption, such as security and how users data is dealt with that require attention from developers, researchers, providers and users. The A4Cloud project tries to help solving the problem of accountability in the cloud by providing tools that support the process of achieving accountability. This paper presents the contents of the first A4Cloud tutorial. These contents include basic concepts and tools developed within the project. In particular, we will review how metrics can aid the accountability process and some of the tools that the A4Cloud project will produce such as the Data Track Tool (DTT) and the Cloud Offering Advisory Tool (COAT).

9th IFIP Summer School on Privacy and Identity Management for the Future Internet in the Age of Globalisation, vol. 457, Springer IFIP AICT, pp. 219-236, 2015. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing is becoming a key IT infrastructure technology being adopted progressively by companies and users. Still, there are issues and uncertainties surrounding its adoption, such as security and how users data is dealt with that require attention from developers, researchers, providers and users. The A4Cloud project tries to help solving the problem of accountability in the cloud by providing tools that support the process of achieving accountability. This paper presents the contents of the first A4Cloud tutorial. These contents include basic concepts and tools developed within the project. In particular, we will review how metrics can aid the accountability process and some of the tools that the A4Cloud project will produce such as the Data Track Tool (DTT) and the Cloud Offering Advisory Tool (COAT).

8th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructures Security, vol. 8328, Springer, pp. 197-203, 2013. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) faces increasing challenges in number and in sophistication, which makes vital to provide new forms of protection to face every day’s threats. In order to make such protection holistic, covering all the needs of the systems from the point of view of security, prevention aspects and situational awareness should be considered. Researchers and Institutions stress the need of providing intelligent and automatic solutions for protection, calling our attention to the need of providing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) with intelligent active reaction capabilities. In this paper, we support the need of automating the processes implicated in the IDS solutions of the critical infrastructures and theorize that the introduction of Machine Learning (ML) techniques in IDS will be helpful for implementing automatic adaptable solutions capable of adjusting to new situations and timely reacting in the face of threats and anomalies. To this end, we study the different levels of automation that the IDS can implement, and outline a methodology to endow critical scenarios with preventive automation. Finally, we analyze current solutions presented in the literature and contrast them against the proposed methodology

7th IFIP WG 11.11 International Conference on Trust Management (IFIPTM 2013), C. Fernandez-Gago, I. Agudo, F. Martinelli, and S. Pearson Eds., AICT 401, Springer, pp. 255-262, Jun 2013. DOI
Abstract
The Future Internet (FI) comprises scenarios where many heterogeneous and dynamic entities must interact to provide services (e.g., sensors, mobile devices and information systems in smart city scenarios). The dynamic conditions under which FI applications must execute call for self-adaptive software to cope with unforeseeable changes in the application environment. Software engineering currently provides frameworks to develop reasoning engines that automatically take reconfiguration decisions and that support the runtime adaptation of distributed, heterogeneous applications. However, these frameworks have very limited support to address security concerns of these application, hindering their usage for FI scenarios. We address this challenge by enhancing self-adaptive systems with the concepts of trust and reputation. Trust will improve decision-making processes under risk and uncertainty, in turn improving security of self-adaptive FI applications. This paper presents an approach that includes a trust and reputation framework into a platform for adaptive, distributed component-based systems, thus providing software components with new abilities to include trust in their reasoning process.

European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2018), vol. 11098, Springer, pp. 555-574, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
Advanced persistent threats pose a serious issue for modern industrial environments, due to their targeted and complex attack vectors that are difficult to detect. This is especially severe in critical infrastructures that are accelerating the integration of IT technologies. It is then essential to further develop effective monitoring and response systems that ensure the continuity of business to face the arising set of cyber-security threats. In this paper, we study the practical applicability of a novel technique based on opinion dynamics, that permits to trace the attack throughout all its stages along the network by correlating different anomalies measured over time, thereby taking the persistence of threats and the criticality of resources into consideration. The resulting information is of essential importance to monitor the overall health of the control system and correspondingly deploy accurate response procedures.

1st International Workshop on the Security of the Internet of Things (SecIoT’10), IEEE, pp. xxxx, December, 2010.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) behave as a digital skin, providing a virtual layer where the information about the physical world can be accessed by any computational system. As a result, they are an invaluable resource for realizing the vision of the Internet of Things (IoT). However, it is necessary to consider whether the devices of a WSN should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. In this paper, we tackle this question from the perspective of security. While we will mention the different security challenges that may arise in such integration process, we will focus on the issues that take place at the network level.

|
"International Workshop on Security and Trust Management 2018", International Workshop on Security and Trust Management, LNCS, vol. 11091, Springer International Publishing, 09/2018. DOI  |  |
|
"Procedings of the 10th European Workshop on Public Key Infrastructures, Services and Applications", 10th European Workshop on Public Key Infrastructures, Services and Applications, LNCS, vol. 8341, Springer, 2014. DOI  |  |
|
"Proceedings of the 12th ACM Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Wireless Ad Hoc, Sensor, & Ubiquitous Networks, PE-WASUN 2015", 12th ACM Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Wireless Ad Hoc, Sensor, & Ubiquitous Networks, PE-WASUN 2015, ACM, 2015.  |  |
|
"Proceedings of the 12th ACM Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Wireless Ad Hoc, Sensor, & Ubiquitous Networks, PE-WASUN 2015", 12th ACM Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Wireless Ad Hoc, Sensor, & Ubiquitous Networks, PE-WASUN 2015, ACM, 2015.  |  |
Trust Management VII, 7th WG11.11 International conference
, vol. 401, Springer, June 2013.
 |  |
International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection (IJCIP), vol. 5, Elsevier, pp. 137–145, 2012. DOI
Abstract
The use of modern information and communications technologies in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems used in the critical infrastructure has become an important topic of research. The modernization significantly enhances operational performance, but also introduces security issues and the associated risks. This paper formally analyzes how the introduction of new technologies can impact control systems and ultimately affect the performance of the critical infrastructure systems being controlled. Five control system requirements are identified with the goal of proposing new operational requirements that trade-off performance and security.

Security and Communication Networks, vol. 9, issue 12, Wiley, pp. 1769-1785, 08/2016. DOI
Abstract
Several generic methods exist for achieving chosen-ciphertext attack (CCA)-secure public-key encryption schemes from weakly secure cryptosystems, such as the Fujisaki–Okamoto and REACT transformations. In the context of proxy re-encryption (PRE), it would be desirable to count on analogous constructions that allow PRE schemes to achieve better security notions. In this paper, we study the adaptation of these transformations to proxy re-encryption and find both negative and positive results. On the one hand, we show why it is not possible to directly integrate these transformations with weakly secure PRE schemes because of general obstacles coming from both the constructions themselves and the security models, and we identify 12 PRE schemes that exhibit these problems. On the other hand, we propose an extension of the Fujisaki–Okamoto transformation for PRE, which achieves a weak form of CCA security in the random oracle model, and we describe the sufficient conditions for applying it

Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 47, issue October, Elsevier, pp. 299-317, 2015. DOI
Abstract
Current Critical Infrastructures (CIs) need intelligent automatic active reaction mechanisms to protect their critical processes against cyber attacks or system anomalies, and avoid the disruptive consequences of cascading failures between interdependent and interconnected systems. In this paper we study the Intrusion Detection, Prevention and Response Systems (IDPRS) that can offer this type of protection mechanisms, their constituting elements and their applicability to critical contexts. We design a methodological framework determining the essential elements present in the IDPRS, while evaluating each of their sub-components in terms of adequacy for critical contexts. We review the different types of active and passive countermeasures available, categorizing them and assessing whether or not they are suitable for Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP). Through our study we look at different reaction systems and learn from them how to better create IDPRS solutions for CIP.

International Journal of Information Security, vol. 13, issue 2, Springer, pp. 199-215, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Identity management is an almost indispensable component of today’s organizations and companies, as it plays a key role in authentication and access control; however, at the same time it is widely recognized as a costly and time-consuming task. The advent of cloud computing technologies, together with the promise of flexible, cheap and efficient provision of services, has provided the opportunity to externalize such a common process, shaping what has been called Identity Management as a Service (IDaaS). Nevertheless, as in the case of other cloud-based services, IDaaS brings with it great concerns regarding security and privacy, such as the loss of control over the outsourced data. In this paper we analyze these concerns and propose BlindIdM, a model for privacy-preserving IDaaS with a focus on data privacy protection. In particular, we describe how a SAML-based system can be augmented to employ proxy re-encryption techniques for achieving data condentiality with respect to the cloud provider, while preserving the ability to supply the identity service. This is an innovative contribution to both the privacy and identity management landscapes.

IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 70, no. 5, IEEE, pp. 4001 - 4010, 05/2021. DOI
Abstract
New mobility paradigms have appeared in recent years, and everything suggests that some more are coming. This fact makes apparent the necessity of modernizing the road infrastructure, the signalling elements and the traffic management systems. Many initiatives have emerged around the term Intelligent Transport System (ITS) in order to define new scenarios and requirements for this kind of applications. We even have two main competing technologies for implementing Vehicular communication protocols (V2X), C-V2X and 802.11p, but neither of them is widely deployed yet.
One of the main barriers for the massive adoption of those technologies is governance. Current solutions rely on the use of a public key infrastructure that enables secure collaboration between the different entities in the V2X ecosystem, but given its global scope, managing such infrastructure requires reaching agreements between many parties, with conflicts of interest between automakers and telecommunication operators. As a result, there are plenty of use cases available and two mature communication technologies, but the complexity at the business layer is stopping the drivers from taking advantage of ITS applications.
Blockchain technologies are defining a new decentralized paradigm for most traditional applications, where smart contracts provide a straightforward mechanism for decentralized governance. In this work, we propose an approach for decentralized V2X (D-V2X) that does not require any trusted authority and can be implemented on top of any communication protocol. We also define a proof-of-concept technical architecture on top of a cheap and highly secure System-on-Chip (SoC) that could allow for massive adoption of D-V2X.

Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, vol. 144, Elsevier, pp. 124-135, 06/2020.
Computer Standards & Interfaces, Special Issue on Security in Information Systems, vol. 36, issue 4, Elsevier, pp. 792-800, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Trust is an essential feature of any system where entities have to collaborate among them. Trust can assist entities making decisions about what is the best entity for establishing a certain collaboration. It would be desirable to simulate behaviour of users as in social environments where they tend to establish relationships or to trust users who have common interests or share some of their opinions, i.e., users who are similar to them to some extent. Thus, in this paper we first introduce the concept of context similarity among entities and from it we derive a similarity network which can be seen as a graph. Based on this similarity network we dene a trust model that allows us also to establish trust along a path of entities. A possible applications of our model are proximity-based trust establishment. We validate our model in this scenario.

International Journal of Information Security, vol. 21, Springer, pp. 1189–1210, 05/2022. DOI
Abstract
Smart grids (SG) draw the attention of cyber attackers due to their vulnerabilities, which are caused by the usage of heterogeneous communication technologies and their distributed nature. While preventing or detecting cyber attacks is a well-studied field of research, making SG more resilient against such threats is a challenging task. This paper provides a classification of the proposed cyber resilience methods against cyber attacks for SG. This classification includes a set of studies that propose cyber-resilient approaches to protect SG and related cyber-physical systems against unforeseen anomalies or deliberate attacks. Each study is briefly analyzed and is associated with the proper cyber resilience technique which is given by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the Special Publication 800-160. These techniques are also linked to the different states of the typical resilience curve. Consequently, this paper highlights the most critical challenges for achieving cyber resilience, reveals significant cyber resilience aspects that have not been sufficiently considered yet and, finally, proposes scientific areas that should be further researched in order to enhance the cyber resilience of SG.

IEEE Wireless Communications, vol. 25, no. 1, IEEE, pp. 76-82, 02/2018. DOI
Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, vol. 21, John Wiley & Sons, pp. 1389-1403, July, 2009. DOI
Abstract
Concurrent access control is an old problem in many fields in Computer Science. It has been solved in many languages and systems, using mechanisms like monitors or priority queues. Nowadays computers implement multi-core capabilities. This means that they are virtually capable of execution of processes in parallel. This requires new techniques and open new issues in the field of concurrent access control. Moreover, most operating systems are multi-user; thus, we have to focus on a multi-processor multi-user scenario. Trust becomes a paramount aspect when building distributed applications; the same applies on a lower scale in modern computers. We propose the use of a trust graph that keeps record of the trust relationships of the system and helps in deciding on concurrent access requests. The information encoded in the graph will be used both in order to decide on the access requests and to order granted requests in terms of their associated trust level

Novática, vol. 141, pp. 24-27, 1999.
IEEE Systems Journal., vol. 13, issue 4, IEEE, pp. 3980-3988, 12/2019. DOI
Abstract
Industry 4.0 advent opens several cyber-threats scenarios originally designed for classic information technology, drawing the attention to the serious risks for the modern industrial control networks. To cope with this problem, in this paper we address the security issues related to covert channels applied to industrial networks, identifying the new vulnerability points when information technologies converge with operational technologies such as edge computing infrastructures. Specifically, we define two signaling strategies where we exploit the Modbus/TCP protocol as target to set up a covert channel. Once the threat channel is established, passive and active offensive attacks (i.e. data exfiltration and command an control, respectively) are further exploited by implementing and testing them on a real Industrial Internet of Things testbed. The experimental results highlight the potential damage of such specific threats, and the easy extrapolation of the attacks to other types of channels in order to show the new risks for Industry 4.0. Related to this, we discuss some countermeasures to offer an overview of possible mitigation and defense measures.

IEEE Computer, vol. 46, no. 10, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 74 - 83, 2013. DOI
Abstract
Information systems, networks, and technologies have become an integral part of modern critical control systems that manage many of today’s critical infrastructures. The continuous operation, maintenance, and protection of critical infrastructures have become a high national priority for governments around the world because our society heavily depends on them for most of our daily activities (travel, power usage, banking transactions, telecommunications, etc) and safety. It is therefore critical that these infrastructures have to be protected from potential accidental incidents or cyberattacks. We present the fundamental architectural components of critical control systems which manage most critical infrastructures. We identify some of the vulnerabilities and threats to modern critical control systems followed by protection solutions that can be deployed to mitigate attacks exploiting these vulnerabilities.
International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection (IJCIP), vol. 8, Elsevier Science, pp. 53–66, 01/2015. DOI
Abstract
Critical infrastructures play a vital role in supporting modern society. The reliability, performance, continuous operation, safety, maintenance and protection of critical infrastructures are national priorities for countries around the world. This paper explores the vulnerabilities and threats facing modern critical infrastructures with special emphasis on industrial control systems, and describes a number of protection measures. The paper also discusses some of the challenging areas related to critical infrastructure protection such as governance and security management, secure network architectures, self-healing, modeling and simulation, wide-area situational awareness, forensics and learning, and trust management and privacy.

Mobile Networks and Applications (MONET), Springer US, pp. 881-889, 10/2018. DOI
Abstract
Crowdsourcing can be a powerful weapon against cyberattacks in 5G networks. In this paper we analyse this idea in detail, starting from the use cases in crowdsourcing focused on security, and highlighting those areas of a 5G ecosystem where crowdsourcing could be used to mitigate local and remote attacks, as well as to discourage criminal activities and cybercriminal behaviour. We pay particular attention to the capillary network, where an infinite number of IoT objects coexist. The analysis is made considering the different participants in a 5G IoT ecosystem.

Computers & Security Journal, vol. 87, Elsevier, 11/2019. DOI
Abstract
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) have become a serious hazard for any critical infrastructure, as a single solution to protect all industrial assets from these complex attacks does not exist. It is then essential to understand what are the defense mechanisms that can be used as a first line of defense. For this purpose, this article will firstly study the spectrum of attack vectors that APTs can use against existing and novel elements of an industrial ecosystem. Afterwards, this article will provide an analysis of the evolution and applicability of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that have been proposed in both the industry and academia.

IEEE Security & Privacy, IEEE, In Press.
IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 12, issue 2, IEEE, pp. 1778-1792, 06/2018. DOI
Abstract
Current Critical Infrastructures (CIs) are complex interconnected industrial systems that, in recent years, have incorporated information and communications technologies such as connection to the Internet and commercial off-the-shelf components. This makes them easier to operate and maintain, but exposes them to the threats and attacks that inundate conventional networks and systems. This paper contains a comprehensive study on the main stealth attacks that threaten CIs, with a special focus on Critical Information Infrastructures (CIIs). This type of attack is characterized by an adversary who is able to finely tune his actions to avoid detection while pursuing his objectives. To provide a complete analysis of the scope and potential dangers of stealth attacks we determine and analyze their stages and range, and we design a taxonomy to illustrate the threats to CIs, offering an overview of the applicable countermeasures against these attacks. From our analysis we understand that these types of attacks, due to the interdependent nature of CIs, pose a grave danger to critical systems where the threats can easily cascade down to the interconnected systems.

IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 12, issue 4, IEEE, pp. 3543-3554, 12/2018. DOI
Abstract
The protection of critical user-centric applications, such as Smart Grids and their monitoring systems, has become one of the most cutting-edge research areas in recent years. The dynamic complexity of their cyber-physical systems (CPSs) and their strong inter-dependencies with power systems, are bringing about a significant increase in security problems that may be exploited by attackers. These security holes may, for example, trigger the disintegration of the structural controllability properties due to the problem of non-locality, affecting, sooner or later, the provision of the essential services to end-users. One way to address these situations could be through automatic checkpoints in charge of inspecting the healthy status of the control network and its critical nature. This inspection can be subject to special mechanisms composed of trustworthy cyberphysical elements capable of detecting structural changes in the control and activating restoration procedures with support for warning. This is precisely the aim of this paper, which presents a CPSs-based checkpoint model with the capacity to manage heterogeneous replications that help ensure data redundancy, thereby guaranteeing the validity of the checkpoints. As a support to this study, a theoretical and practical analysis is addressed to show the functionality of the approach in real contexts.

Information Security Technical Report, vol. 12, no. 3, Elsevier, pp. 139-147, Jun 2007. DOI
Abstract
This paper explains the evolution of the concept of delegation since its first references in the context of distributed authorization to the actual use as a fundamental part of a privilege management architecture. The work reviews some of the earliest contributions that pointed out the relevance of delegation when dealing with distributed authorization, in particular we comment on PolicyMaker and Keynote, and also on SDSI/SPKI. Then, we elaborate on Federation as a particular case of delegation, and remark the importance given to federation by the industry. Finally, the paper discusses about privilege management infrastructures, introducing a new mechanism to extend their functionality using advanced delegation services.

IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 13, issue 1, IEEE, pp. 238 - 247, 03/2019.
Computer Standards & Interfaces, vol. 36, issue 3, Elsevier, pp. 501-512, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Situational awareness for critical infrastructure protection, such as for energy control systems, has become a topic of interest in recent years. Despite attempts to address this area of research, more progress is still necessary to find attractive solutions that help bring about prevention and response at all times from anywhere and at any time. Given this need, we therefore propose in this paper, a smart mechanism able to offer a wide-area situational awareness with the ability to: (i) Control the real state of the observed infrastructure, (ii) respond to emergency situations and (iii) assess the degree of ccuracy of the entire control system. To address these aspects, the mechanism is based on a hierarchical configuration of industrial sensors for control, the ISA100.11a standard for the prioritization and alarm management, and the F-Measure technique to study the level of accuracy of a sensor inside a neighbourhood. As proof of the functionality and feasibility of the mechanism for critical contexts, a software application implemented in nesC and Java is also presented in this paper.

UPGRADE - The European Journal of the Informatics Professional, vol. 2010, CEPIS, pp. 6 - 12, 2010.
Abstract
There are many technologies for identity management available in the form of open specifications, open source tools and commercial applications. Currently, there are some competing standards for identity management. At the beginning SAML was the only viable choice with a higher enough acceptance level. Recently, another technology called WS-Federation has also gain some attention from the community. Although this technology is not as mature as SAML, it modular design gives it some advantages over SAML. It this work we mainly focus on the WS-Federation and the family of specifications that surround it.

IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 24, issue 3, no. thirdquarter 2022, IEEE, pp. 1475 - 1503, 04/2022. DOI
Abstract
Industry 4.0 is having an increasingly positive impact on the value chain by modernizing and optimizing the production and distribution processes. In this streamline, the digital twin (DT) is one of the most cutting-edge technologies of Industry 4.0, providing simulation capabilities to forecast, optimize and estimate states and configurations. In turn, these technological capabilities are encouraging industrial stakeholders to invest in the new paradigm, though an increased focus on the risks involved is really needed. More precisely, the deployment of a DT is based on the composition of technologies such as cyber-physical systems, the Industrial Internet of Things, edge computing, virtualization infrastructures, artificial intelligence and big data. However, the confluence of all these technologies and the implicit interaction with the physical counterpart of the DT in the real world generate multiple security threats that have not yet been sufficiently studied. In that context, this paper analyzes the current state of the DT paradigm and classifies the potential threats associated with it, taking into consideration its functionality layers and the operational requirements in order to achieve a more complete and useful classification. We also provide a preliminary set of security recommendations and approaches that can help to ensure the appropriate and trustworthy use of a DT.

IEEE Wireless Communications, vol. 28, issue 2, IEEE, pp. 48-55, 04/2021. DOI
Abstract
Beyond fifth generation (B5G) communication networks and computation paradigms in the edge are expected to be integrated into power grid infrastructures over the coming years. In this sense, AI technologies will play a fundamental role to efficiently manage dynamic information flows of future applications, which impacts the authorization policies applied in such a complex scenario. This article studies how digital twins can evolve their context awareness capabilities and simulation technologies to anticipate faults or to detect cyber-security issues in real time, and update access control policies accordingly. Our study analyzes the evolution of monitoring platforms and architecture decentralization, including the application of machine learning and blockchain technologies in the smart grid, toward the goal of implementing autonomous and self-learning agents in the medium and long term. We conclude this study with future challenges on applying digital twins to B5G-based smart grid deployments.

IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 2, no. 4, IEEE, pp. 827-834, Nov 2011. DOI
Abstract
Most of energy control or SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are very dependent on advanced technologies and on traditional security mechanisms for protecting the a system against anomalous events. Security mechanisms are not enough to be used in critical systems, since they can only detect anomalous events occurring at a certain moment in time. For this reason it becomes of paramount importance the usage of intelligent systems with capability for preventing anomalous situations and reacting against them on time. This type of systems are, for example, Early Warning Systems (EWS). In this paper, we propose an EWS based on Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) (under the ISA100.11a standard) and reputation for controling the network behaviour. The WSN are organized into clusters where a Cluster Head (CH) is designated. This CH will contain a Reputation Manager Module. The usability of this approach is also analyzed considering a Smart Grid scenario.} keywords = {Critical Information Infrastructures, Sensor Networks, Early Warning Systems, Reputation, SCADA Systems, Smart Grid.

Mobile Networks and Applications, vol. 13, no. 3-4, Springer, pp. 398-410, August, 2008. DOI
Abstract
When delegation is implemented using the attribute certificates in a Privilege Management Infrastructure (PMI), it is possible to reach a considerable level of distributed functionality. However, the approach is not flexible enough for the requirements of ubiquitous environments. The PMI can become a too complex solution for devices such as smartphones and PDAs, where resources are limited. In this work we present an approach to solve the previous limitations by defining a second class of attributes, called domain attributes, which are managed directly by users and are not right under the scope of the PMI, thus providing a light solution for constrained devices. However, we relate the two classes of attributes are related by defining a simple ontology. While domain attribute credentials are defined using SAML notation, global attributes are defined using X.509 certificates. For this reason, we additionally introduce XSAML so that both kinds of credentials are integrated. We also introduce the concept of Attribute Federation which is responsible for supporting domain attributes and the corresponding ontology.

IET Information Security, vol. 13, issue 5, IET, pp. 498 -- 507, 09/2019.
Abstract
Escrowed decryption schemes (EDSs) are public-key encryption schemes with an escrowed decryption functionality that allows authorities to decrypt encrypted messages under investigation, following a protocol that involves a set of trusted entities called `custodians'; only if custodians collaborate, the requesting authority is capable of decrypting encrypted data. This type of cryptosystem represents an interesting trade-off to privacy versus surveillance dichotomy. In this study, the authors propose two EDSs where they use proxy re-encryption to build the escrowed decryption capability, so that custodians re-encrypt ciphertexts, in a distributed way, upon request from an escrow authority, and the re-encrypted ciphertexts can be opened only by the escrow authority. Their first scheme, called EDS, follows an all-or-nothing approach, which means that escrow decryption only works when all custodians collaborate. Their second scheme, called threshold EDS, supports a threshold number of custodians for the escrow decryption operation. They propose definitions of semantic security with respect to the authorities, custodians and external entities, and prove the security of their schemes, under standard pairing-based hardness assumptions. Finally, they present a theoretical and experimental analysis of the performance of both schemes, which show that they are applicable to real-world scenarios.

European CIIP Newsletter, vol. 7, European_CIIP_Newsletter, pp. 11-13, Nov 2013.
Abstract
FACIES aims to protect water treatment systems and their control systems against accidental or intentional incidents such as failures, anomalies and cyber-attacks with a particular emphasis on stealth attacks.
Nuevas tendencias en gestión de redes, Novática, no. 196, CEPIS, pp. 20-25, December, 2008.
Abstract
En el momento que se introduce en el mercado nuevas tecnologías basadas en entornos distribuidos comienzan a surgir en paralelo nuevos problemas de seguridad en los sistemas SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), los cuales monitorizan y gestionan otras infraestructuras de gran complejidad y escala. Un fallo o una interrupción en uno de sus componentes podría suponer un impacto negativo sobre la funcionalidad de otras infraestructuras, por lo que se hace necesario realizar frecuentes análisis de seguridad para así mantener actualizado el conocimiento y proveer recomendaciones y/o soluciones para mitigar o evitar futuras ocurrencias, garantizando una gestión de red fiable y siempre disponible.

ERCIM News, no. 63, ERCIM, pp. 33-34, October, 2005.

Novática, vol. 145, pp. 65-71, 2000.
Abstract
El comercio electrónico está llamado a ser el fenómeno de mayor importancia en el futuro de Internet. Entre sus aplicaciones se encuentran las compras en línea, la banca electrónica, la tele-educación, los casinos virtuales, los servicios de pago por visión y vídeo bajo demanda, etc. Desde el punto de vista de la Seguridad, estas aplicaciones presentan una serie de nuevos requisitos que van a imponer un gran esfuerzo investigador a corto y medio plazo. En este artículo se presentan algunos de los más importantes, como la administración de la confianza, la utilización de pagos electrónicos, la necesidad de la protección de la propiedad intelectual, los servicios de protección de privacidad y anonimato, y la autonomía de código y la detección de fraudes, identificándose las áreas de investigación relacionadas.

Computers & Electrical Engineering, vol. 37, Elsevier, pp. 147-159, Mar 2011. DOI
Abstract
If a wireless sensor network (WSN) is to be completely integrated into the Internet as part of the Internet of Things (IoT), it is necessary to consider various security challenges, such as the creation of a secure channel between an Internet host and a sensor node. In order to create such a channel, it is necessary to provide key management mechanisms that allow two remote devices to negotiate certain security credentials (e.g. secret keys) that will be used to protect the information flow. In this paper we will analyse not only the applicability of existing mechanisms such as public key cryptography and pre-shared keys for sensor nodes in the IoT context, but also the applicability of those link-layer oriented key management systems (KMS) whose original purpose is to provide shared keys for sensor nodes belonging to the same WSN.

IEEE Access , IEEE, 2022. DOI
Abstract
Neural networks based cryptography has seen a significant growth since the introduction of adversarial cryptography which makes use of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to build neural networks that can learn encryption. The encryption has been proven weak at first but many follow up works have shown that the neural networks can be made to learn the One Time Pad (OTP) and produce perfectly secure ciphertexts. To the best of our knowledge, existing works only considered communications between two or three parties. In this paper, we show how multiple neural networks in an adversarial setup can remotely synchronize and establish a perfectly secure communication in the presence of different attackers eavesdropping their communication. As an application, we show how to build Secret Sharing Scheme based on this perfectly secure multi-party communication. The results show that it takes around 45,000 training steps for 4 neural networks to synchronize and reach equilibria. When reaching equilibria, all the neural networks are able to communicate between each other and the attackers are not able to break the ciphertexts exchanged between them.
Requirements Engineering, vol. 16, no. 1, Springer, pp. 55-73, Mar 2011. DOI
Abstract
In this work, we introduce an assurance methodology that integrates assurance case creation with system development. It has been developed in order to provide trust and privacy assurance to the evolving European project PICOS (Privacy and Identity Management for Community Services), an international research project focused on mobile communities and community-supporting services, with special emphasis on aspects such as privacy, trust, and identity management. The leading force behind the approach is the ambition to develop a methodology for building and maintaining security cases throughout the system development life cycle in a typical system engineering effort, when much of the information relevant for assurance is produced and feedback can be provided to system developers. The first results of the application of the methodology to the development of the PICOS platform are presented.

International Journal of Information Security, Springer, In Press. DOI
Abstract
Undoubtedly, Industry 4.0 in the energy sector improves the conditions for automation, generation and distribution of energy, increasing the rate of electric vehicle manufacturing in recent years. As a result, more grid-connected charging infrastructures are being installed, whose charging stations (CSs) can follow standardized architectures, such as the one proposed by the open charge point protocol (OCPP). The most recent version of this protocol is v.2.0.1, which includes new security measures at device and communication level to cover those security issues identified in previous versions. Therefore, this paper analyzes OCPP-v2.0.1 to determine whether the new functions may still be susceptible to specific cyber and physical threats, and especially when CSs may be connected to microgrids. To formalize the study, we first adapted the well-known threat analysis methodology, STRIDE, to identify and classify threats in terms of control and energy, and subsequently we combine it with DREAD for risk assessment. The analyses indicate that, although OCPP-v2.0.1 has evolved, potential security risks still remain, requiring greater protection in the future.
IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 8, issue 5, IEEE, pp. 2452 - 2459, 02/2017. DOI
Abstract
One benefit postulated for the adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs) is their ability to act as stabilizing entities in smart grids through bi-directional charging, allowing local or global smoothing of peaks and imbalances. This benefit, however, hinges indirectly on the reliability and security of the power flows thus achieved. Therefore this paper studies key security properties of the alreadydeployed Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) specifying communication between charging points and energy management systems. It is argued that possible subversion or malicious endpoints in the protocol can also lead to destabilization of power networks. Whilst reviewing these aspects, we focus, from a theoretical and practical standpoint, on attacks that interfere with resource reservation originating with the EV, which may also be initiated by a man in the middle, energy theft or fraud. Such attacks may even be replicated widely, resulting in over- or undershooting of power network provisioning, or the (total/partial) disintegration of the integrity and stability of power networks.

Computer and Security, vol. 29, elsevier, pp. 501-514, 2010. DOI
Abstract
Network and device heterogeneity, nomadic mobility, intermittent connectivity and, more generally, extremely dynamic operating conditions, are major challenges in the design of security infrastructures for pervasive computing. Yet, in a ubiquitous computing environment, limitations of traditional solutions for authentication and authorization can be overcome with a pervasive public key infrastructure (pervasive-PKI). This choice allows the validation of credentials of users roaming between heterogeneous networks, even when global connectivity is lost and some services are temporarily unreachable. Proof-of-concept implementations and testbed validation results demonstrate that strong security can be achieved for users and applications through the combination of traditional PKI services with a number of enhancements like: (i) dynamic and collaborative trust model, (ii) use of attribute certificates for privilege management, and (iii) modular architecture enabling nomadic mobility and enhanced with reconfiguration capabilities.

Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 59, Elsevier, pp. 301–314, 01/2016.
Abstract
Interoperability of distributed systems in charge of monitoring and maintaining the different critical domains belonging to Smart Grid scenarios comprise the central topic of this paper. Transparency in control transactions under a secure and reliable architecture is the aim of the policy enforcement system proposed here. The approach is based on the degree of observation of a context and on the role-based access control model defined by the IEC-62351-8 standard. Only authenticated and authorised entities are able to take control of those distributed elements (e.g., IEC-61850 objects) located at distant geographical locations and close to the critical infrastructures (e.g., substations). To ensure the effectiveness of the approach, it is built on graphical-theoretical formulations corresponding to graph theory, where it is possible to illustrate power control networks through power-law distributions whose monitoring relies on structural controllability theory. The interconnection of these distributions is subject to a network architecture based on the concept of the supernode where the interoperability depends on a simple rule-based expert system. This expert system focuses not only on accepting or denying access, but also on providing the means to attend to extreme situations, avoiding, as much as possible, the overloading of the communication. Through one practical study we also show the functionalities of the approach and the benefits that the authorisation itself can bring to the interoperability.

Computers & Security, vol. 39 (B), Elsevier, pp. 117-126, 11/2013. DOI
Abstract
Continuous authentication is mainly associated with the use of biometrics to guarantee that a resource is being accessed by the same user throughout the usage period. Wireless devices can also serve as a supporting technology for continuous authentication or even as a complete alternative to biometrics when accessing proximity-based services. In this paper we present the implementation of a secure, non-invasive continuous authentication scheme supported by the use of Wearable Wireless Devices (WWD), which allow users to gain access to proximity-based services while preserving their privacy. Additionally we devise an improved scheme that circumvents some of the limitations of our implementation.

Computer Science Review, vol. 49, no. 100567, Elsevier, 05/2023. DOI
Abstract
Secure Multi-party Computation (SMPC) is a family of protocols which allow some parties to compute a function on their private inputs, obtaining the output at the end and nothing more. In this work, we focus on a particular SMPC problem named Private Set Intersection (PSI). The challenge in PSI is how two or more parties can compute the intersection of their private input sets, while the elements that are not in the intersection remain private. This problem has attracted the attention of many researchers because of its wide variety of applications, contributing to the proliferation of many different approaches. Despite that, current PSI protocols still require heavy cryptographic assumptions that may be unrealistic in some scenarios. In this paper, we perform a Systematic Literature Review of PSI solutions, with the objective of analyzing the main scenarios where PSI has been studied and giving the reader a general taxonomy of the problem together with a general understanding of the most common tools used to solve it. We also analyze the performance using different metrics, trying to determine if PSI is mature enough to be used in realistic scenarios, identifying the pros and cons of each protocol and the remaining open problems.

IEEE Network Magazine, IEEE, In Press.
European CIIP Newsletter, vol. 11, issue 26, no. 1, European CIIP Newsletter, pp. 27-29, 03/2017.

Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 87, Elsevier, pp. 193-209, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
This paper analyzes the secure access delegation problem, which occurs naturally in the cloud, and postulate that Proxy Re-Encryption is a feasible cryptographic solution, both from the functional and efficiency perspectives. Proxy re-encryption is a special type of public-key encryption that permits a proxy to transform ciphertexts from one public key to another, without the proxy being able to learn any information about the original message. Thus, it serves as a means for delegating decryption rights, opening up many possible applications that require of delegated access to encrypted data. In particular, sharing information in the cloud is a prime example. In this paper, we review the main proxy re-encryption schemes so far, and provide a detailed analysis of their characteristics. Additionally, we also study the efficiency of selected schemes, both theoretically and empirically, based on our own implementation. Finally, we discuss some applications of proxy re-encryption, with a focus on secure access delegation in the cloud.

Pervasive and Mobile Computing, vol. 41, Pervasive and Mobile Computing, pp. 205-218, 10/2017.
Abstract
Nowadays, Smart Grid is envisaged to provide several benefits to both customers and grid operators. However, Smart Meters introduce many privacy issues if consumption data is analysed. In this paper we analyse the main techniques that address privacy when collecting electricity readings. In addition to privacy, it is equally important to preserve efficiency to carry on with monitoring operations, so further control requirements and communication protocols are also studied. Our aim is to provide guidance to installers who intend to integrate such mechanisms on the grid, presenting an expert system to recommend an appropriate deployment strategy.

IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 14, issue 8, IEEE, pp. 3745-3753, 08/2019, 2018. DOI
Abstract
The Smart Grid offers many benefits due to the bidirectional communication between the users and the utility company, which makes it possible to perform a fine-grain consumption metering. This can be used for Demand Response purposes with the generation and delivery of electricity in real time. It is essential to rapidly anticipate high peaks of demand or potential attacks, so as to avoid power outages and denial of service, while effectively supplying consumption areas. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture where cloud computing resources are leveraged (and tested in practice) to enable, on the one hand, the consumption prediction through time series forecasting, as well as load balancing to uniformly distribute the demand over a set of available generators. On the other and, it also allows the detection of connectivity losses and intrusions within the control network by using controllability concepts.

International Journal of Critical Infrastructures (IJCIS), vol. 13, no. 2/3, Inderscience Publisher, pp. 278 - 295, 11/2017. DOI
Abstract
The incessant search for cost-effective recovery solutions for structural controllability has led to one of the most challenging research areas within the field of critical infrastructure protection. The resilience of large heterogeneous distributions, like industrial control scenarios, is proving to be a complicated mission due to the inherent non-locality problems of structural controllability and its susceptibility to advanced threats. To address these issues, this paper proposes a new repair approach based on multiple redundant pathways and the lessons learnt from the work presented in [1]. From [1], we have adapted the local measures, to combine them with each of the five strategies of remote reconnection described in this paper. To validate the sustainability of the combined approaches, two practical case studies are presented here, showing that a local dependence on a brother driver node together with remote dependence is enough to reach optimal states in linear times.
Computers & Security, vol. 71, Elsevier, pp. 2-14, 11/2017. DOI
Abstract
Secure interconnection between multiple cyber-physical systems has become a fundamental requirement in many critical infrastructures, where security may be centralized in a few nodes of the system. These nodes could, for example, have the mission of addressing the authorization services required for access in highlyrestricted remote substations. For this reason, the main aim of this paper is to unify all these features, together with the resilience measures so as to provide control at all times under a limited access in the field and avoid congestion. Concretely, we present here an optimal reachability-based restoration approach, capable of restoring the structural control in linear times taking into account: structural controllability, the supernode theory, the good practices of the IEC-62351 standard and the contextual conditions. For context management, a new attribute is specified to provide a more complete authorization service based on a practical policy, role and attribute-based access control (PBAC + RBAC + ABAC). To validate the approach, two case studies are also discussed under two strategic adversarial models.

Information Security Technical Report, vol. 12, no. 1, Elsevier, pp. 24-31, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructures, such as energy, banking, and transport, are an essential pillar to the well-being of the national and international economy, security and quality of life. These infrastructures are dependent on a spectrum of highly interconnected information infrastructures for their smooth, reliable and continuous operation. The field of protecting such Critical Information Infrastructures, or CIIP, faces numerous challenges, such as managing the secure interaction between peers, assuring the resilience and robustness of the overall system, and deploying warning and alert systems, amongst others. In this tapestry of CIIP, Wireless Sensor Networks can be used as an invaluable tool due to their intelligent distributed control capabilities, alongside with their capability to work under severe conditions. In this paper, we justify why Wireless Sensor Networks technology is suitable for providing security for these scenarios, describing both their advantages and research issues and their role in the overall scheme of protecting the Critical Information Infrastructures.

Computers and Mathematics with Applications, vol. 60, Elsevier, pp. 209-216, July, 2010. DOI
Abstract
When interactions among users of a system have to take place, for example, over the internet, establishing trust relationships among these users becomes crucial. However, the way this trust is established depends to a certain extent on the context where the interactions take place. Most of the time, trust is encoded as a numerical value that might not be very meaningful for a not very experienced user. In this paper we propose a model that takes into account the semantic and the computational sides of trust. This avoids users having to deal directly with the computational side; they instead deal with meaningful labels such as Bad or Good in a given context.

Novatica, New Trends in Network Management, vol. 9, no. 6, Cepis UPGRADE, pp. 22-28, December, 2008.
Abstract
When a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system monitors and manages other complex infrastructures through the use of distributed technologies, it becomes a critical infrastructure by itself: A failure or disruption in any of its components could implicate a serious impact on the performance of the other infrastructures. The connection with other systems makes a SCADA system more vulnerable against attacks, generating new security problems. As a result, it is essential to perform diverse security analysis frequently in order to keep an updated knowledge and to provide recommendations and/or solutions to mitigate or avoid anomalous events. This will facilitate the existence of a suitable, reliable, and available control network.

Concurrency and Computation Practice & Experience, vol. 23, no. 12, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 1414-1430, Aug 2011. DOI
Abstract
Energy distribution systems are becoming increasingly widespread in today’s society. One of the elements that is used to monitor and control these systems are the SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. In particular, these control systems and their complexities, together with the emerging use of the Internet and wireless technologies, bring new challenges that must be carefully considered. Examples of such challenges are the particular bene¯ts of the integration of those new technologies, and also the e®ects they may have on the overall SCADA security. The main task of this paper is to provide a framework that shows how the integration of di®erent state-of-the-art technologies in an energy control system, such as Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETs), and the Internet, can bring some interesting benefits such as status management and anomaly prevention, while maintaining the security of the whole system.

IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, vol. 40, no. 4, IEEE, pp. 419-428, July, 2010. DOI
Abstract
Nowadays, critical control systems are a fundamental component contributing to the overall performance of critical infrastructures in our society, most of which belong to the industrial sector. These complex systems include in their design different types of information and communication technology systems, such as wireless (mesh) sensor networks, to carry out control processes in real time. This fact has meant that several communication standards, such as Zigbee PRO, WirelessHART, and ISA100.11a, have been specified to ensure coexistence, reliability, and security in their communications. The main purpose of this paper has been to review these three standards and analyze their security. We have identified a set of threats and potential attacks in their routing protocols, and we consequently provide recommendations and countermeasures to help Industry protect its infrastructures.

Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 11, Elsevier, pp. 1091–1104, 2013. DOI
Abstract
The main objective of remote substations is to provide the central system with sensitive information from critical infrastructures, such as generation, distribution or transmission power systems. Wireless sensor networks have been recently applied in this particular context due to their attractive services and inherent benefits, such as simplicity, reliability and cost savings. However, as the number of control and data acquisition systems that use the Internet infrastructure to connect to substations increases, it is necessary to consider what connectivity model the sensor infrastructure should follow: either completely isolated from the Internet or integrated with it as part of the Internet of Things paradigm. This paper therefore addresses this question by providing a thorough analysis of both security requirements and infrastructural requirements corresponding to all those TCP/IP integration strategies that can be applicable to networks with constrained computational resources.

Computers & Security, vol. 31, no. 38, Elsevier, pp. 956–966, Nov 2012. DOI
Abstract
Key management in wireless sensor networks (WSN) is an active research topic. Due to the fact that a large number of key management schemes (KMS) have been proposed in the literature, it is not easy for a sensor network designer to know exactly which KMS best fits in a particular WSN application. In this article, we offer a comprehensive review on how the application requirements and the properties of various key management schemes influence each other. Based on this review, we show that the KMS plays a critical role in determining the security performance of a WSN network with given application requirements. We also develop a method that allows the network designers to select the most suitable KMS for a specific WSN network setting. In addition, the article also addresses the issues on the current state-of-the-art research on the KMS for homogeneous (i.e. non-hierarchical) networks to provide solutions for establishing link-layer keys in various WSN applications and scenarios.

Computers & Security, vol. 38, Elsevier, pp. 14-27, OCT 2013. DOI
Abstract
Any deliberate or unsuitable operational action in control tasks of critical infrastructures, such as energy generation, transmission and distribution systems that comprise sub-domains of a Smart Grid, could have a significant impact on the digital economy: without energy, the digital economy cannot live. In addition, the vast majority of these types of critical systems are configured in isolated locations where their control depends on the ability of a few, supposedly trustworthy, human operators. However, this assumption of reliabilty is not always true. Malicious human operators (criminal insiders) might take advantage of these situations to intentionally manipulate the critical nature of the underlying infrastructure. These criminal actions could be not attending to emergency events, inadequately responding to incidents or trying to alter the normal behaviour of the system with malicious actions. For this reason, in this paper we propose a smart response mechanism that controls human operators’ operational threats at all times. Moreover, the design of this mechanism allows the system to be able to not only evaluate by itself, the situation of a particular scenario but also to take control when areas are totally unprotected and/or isolated. The response mechanism, which is based on Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (IWSNs) for the constant monitoring of observed critical infrastructures, on reputation for controlling human operators’ actions, and on the ISA100.11a standard for alarm management, has been implemented and simulated to evaluate its feasibility for critical contexts.

Journal of Information Security and Applications, vol. 61, no. 102916, Elsevier, 09/2021. DOI
Journal of Information Security and Applications, vol. 61, no. 102916, Elsevier, 09/2021. DOI
Mobile Networks and Applications, vol. 12, no. 4, Springer, pp. 231-244, August, 2007. DOI
Abstract
In a wireless sensor network environment, a sensor node is extremely constrained in terms of hardware due to factors such as maximizing lifetime and minimizing physical size and overall cost. Nevertheless, these nodes must be able to run cryptographic operations based on primitives such as hash functions, symmetric encryption and public key cryptography in order to allow the creation of secure services. Our objective in this paper is to survey how the existing research-based and commercial-based sensor nodes are suitable for this purpose, analyzing how the hardware can influence the provision of the primitives and how software implementations tackles the task of implementing instances of those primitives. As a result, it will be possible to evaluate the influence of provision of security in the protocols and applications/scenarios where sensors can be used.

IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 20, issue 4, IEEE, pp. 3453-3495, 07/2018. DOI
Abstract
As the deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) is experiencing an exponential growth, it is no surprise that many recent cyber attacks are IoT-enabled: The attacker initially exploits some vulnerable IoT technology as a first step towards compromising a critical system that is connected, in some way, with the IoT. For some sectors, like industry, smart grids, transportation and medical services, the significance of such attacks is obvious, since IoT technologies are part of critical backend systems. However, in sectors where IoT is usually at the enduser side, like smart homes, such attacks can be underestimated, since not all possible attack paths are examined. In this paper we survey IoT-enabled cyber attacks, found in all application domains since 2010. For each sector, we emphasize on the latest, verified IoT-enabled attacks, based on known real-world incidents and published proof-of-concept attacks. We methodologically analyze representative attacks that demonstrate direct, indirect and subliminal attack paths against critical targets. Our goal is threefold: (i) To assess IoT-enabled cyber attacks in a risk-like approach, in order to demonstrate their current threat landscape; (ii) To identify hidden and subliminal IoT-enabled attack paths against critical infrastructures and services, and (iii) To examine mitigation strategies for all application domains.
Computers & Security, vol. 55, no. November, Elsevier, pp. 235-250, 2015.
Abstract
The correct operation of Critical Infrastructures (CIs) is vital for the well being of society, however these complex systems are subject to multiple faults and threats every day. International organizations around the world are alerting the scientific community to the need for protection of CIs, especially through preparedness and prevention mechanisms. One of the main tools available in this area is the use of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs). However, in order to deploy this type of component within a CI, especially within its Control System (CS), it is necessary to verify whether the characteristics of a given IDS solution are compatible with the special requirements and constraints of a critical environment. In this paper, we carry out an extensive study to determine the requirements imposed by the CS on the IDS solutions using the Non-Functional Requirements (NFR) Framework. The outcome of this process are the abstract properties that the IDS needs to satisfy in order to be deployed within a CS, which are refined through the identification of satisficing techniques for the NFRs. To provide quantifiable measurable evidence on the suitability of the IDS component for a CI, we broaden our study using the Goal Question Metric (GQM) approach to select a representative set of metrics. A requirements model, refined with satisficing techniques and sets of metrics which help assess, in the most quantifiable way possible, the suitability and performance of a given IDS solution for a critical scenario, constitutes the results of our analysis.

Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 73, Springer, pp. 23-50, Nov 2013, 2012. DOI
Abstract
The smart grid is an electronically controlled electrical grid that connects power generation, transmission, distribution, and consumers using information communication technologies. One of the key characteristics of the smart grid is its support for bi-directional information flow between the consumer of electricity and the utility provider. This two-way interaction allows electricity to be generated in real-time based on consumers’ demands and power requests. As a result, consumer privacy becomes an important concern when collecting energy usage data with the deployment and adoption of smart grid technologies. To protect such sensitive information it is imperative that privacy protection mechanisms be used to protect the privacy of smart grid users. We present an analysis of recently proposed smart grid privacy solutions and identify their strengths and weaknesses in terms of their implementation complexity, efficiency, robustness, and simplicity.

IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, IEEE, 2022. DOI
Abstract
The class of Trustworthy Autonomous Systems (TAS) includes cyber-physical systems leveraging on self-x technologies that make them capable to learn, adapt to changes, and reason under uncertainties in possibly critical applications and evolving environments. In the last decade, there has been a growing interest in enabling artificial intelligence technologies, such as advanced machine learning, new threats, such as adversarial attacks, and certification challenges, due to the lack of sufficient explainability. However, in order to be trustworthy, those systems also need to be dependable, secure, and resilient according to well-established taxonomies, methodologies, and tools. Therefore, several aspects need to be addressed for TAS, ranging from proper taxonomic classification to the identification of research opportunities and challenges. Given such a context, in this paper address relevant taxonomies and research perspectives in the field of TAS. We start from basic definitions and move towards future perspectives, regulations, and emerging technologies supporting development and operation of TAS.

Journal of Computer Security, vol. 27, issue 5, Elsevier, pp. 521-546, 09/2019.
Computer Communications, vol. 33, no. 9, Elsevier, pp. 0140-3664, 2010. DOI
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have been proven a useful technology for perceiving information about the physical world and as a consequence has been used in many applications such as measurement of temperature, radiation, flow of liquids, etc. The nature of this kind of technology, and also their vulnerabilities to attacks make the security tools required for them to be considered in a special way. The decision making in a WSN is essential for carrying out certain tasks as it aids sensors establish collaborations. In order to assist this process, trust management systems could play a relevant role. In this paper, we list the best practices that we consider are essential for developing a good trust management system for WSN and make an analysis of the state of the art related to these practices.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 30, Elsevier, pp. 146-154, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Control from anywhere and at anytime is nowadays a matter of paramount importance in critical systems. This is the case of the Smart Grid and its domains which should be monitored through intelligent and dynamic mechanisms able to anticipate, detect and respond before disruptions arise within the system. Given this fact and its importance for social welfare and the economy, a model for wide-area situational awareness is proposed in this paper. The model is based on a set of current technologies such as the wireless sensor networks, the ISA100.11a standard and cloud-computing together with a set of high-level functional services. These services include global and local support for prevention through a simple forecast scheme, detection of anomalies in the observation tasks, response to incidents, tests of accuracy and maintenance, as well as recovery of states and control in crisis situations.

IEEE Computer, vol. 46, no. 4, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 30-37, 2013. DOI
Abstract
Combining a wide-area situational awareness (WASA) methodological framework with a set of requirements for awareness construction can help in the development and commissioning of future WASA cyberdefense solutions




