 ]
] ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security (TOPS), vol. 25, issue 2, no. 10, Association for Computer Machinery (ACM), pp. 1 - 29, 05/2022. DOI
Abstract
Proximity attacks allow an adversary to uncover the location of a victim by repeatedly issuing queries with fake location data. These attacks have been mostly studied in scenarios where victims remain static and there are no constraints that limit the actions of the attacker. In such a setting, it is not difficult for the attacker to locate a particular victim and quantifying the effort for doing so is straightforward. However, it is far more realistic to consider scenarios where potential victims present a particular mobility pattern. In this paper, we consider abstract (constrained and unconstrained) attacks on services that provide location information on other users in the proximity. We derive strategies for constrained and unconstrained attackers, and show that when unconstrained they can practically achieve success with theoretically optimal effort. We then propose a simple yet effective constraint that may be employed by a proximity service (for example, running in the cloud or using a suitable two-party protocol) as countermeasure to increase the effort for the attacker several orders of magnitude both in simulated and real-world cases.

IEEE Security & Privacy , vol. 20, issue 1, IEEE, pp. 23 - 32, 01/2022. DOI
Abstract
This article introduces a privacy manager for IoT data based on Edge Computing. This poses the advantage that privacy is enforced before data leaves the control of the user, who is provided with a tool to express data sharing preferences based on a novel context-aware privacy language.

IEEE Security & Privacy , vol. 20, issue 1, IEEE, pp. 23 - 32, 01/2022. DOI
Abstract
This article introduces a privacy manager for IoT data based on Edge Computing. This poses the advantage that privacy is enforced before data leaves the control of the user, who is provided with a tool to express data sharing preferences based on a novel context-aware privacy language.

VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
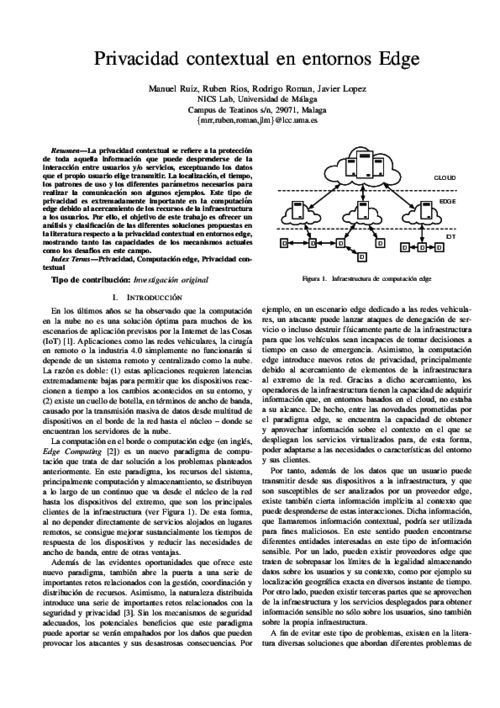
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.
VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.

VII Jornadas Nacionales de Investigación en Ciberseguridad (JNIC 2022), pp. 122-129, 06/2022.
Abstract
La privacidad contextual se refiere a la protección de toda aquella información que puede desprenderse de la interacción entre usuarios y/o servicios, exceptuando los datos que el propio usuario elige transmitir. La localización, el tiempo, los patrones de uso y los diferentes parámetros necesarios para realizar la comunicación son algunos ejemplos. Este tipo de privacidad es extremadamente importante en la computación edge debido al acercamiento de los recursos de la infraestructura a los usuarios. Por ello, el objetivo de este trabajo es ofrecer un análisis y clasificación de las diferentes soluciones propuestas en la literatura respecto a la privacidad contextual en entornos edge, mostrando tanto las capacidades de los mecanismos actuales como los desafíos en este campo.

IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16, issue 10, no. 6575-6583, IEEE, 10/2020. DOI
Abstract
In Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) scenarios, where a plethora of IoT technologies coexist with consolidated industrial infrastructures, the integration of security mechanisms that provide protection against cyber-security attacks becomes a critical challenge. Due to the stealthy and persistent nature of some of these attacks, such as Advanced Persistent Threats, it is crucial to go beyond traditional Intrusion Detection Systems for the traceability of these attacks. In this sense, Opinion Dynamics poses a novel approach for the correlation of anomalies, which has been successfully applied to other network security domains. In this paper, we aim to analyze its applicability in the IIoT from a technical point of view, by studying its deployment over different IIoT architectures and defining a common framework for the acquisition of data considering the computational constraints involved. The result is a beneficial insight that demonstrates the feasibility of this approach when applied to upcoming IIoT infrastructures.

IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16, issue 10, no. 6575-6583, IEEE, 10/2020. DOI
Abstract
In Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) scenarios, where a plethora of IoT technologies coexist with consolidated industrial infrastructures, the integration of security mechanisms that provide protection against cyber-security attacks becomes a critical challenge. Due to the stealthy and persistent nature of some of these attacks, such as Advanced Persistent Threats, it is crucial to go beyond traditional Intrusion Detection Systems for the traceability of these attacks. In this sense, Opinion Dynamics poses a novel approach for the correlation of anomalies, which has been successfully applied to other network security domains. In this paper, we aim to analyze its applicability in the IIoT from a technical point of view, by studying its deployment over different IIoT architectures and defining a common framework for the acquisition of data considering the computational constraints involved. The result is a beneficial insight that demonstrates the feasibility of this approach when applied to upcoming IIoT infrastructures.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 5, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 8038-8045, 10/2019. DOI
Abstract
Edge Computing paradigms are expected to solve some major problems affecting current application scenarios that rely on Cloud computing resources to operate. These novel paradigms will bring computational resources closer to the users and by doing so they will not only reduce network latency and bandwidth utilization but will also introduce some attractive context-awareness features to these systems. In this paper we show how the enticing features introduced by Edge Computing paradigms can be exploited to improve security and privacy in the critical scenario of vehicular networks (VN), especially existing authentication and revocation issues. In particular, we analyze the security challenges in VN and describe three deployment models for vehicular edge computing, which refrain from using vehicular- to-vehicular communications. The result is that the burden imposed to vehicles is considerably reduced without sacrificing the security or functional features expected in vehicular scenarios.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 3, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 4774-4781, 06/2019. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing are starting to go hand in hand. By providing cloud services close to end-users, edge paradigms enhance the functionality of IoT deployments, and facilitate the creation of novel services such as augmented systems. Furthermore, the very nature of these paradigms also enables the creation of a proactive defense architecture, an immune system, which allows authorized immune cells (e.g., virtual machines) to traverse edge nodes and analyze the security and consistency of the underlying IoT infrastructure. In this article, we analyze the requirements for the development of an immune system for the IoT, and propose a security architecture that satisfies these requirements. We also describe how such a system can be instantiated in Edge Computing infrastructures using existing technologies. Finally, we explore the potential application of immune systems to other scenarios and purposes.

IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, issue 3, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 4774-4781, 06/2019. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing are starting to go hand in hand. By providing cloud services close to end-users, edge paradigms enhance the functionality of IoT deployments, and facilitate the creation of novel services such as augmented systems. Furthermore, the very nature of these paradigms also enables the creation of a proactive defense architecture, an immune system, which allows authorized immune cells (e.g., virtual machines) to traverse edge nodes and analyze the security and consistency of the underlying IoT infrastructure. In this article, we analyze the requirements for the development of an immune system for the IoT, and propose a security architecture that satisfies these requirements. We also describe how such a system can be instantiated in Edge Computing infrastructures using existing technologies. Finally, we explore the potential application of immune systems to other scenarios and purposes.

IEEE Computer, vol. 51, issue 7, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 16-25, 07/2018. DOI
KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, vol. 12, no. 8, KSII, pp. 3567-3588, 08/2018. DOI
Abstract
In the Internet of Things (IoT) concept, devices communicate autonomously with applications in the Internet. A significant aspect of IoT that makes it stand apart from present-day networked devices and applications is a) the very large number of devices, produced by diverse makers and used by an even more diverse group of users; b) the applications residing and functioning in what were very private sanctums of life e.g. the car, home, and the people themselves. Since these diverse devices require high-level security, an operational model for an IoT system is required, which has built-in security. We have proposed the societal model as a simple operational model. The basic concept of the model is borrowed from human society – there will be infants, the weak and the handicapped who need to be protected by guardians. This natural security mechanism works very well for IoT networks which seem to have inherently weak security mechanisms. In this paper, we discuss the requirements of the societal model and examine its feasibility by doing a proof-of-concept implementation.

23rd European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2018), LNCS 11099, Springer, pp. 373-392, 2018. DOI
Abstract
Location privacy has mostly focused on scenarios where users remain static. However, investigating scenarios where the victims present a particular mobility pattern is more realistic. In this paper, we consider abstract attacks on services that provide location information on other users in the proximity. In that setting, we quantify the required effort of the attacker to localize a particular mobile victim. We prove upper and lower bounds for the effort of an optimal attacker. We experimentally show that a Linear Jump Strategy (LJS) practically achieves the upper bounds for almost uniform initial distributions of victims. To improve performance for less uniform distributions known to the attacker, we propose a Greedy Updating Attack Strategy (GUAS). Finally, we derive a realistic mobility model from a real-world dataset and discuss the performance of our strategies in that setting.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 78, issue 1, Elsevier, pp. 680-698, 01/2018. DOI
Abstract
For various reasons, the cloud computing paradigm is unable to meet certain requirements (e.g. low latency and jitter, context awareness, mobility support) that are crucial for several applications (e.g. vehicular networks, augmented reality). To fulfil these requirements, various paradigms, such as fog computing, mobile edge computing, and mobile cloud computing, have emerged in recent years. While these edge paradigms share several features, most of the existing research is compartmentalised; no synergies have been explored. This is especially true in the field of security, where most analyses focus only on one edge paradigm, while ignoring the others. The main goal of this study is to holistically analyse the security threats, challenges, and mechanisms inherent in all edge paradigms, while highlighting potential synergies and venues of collaboration. In our results, we will show that all edge paradigms should consider the advances in other paradigms.

Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 75, Elsevier, pp. 46–57, 10/2017. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) envisions a world covered with billions of smart, interacting things capable of offering all sorts of services to near and remote entities. The benefits and comfort that the IoT will bring about are undeniable, however, these may come at the cost of an unprecedented loss of privacy. In this paper we look at the privacy problems of one of the key enablers of the IoT, namely wireless sensor networks, and analyse how these problems may evolve with the development of this complex paradigm. We also identify further challenges which are not directly associated with already existing privacy risks but will certainly have a major impact in our lives if not taken into serious consideration.

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

2nd IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Mobile Computing (FMEC 2017), IEEE Computer Society, pp. 56-61, 06/2017. DOI
Abstract
Cloud computing has some major limitations that hinder its application to some specific scenarios (e.g., Industrial IoT, and remote surgery) where there are particularly stringent requirements, such as extremely low latency. Fog computing is a specialization of the Cloud that promises to overcome the aforementioned limitations by bringing the Cloud closer to end-users. Despite its potential benefits, Fog Computing is still a developing paradigm which demands further research, especially on security and privacy aspects. This is precisely the focus of this paper: to make evident the urgent need for security mechanisms in Fog computing, as well as to present a research strategy with the necessary steps and processes that are being undertaken within the scope of the SMOG project, in order to enable a trustworthy and resilient Fog ecosystem.

32nd International Conference on ICT Systems Security and Privacy Protection (IFIP SEC 2017), S. De Capitan di Vimercati, and F. Martinelli Eds., IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology (AICT) 502, Springer, pp. 141–154, 05/2017. DOI
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) promises to revolutionize the way we interact with the physical world. Even though this paradigm is still far from being completely realized, there already exist Sensing-as-a-Service (S2aaS) platforms that allow users to query for IoT data. While this model offers tremendous benefits, it also entails increasingly challenging privacy issues. In this paper, we concentrate on the protection of user privacy when querying sensing devices through a semi-trusted S2aaS platform. In particular, we build on techniques inspired by proxy re-encryption and k-anonymity to tackle two intertwined problems, namely query privacy and query confidentiality. The feasibility of our solution is validated both analytically and empirically.

XIV Reunión Española sobre Criptología y Seguridad de la Información, pp. 209-213, 10/2016.
Abstract
La Internet de las Cosas (en inglés, Internet of Things (IoT)) es una evolución de la Internet tal y como lo conocemos. Esta nueva versión de Internet incorpora objetos de la vida cotidiana, rompiendo así barrera de los digital y extendiéndose al mundo físico. Estos objetos interactuarán entre sí y con otras entidades tanto de manera local como remota, y estarán dotados de cierta capacidad computacional y sensores para que sean conscientes de lo que ocurre en su entorno. Esto traerá consigo un sinfín de posibilidades y nuevos servicios, pero también dará lugar a nuevos y mayores riesgos de privacidad para los ciudadanos. En este artículo, estudiamos los problemas de privacidad actuales de una de las tecnologías claves para el desarrollo de este prometedor paradigma, las redes de sensores, y analizamos como pueden evolucionar y surgir nuevos riesgos de privacidad al ser completamente integradas en la Internet.

Computer Networks, vol. 57, Elsevier, pp. 2266–2279, July 2013. DOI
Abstract
In the Internet of Things, services can be provisioned using centralized architectures, where central entities acquire, process, and provide information. Alternatively, distributed architectures, where entities at the edge of the network exchange information and collaborate with each other in a dynamic way, can also be used. In order to understand the applicability and viability of this distributed approach, it is necessary to know its advantages and disadvantages – not only in terms of features but also in terms of security and privacy challenges. The purpose of this paper is to show that the distributed approach has various challenges that need to be solved, but also various interesting properties and strengths.

Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 11, Elsevier, pp. 1091–1104, 2013. DOI
Abstract
The main objective of remote substations is to provide the central system with sensitive information from critical infrastructures, such as generation, distribution or transmission power systems. Wireless sensor networks have been recently applied in this particular context due to their attractive services and inherent benefits, such as simplicity, reliability and cost savings. However, as the number of control and data acquisition systems that use the Internet infrastructure to connect to substations increases, it is necessary to consider what connectivity model the sensor infrastructure should follow: either completely isolated from the Internet or integrated with it as part of the Internet of Things paradigm. This paper therefore addresses this question by providing a thorough analysis of both security requirements and infrastructural requirements corresponding to all those TCP/IP integration strategies that can be applicable to networks with constrained computational resources.

Security and Communication Networks, vol. 6, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 1177–1197, Oct 2013. DOI
Abstract
A personal network (PN) should enable the collaboration of user’s devices and services in a flexible, self-organizing and friendly manner. For such purpose, the PN must securely accommodate heterogeneous technologies with uneven computational and communication resources. In particular, personal RFID tags can enable seamless recognition of user’s context, provide user authentication and enable novel services enhancing the quality and quantity of data handled by the PN. However, the highly constrained features of common RFID tags and their passive role in the network highlights the need of an adequate secure communication model with personal tags which enables their participation as a member of the PN. In this paper, we present our concept of PN, with special emphasis on the role of RFID and sensor networks, and define a secure architecture for PNs including methods for the secure access to context-aware technologies from both local PN members and the Internet of Things. The PN architecture is designed to support differentiated security mechanisms to maximize the level of security for each type of personal device. Furthermore, we analyze which security solutions available in the literature can be adapted for our architecture, as well as the challenges and security mechanisms still necessary in the secure integration of personal tags.
Proceedings of the First International Conference on Security of Internet of Things, ACM, pp. 172–178, 2012. DOI
Abstract
While there has been considerable progress in the research and technological development (RTD) of the Internet of Things (IoT), there is still considerable RTD required by international communities for the trust, privacy and security research challenges arising from the constitution of the IoT architectures, infrastructures, communications, devices, objects, applications and services. In this paper, we present an thorough analysis of the ongoing and future RTD work, specifically in Europe, regarding trust, privacy and security of the Internet of Things with a view towards enabling international cooperation efforts around the globe to solve these major research challenges.
Computers & Electrical Engineering, vol. 37, Elsevier, pp. 147-159, Mar 2011. DOI
Abstract
If a wireless sensor network (WSN) is to be completely integrated into the Internet as part of the Internet of Things (IoT), it is necessary to consider various security challenges, such as the creation of a secure channel between an Internet host and a sensor node. In order to create such a channel, it is necessary to provide key management mechanisms that allow two remote devices to negotiate certain security credentials (e.g. secret keys) that will be used to protect the information flow. In this paper we will analyse not only the applicability of existing mechanisms such as public key cryptography and pre-shared keys for sensor nodes in the IoT context, but also the applicability of those link-layer oriented key management systems (KMS) whose original purpose is to provide shared keys for sensor nodes belonging to the same WSN.

IEEE Computer, vol. 44, no. 9, IEEE, pp. 51 -58, Sept 2011. DOI
Abstract
This paper presents security of Internet of things. In the Internet of Things vision, every physical object has a virtual component that can produce and consume services Such extreme interconnection will bring unprecedented convenience and economy, but it will also require novel approaches to ensure its safe and ethical use. The Internet and its users are already under continual attack, and a growing economy-replete with business models that undermine the Internet’s ethical use-is fully focused on exploiting the current version’s foundational weaknesses.

Revista SIC, vol. 88, Ediciones CODA, pp. 66-73, Feb 2010.
Abstract
El paradigma de la Internet de los Objetos, donde todos aquellos objetos físicos que nos rodean tendrán la capacidad de generar y consumir información en el ámbito de un mundo virtual, se encuentra cada vez más cerca. Es ahora un buen momento para llamar la atención sobre sus principales desafíos de seguridad, tanto desde un punto de vista global como asociados a sus elementos más importantes (la tecnología RFID y las redes de sensores). Así, este paradigma puede ser plenamente comprendido y protegido, evolucionando hacia uno de los nuevos pilares del futuro.

1st International Workshop on the Security of the Internet of Things (SecIoT’10), IEEE, pp. xxxx, December, 2010.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) behave as a digital skin, providing a virtual layer where the information about the physical world can be accessed by any computational system. As a result, they are an invaluable resource for realizing the vision of the Internet of Things (IoT). However, it is necessary to consider whether the devices of a WSN should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. In this paper, we tackle this question from the perspective of security. While we will mention the different security challenges that may arise in such integration process, we will focus on the issues that take place at the network level.

3rd CompanionAble Workshop - Future Internet of People, Things and Services (IoPTS) eco-Systems, xxxx, pp. xxxx, December, 2009.
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks are considered as an integral part of the Internet of Things paradigm. Not only they provide a virtual presence to elements of the real world, but also allow any computationalsystem to know about the physical state of those elements thanks to the use of embedded sensors. In order to belong to the Internet of Things, the elements of a sensor network can implement Internet protocols and services such as the TCP/IP stack and web services. Still, a question that must be raised at this point of time is whether all sensor network applications should be completely integrated into the Internet or not. The purpose of this paper is to analyze this question, reviewing the challenges and security requirements of Internet-enabled sensor networks.

Internet Research, vol. 19, no. 2, Emerald, pp. 246-259, Mar 2009. DOI
Abstract
Purpose: This paper aims to analyze the security issues that arise when integrating wireless sensor networks (WSN) and the internet. Also, it seeks to review whether existing technology mechanisms are suitable and can be applied in this context.
Design/methodology/approach: The paper considers the possible approaches that can be used to connect a WSN with the internet, and analyzes the security of their interactions.
Findings: By providing the services of the network through a front-end proxy, a sensor network and the internet can interact securely. There are other challenges to be solved if the sensor nodes are integrated into the internet infrastructure, although there exists interesting advances on his matter.
Research limitations and implications: The complete integration of sensor networks and the internet still remains as an open issue.
Practical implications: With the current state of the art, it is possible to develop a secure sensor network that can provide its services to internet hosts with certain security properties.
Originality/value: The paper studies the interactions between sensor networks and the internet from the point of view of security. It identifies both solutions and research challenges.

