Digital Privacy: Theory, Technologies, and Practices, A.. Acquisti, S. Gritzalis, C.. Lambrinoudakis, and S. De Capitan di Vimercati Eds., Auerbach Publications, pp. 285-306, December, 2007.
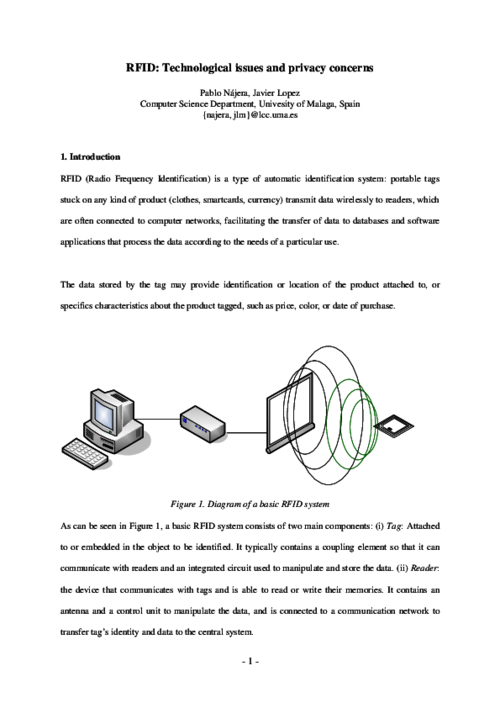
Advances in Core Computer Science-Based Technologies, Springer International Publishing, pp. 157-173, 2021. DOI
Abstract
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have enabled Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to become fully interconnected. This connectivity however has radically changed their threat landscape. Existing risk assessment methodologies often fail to identify various attack paths that stem from the new connectivity/functionality features of IoT-enabled CPS. Even worse, due to their inherent characteristics, IoT systems are usually the weakest link in the security chain and thus many attacks utilize IoT technologies as their key enabler. In this paper we review risk assessment methodologies for IoT-enabled CPS. In addition, based on our previous work (Stellios et al. in IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 20:3453–3495, 2018, [47]) on modeling IoT-enabled cyberattacks, we present a high-level risk assessment approach, specifically suited for IoT-enabled CPS. The mail goal is to enable an assessor to identify and assess non-obvious(indirect or subliminal) attack paths introduced by IoT technologies, that usually target mission critical components of an CPS.
19th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2022), Scitepress, pp. 249-260, 07/2022. DOI
Abstract
Crowd Counting is a very interesting problem aiming at counting people typically based on density averages and/or aerial images. This is very useful to prevent crowd crushes, especially on urban environments with high crowd density, or to count people in public demonstrations. In addition, in the last years, it has become of paramount importance for pandemic management. For those reasons, giving users automatic mechanisms to anticipate high risk situations is essential. In this work, we analyze ID-based Crowd Counting, and propose a real-time Crowd Counting system based on the Ephemeral ID broadcast by contact tracing applications on wearable devices. We also performed some simulations that show the accuracy of our system in different situations.

Eighth IFIP WG 11.10 International Conference on Critical Infrastructure Protection, SRI International, Arlington, Virginia, USA , vol. 441, Springer, pp. 47-63, 2014. DOI
Abstract
Fundamental problems in control systems theory are controllability and observability, and designing control systems so that these properties are satisfied or approximated sufficiently. However, it is prudent to as- sume that an attacker will not only be able to subvert measurements but also control the system. Moreover, an advanced adversary with an understanding of the control system may seek to take over control of the entire system or parts thereof, or deny the legitimate operator this capability. The effectiveness of such attacks has been demonstrated in previous work. Indeed, these attacks cannot be ruled out given the likely existence of unknown vulnerabilities, increasing connectivity of nominally air-gapped systems and supply chain issues. The ability to rapidly recover control after an attack has been initiated and to detect an adversary’s presence is, therefore, critical. This paper focuses on the problem of structural controllability, which has recently attracted substantial attention through the equivalent problem of the power dom- inating set introduced in the context of electrical power network control. However, these problems are known to be NP-hard with poor approx- imability. Given their relevance to many networks, especially power networks, this paper studies strategies for the efficient restoration of controllability following attacks and attacker-defender interactions in power-law networks.

3th International Conference on Trust Management (iTRUST’05), LNCS 3477, Springer, pp. 9-22, May, 2005. DOI
Abstract
Logic languages establish a formal framework to solve authorization and delegation conflicts. However, we consider that a visual representation is necessary since graphs are more expressive and understandable than logic languages. In this paper, and after overviewing previous works using logic languages, we present a proposal for graph representation of authorization and delegation statements. Our proposal is based on Varadharajan et al. solution, though improve several elements of that work. We also discuss about the possible implementation of our proposal using attribute certificates.

III Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2017), vol. Actas del JNIC 2017, Servicio de Publicaciones de la URJC, pp. 51-58, 2017.

Workshop on Software Engineering for Secure Systems, IEEE, pp. 1-8, 2009.
Abstract
Due to the growing complexity of softwaredevelopment, developing software through systematicprocesses is becoming more and more important.Likewise, it is important that the development processused integrates security aspects from the first stages atthe same level as other functional and non-functionalrequirements. In the last years, GRID technology hasshown to be the most important one and it allows us tobuild very complex information systems with differentand remarkable features (interoperability betweenmultiple security domains, cross-domainauthentication and authorization, dynamic,heterogeneous and limited mobile devices, etc).Traditionally, systems based on GRID Computing havenot been developed through adequate methodologiesand have not taken into account security requirementsthroughout their development, only offering securitytechnical solutions at the implementation stages. Thispaper shows part of a development methodology thatwe are elaborating for the construction of informationsystems based on Grid Computing highly dependent onmobile devices where security plays a very importantrole. Specifically, in this paper, we will present theanalysis phase, managed by reusable use casesthrough which we can define the requirements andneeds of these systems obtaining an analysis modelthat can be used as input to the following phase of themethodology, the design phase of mobile Grid systems.

XII Conferencia Iberoamericana de Ingeniería de Requisitos y Ambientes de Software (IDEAS’09), University of Colombia, pp. 388-393, 2009.
Abstract
El desarrollo software debe estar basado en un proceso sistemático y estructurado donde se definan los métodos y técnicas a utilizar en todo su ciclo de vida, ayudando así a obtener un producto de calidad. Es igualmente importante que el proceso sistemático considere aspectos de seguridad desde las primeras etapas, integrándola como un elemento más en el ciclo de desarrollo. En este artículo mostramos la metodología de desarrollo sistemático que sirve de guía para el desarrollo de cualquier sistema Grid con dispositivos móviles, considerando la seguridad durante todas las fases de desarrollo, lo que nos permitirá obtener como resultado sistemas Grid seguros, robustos y escalables. Este artículo presenta la fase de análisis, dirigida por casos de uso reutilizables, mediante los cuales se definen los requisitos y necesidades de estos sistemas, y es aplicada a un caso de estudio real de un Grid para el acceso de contenidos multimedia en un contexto periodístico.
17th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2012), S. Foresti, M. Yung, and F. Martinelli Eds., LNCS 7459, Springer, pp. 163-180, Sep 2012. DOI
Abstract
The singular communication model in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) originate pronounced traffic patterns that allow a local observer to deduce the location of the base station, which must be kept secret for both strategical and security reasons. In this work we present a new receiver-location privacy solution called HISP (Homogenous Injection for Sink Privacy). Our scheme is based on the idea of hiding the flow of real traffic by carefully injecting fake traffic to homogenize the transmissions from a node to its neighbors. This process is guided by a lightweight probabilistic approach ensuring that the adversary cannot decide with sufficient precision in which direction to move while maintaining a moderate amount of fake traffic. Our system is both validated analytically and experimentally through simulations.

Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 34, Elsevier, pp. pp. 980-989, 2011. DOI
Abstract
RFID technology meets identification and tracking requirements in healthcare environments with potential to speed up and increase reliability of involved processes. Due to this, high expectations for this integration have emerged, but hospital and medical centers interested in adoption of RFID technology require prior knowledge on how to squeeze RFID capabilities, real expectations and current challenges. In this paper, we show our lab tested solutions in two specific healthcare scenarios. On the one hand, we analyze the case of a medical equipment tracking system for healthcare facilities enabling both real-time location and theft prevention. Worth-noting aspects such as possible EMI interferences, technology selection and management of RFID data from hospital information system are analyzed. Lab testing of system reliability based on passive UHF RFID is provided for this case. On the other hand, we analyze and provide a solution for care and control of patients in a hospital based on passive HF RFID with the result of a fully functional demonstrator. Our prototype squeezes RFID features in order to provide a backup data source from patient’s wristband. It also provides an offline working mode aiming to increase application reliability under network fail down and therefore, improving patient’s safety. Considerations regarding lessons learned and challenges faced are exposed.

Pervasive and Mobile Computing, vol. 41, Pervasive and Mobile Computing, pp. 205-218, 10/2017.
Abstract
Nowadays, Smart Grid is envisaged to provide several benefits to both customers and grid operators. However, Smart Meters introduce many privacy issues if consumption data is analysed. In this paper we analyse the main techniques that address privacy when collecting electricity readings. In addition to privacy, it is equally important to preserve efficiency to carry on with monitoring operations, so further control requirements and communication protocols are also studied. Our aim is to provide guidance to installers who intend to integrate such mechanisms on the grid, presenting an expert system to recommend an appropriate deployment strategy.

Telecommunication Systems , vol. 59, issue 1, Springer US, pp. 169-187, 05/2015. DOI
Abstract
In this article, we present relay selection policies in applications with secrecy requirements which are of interest in the fifth generation (5G) of wireless networks. More specifically, we provide a classification of relays based on their distinct communication attributes, such as processing, multiple antennas, storage, channel estimation, density and security level. In addition, we discuss the level of efficiency exhibited by each relay class, regarding their impact in delay-critical applications and green communications applications, while aiming at a specific security level at the physical layer. Then, relay selection policies are proposed taking into consideration the goals set by each application. Numerical evaluation of the proposed policies in terms of the average secrecy rate, average delay and power reduction show improved performance compared to other state-of-the-art solutions.
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 14, issue 8, IEEE, pp. 3745-3753, 08/2019, 2018. DOI
Abstract
The Smart Grid offers many benefits due to the bidirectional communication between the users and the utility company, which makes it possible to perform a fine-grain consumption metering. This can be used for Demand Response purposes with the generation and delivery of electricity in real time. It is essential to rapidly anticipate high peaks of demand or potential attacks, so as to avoid power outages and denial of service, while effectively supplying consumption areas. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture where cloud computing resources are leveraged (and tested in practice) to enable, on the one hand, the consumption prediction through time series forecasting, as well as load balancing to uniformly distribute the demand over a set of available generators. On the other and, it also allows the detection of connectivity losses and intrusions within the control network by using controllability concepts.

International Journal of Critical Infrastructures (IJCIS), vol. 13, no. 2/3, Inderscience Publisher, pp. 278 - 295, 11/2017. DOI
Abstract
The incessant search for cost-effective recovery solutions for structural controllability has led to one of the most challenging research areas within the field of critical infrastructure protection. The resilience of large heterogeneous distributions, like industrial control scenarios, is proving to be a complicated mission due to the inherent non-locality problems of structural controllability and its susceptibility to advanced threats. To address these issues, this paper proposes a new repair approach based on multiple redundant pathways and the lessons learnt from the work presented in [1]. From [1], we have adapted the local measures, to combine them with each of the five strategies of remote reconnection described in this paper. To validate the sustainability of the combined approaches, two practical case studies are presented here, showing that a local dependence on a brother driver node together with remote dependence is enough to reach optimal states in linear times.
Computers & Security, vol. 71, Elsevier, pp. 2-14, 11/2017. DOI
Abstract
Secure interconnection between multiple cyber-physical systems has become a fundamental requirement in many critical infrastructures, where security may be centralized in a few nodes of the system. These nodes could, for example, have the mission of addressing the authorization services required for access in highlyrestricted remote substations. For this reason, the main aim of this paper is to unify all these features, together with the resilience measures so as to provide control at all times under a limited access in the field and avoid congestion. Concretely, we present here an optimal reachability-based restoration approach, capable of restoring the structural control in linear times taking into account: structural controllability, the supernode theory, the good practices of the IEC-62351 standard and the contextual conditions. For context management, a new attribute is specified to provide a more complete authorization service based on a practical policy, role and attribute-based access control (PBAC + RBAC + ABAC). To validate the approach, two case studies are also discussed under two strategic adversarial models.

ERCIM News, vol. 49, pp. 38-40, 2002.
Abstract
The transition from traditional commerce to electronic and mobile commerce is fostered by aspects like convenience, speed and ease of use. However, security issues remain unsolved. Smart cards open new possibilities for the development of security schemes and protocols that can provide security in applications such as electronic payments or software protection where traditional cryptographic tools are not useful. The GISUM group is involved in several research projects that make use of smart cards. Current applications include a secure electronic forms framework for government-citizen relations, electronic ticketing systems for GMS phones and Internet, a PDA-based digital signature environment, public transport, access control systems, software protection and banking applications. This report focuses on two recent projects: the eTicket electronic ticketing project (1FD97 1269 C02 02 (TAP)), a coordinated project with the Carlos III University of Madrid; and the Alcance project, consisting of the development of a secure electronic forms framework for secure Internet-based communication between citizens and the public administration (1FD97 0850 (TIC)).

Information Security Technical Report, vol. 12, no. 1, Elsevier, pp. 24-31, 2007. DOI
Abstract
Critical Infrastructures, such as energy, banking, and transport, are an essential pillar to the well-being of the national and international economy, security and quality of life. These infrastructures are dependent on a spectrum of highly interconnected information infrastructures for their smooth, reliable and continuous operation. The field of protecting such Critical Information Infrastructures, or CIIP, faces numerous challenges, such as managing the secure interaction between peers, assuring the resilience and robustness of the overall system, and deploying warning and alert systems, amongst others. In this tapestry of CIIP, Wireless Sensor Networks can be used as an invaluable tool due to their intelligent distributed control capabilities, alongside with their capability to work under severe conditions. In this paper, we justify why Wireless Sensor Networks technology is suitable for providing security for these scenarios, describing both their advantages and research issues and their role in the overall scheme of protecting the Critical Information Infrastructures.

 ]
]